Ann Dermatol.
2018 Apr;30(2):218-221. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.2.218.
Pagetoid Bowen Disease Initially Misdiagnosed as Ectopic Extramammary Paget's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. snuhdm@gmail.com
- KMID: 2414685
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.2.218
Abstract
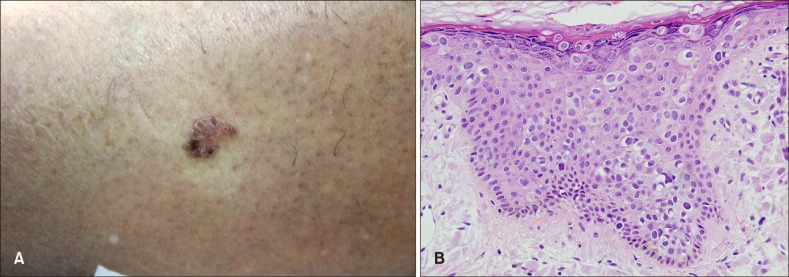
- Pagetoid Bowen disease is a histological variant of Bowen disease which demonstrates large pale staining cells (pagetoid cells). It requires differential diagnosis from other cutaneous malignancies with similar patterns, such as extramammary Paget's disease (EMPD) and Pagetoid melanoma in situ. Herein, we report a case of Pagetoid Bowen disease which was initially misdiagnosed as ectopic EMPD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sawada Y, Bito T, Kabashima R, Yoshiki R, Hino R, Nakamura M, et al. Ectopic extramammary Paget's disease: case report and literature review. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010; 90:502–505. PMID: 20814627.
Article2. Guldhammer B, Nørgaard T. The differential diagnosis of intraepidermal malignant lesions using immunohistochemistry. Am J Dermatopathol. 1986; 8:295–301. PMID: 2429574.
Article3. Shah KD, Tabibzadeh SS, Gerber MA. Immunohistochemical distinction of Paget's disease from Bowen's disease and superficial spreading melanoma with the use of monoclonal cytokeratin antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987; 88:689–695. PMID: 2446491.
Article4. Lau J, Kohler S. Keratin profile of intraepidermal cells in Paget's disease, extramammary Paget's disease, and pagetoid squamous cell carcinoma in situ. J Cutan Pathol. 2003; 30:449–454. PMID: 12859743.5. Memezawa A, Okuyama R, Tagami H, Aiba S. p63 constitutes a useful histochemical marker for differentiation of pagetoid Bowen's disease from extramammary Paget's disease. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008; 88:619–620. PMID: 19002351.6. Rosen L, Amazon K, Frank B. Bowen's disease, Paget's disease, and malignant melanoma in situ. South Med J. 1986; 79:410–413. PMID: 2422766.
Article7. Reed W, Oppedal BR, Eeg Larsen T. Immunohistology is valuable in distinguishing between Paget's disease, Bowen's disease and superficial spreading malignant melanoma. Histopathology. 1990; 16:583–588. PMID: 1695889.
Article8. Williamson JD, Colome MI, Sahin A, Ayala AG, Medeiros LJ. Pagetoid Bowen disease: a report of 2 cases that express cytokeratin 7. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000; 124:427–430. PMID: 10705400.9. Mai KT, Alhalouly T, Landry D, Stinson WA, Perkins DG, Yazdi HM. Pagetoid variant of actinic keratosis with or without squamous cell carcinoma of sun-exposed skin: a lesion simulating extramammary Paget's disease. Histopathology. 2002; 41:331–336. PMID: 12383215.
Article10. Armes JE, Lourie R, Bowlay G, Tabrizi S. Pagetoid squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the vulva: comparison with extramammary paget disease and nonpagetoid squamous cell neoplasia. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2008; 27:118–124. PMID: 18156986.11. Raju RR, Goldblum JR, Hart WR. Pagetoid squamous cell carcinoma in situ (pagetoid Bowen's disease) of the external genitalia. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2003; 22:127–135. PMID: 12649666.
Article12. Jang EJ, Bae YK, Shin DH, Lee DJ. Extramammary Paget's disease combined with squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the vulva: a case report and differential diagnosis. Ann Dermatol. 2016; 28:497–498. PMID: 27489435.
Article13. Chung J, Kim JY, Gye J, Namkoong S, Hong SP, Park BC, et al. Extramammary Paget's disease of external genitalia with bowenoid features. Ann Dermatol. 2013; 25:88–91. PMID: 23467383.
Article14. Peralta OC, Barr RJ, Romansky SG. Mixed carcinoma in situ: an immunohistochemical study. J Cutan Pathol. 1983; 10:350–358. PMID: 6313778.
Article15. Baldovini C, Betts CM, Reggiani C, Reggiani M, Foschini MP. Ultrastructural examination of a case of pagetoid Bowen disease exhibiting immunohistochemical features in common with extramammary paget disease. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015; 37:e83–e86. PMID: 24786579.
Article16. Kim YK, Lew W, Lee SH. Multiple pagetoid Bowen's disease. Ann Dermatol. 1999; 11:248–251.
Article17. Kim SA, Kwon JI, Jung HR, Lee KS, Cho JW. Primary extramammary Paget's disease combined with Bowen's disease in vulva. Ann Dermatol. 2011; 23(Suppl 2):S222–S225. PMID: 22148056.
Article18. Sohn IB, Kim SC, Ahn SK. A case of pigmented Pagetoid Bowen's disease. Korean J Dermatol. 2000; 38:1691–1692.