J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2018 Jul;59(7):680-686. 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.7.680.
A Case of Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy and Serous Retinal Detachment in a Bilateral Dome-shaped Macula
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. Jps11@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2416272
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2018.59.7.680
Abstract
- PURPOSE
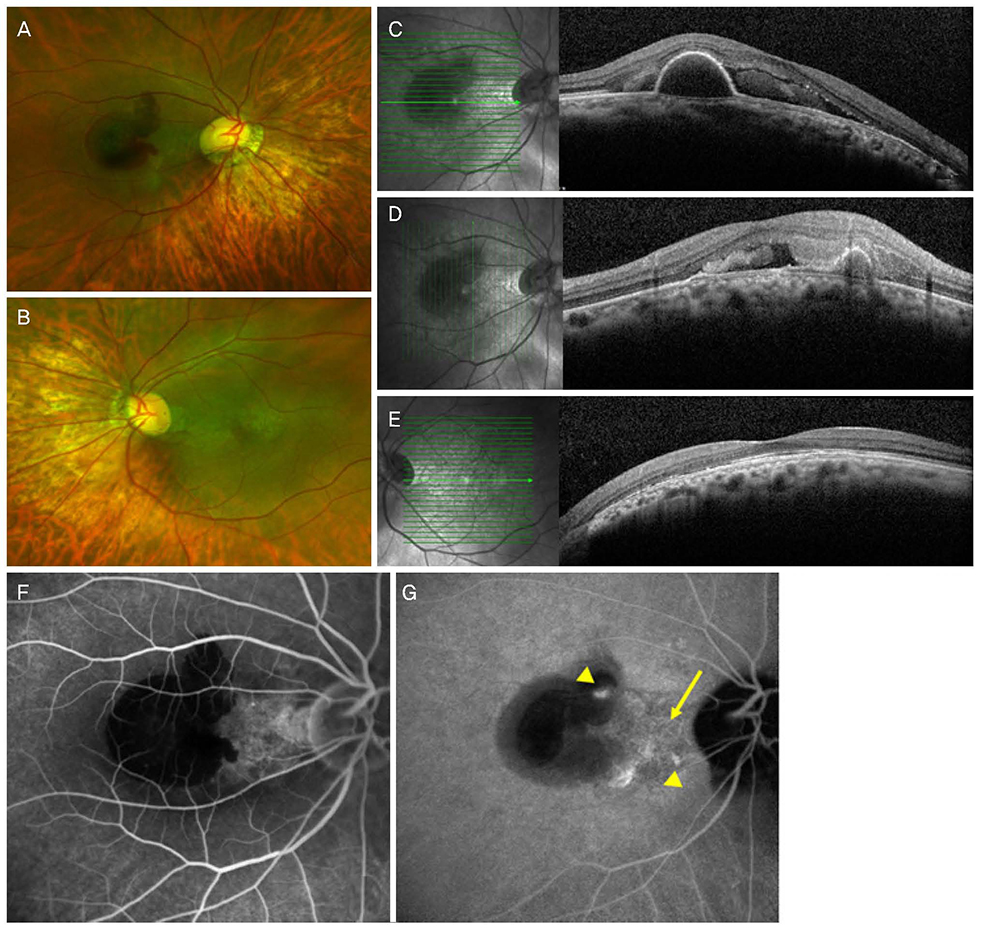
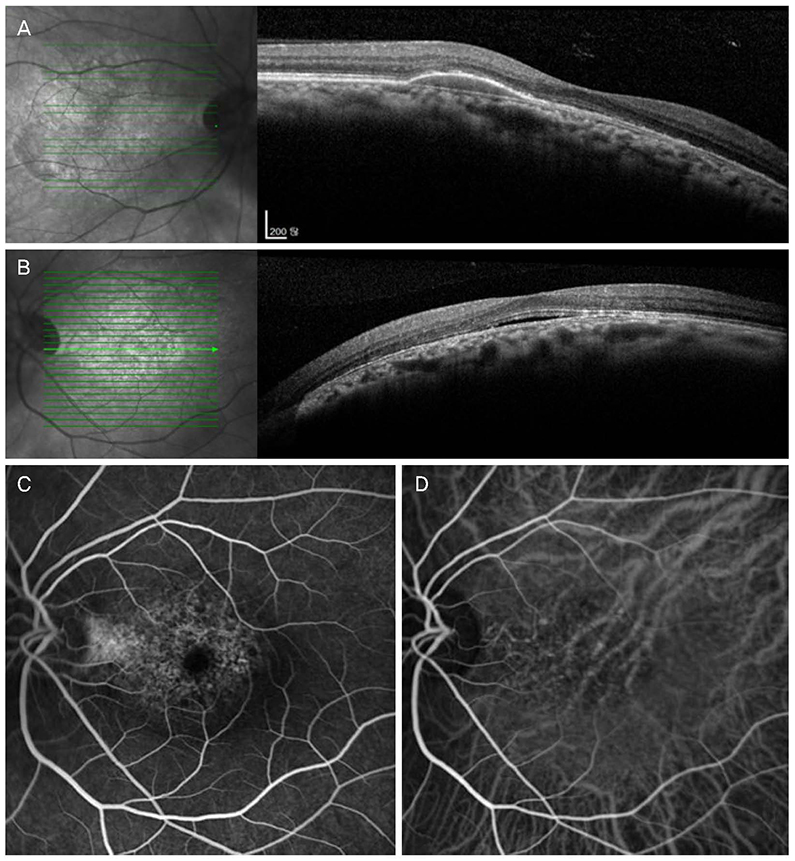
To report a case of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in the right eye which improved after intravitreal injection of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor, and serous retinal detachment (SRD) in the left eye which improved spontaneously in a patient with a bilateral dome-shaped macula (DSM) with a tilted optic disc and inferonasal posterior staphyloma.
CASE SUMMARY
A 50-year-old female visited our clinic with visual disturbance of the right eye for 5 days. A tilted optic disc with inferonasal posterior staphyloma and DSM were observed in both eyes by fundus examination and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT), and there was no specific finding in the left eye, but pigment epithelial detachment (PED) with subretinal hemorrhage was observed in the right eye. Polyps and branching vascular networks were found using indocyanine green angiography. We performed intravitreal C3F8 gas and aflibercept injection. After 3 months, SD-OCT of the right eye showed no subretinal hemorrhage and diminished PED. SD-OCT of the left eye showed SRD but the SRD disappeared after 1 month. SD-OCT of the left eye showed no recurrence of the SRD.
CONCLUSIONS
In a patient with a tilted optic disc and dome-shaped macula, polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and SRD may occur, so appropriate treatment will be necessary.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gaucher D, Erginay A, Lecleire-Collet A, et al. Dome-shaped macula in eyes with myopic posterior staphyloma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008; 145:909–914.
Article2. Ohsugi H, Ikuno Y, Oshima K, et al. Morphologic characteristics of macular complications of a dome-shaped macula determined by swept-source optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014; 158:162–170.e1.
Article3. Errera MH, Michaelides M, Keane PA, et al. The extended clinical phenotype of dome-shaped macula. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014; 252:499–508.
Article4. Ellabban AA, Tsujikawa A, Matsumoto A, et al. Three dimensional tomographic features of dome-shaped macula by swept-source optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 155:320–328.e2.5. Imamura Y, Iida T, Maruko I, et al. Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the sclera in dome-shaped macula. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 151:297–302.
Article6. Witmer MT, Margo CE, Drucker M. Tilted optic disks. Surv Ophthalmol. 2010; 55:403–428.
Article7. Pardo-López D, Gallego-Pinazo R, Mateo C, et al. Serous macular detachment associated with dome-shaped macula and tilted disc. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2011; 2:111–115.
Article8. Byeon SH, Chu YK. Dome-shaped macula. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 151:1101. author reply 1101-2.
Article9. Nakanishi H, Tsujikawa A, Gotoh N, et al. Macular complications on the border of an inferior staphyloma associated with tilted disc syndrome. Retina. 2008; 28:1493–1501.
Article10. Mauget-Faÿsse M, Cornut PL, Quaranta El-Maftouhi M, Leys A. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in tilted disk syndrome and high myopia with staphyloma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:970–975.11. Furuta M, Iida T, Maruko I, et al. Submacular choroidal neovascularization at the margin of staphyloma in tilted disk syndrome. Retina. 2013; 33:71–76.
Article12. Cohen SY, Dubois L, Nghiem-Buffet S, et al. Spectral domain optical coherence tomography analysis of macular changes in tilted disk syndrome. Retina. 2013; 33:1338–1345.
Article13. Maruko I, Iida T, Sugano Y, et al. Morphologic choroidal and scleral changes at the macula in tilted disc syndrome with staphyloma using optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:8763–8768.
Article14. Mehdizadeh M, Nowroozzadeh MH. Dome-shaped macula in eyes with myopic posterior staphyloma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008; 146:478. author reply 478-9.
Article15. Kang HM, Koh HJ. Lack of polypoidal lesions in patients with myopic choroidal neovascularization as evaluated by indocyanine green angiography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014; 157:378–383.e1.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Choroidal Venous Pulsations at an Arterio-venous Crossing in Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
- Laser Photocoaculation Treatment in a Case of Circumscribged Choroidal hmangioma Associated with Serous Retinal Detachment
- Neovascularizations Associated with Large Serous Retinal Pigment Epithelial Detachment: Classification According to the Angiographic Features
- Takayasu's Arteritis Associated with Serous Retinal Detachment
- Transpupillary Thermotherapy in Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma