Ann Dermatol.
2018 Apr;30(2):202-210. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.2.202.
Antifungal Effects of Bee Venom Components on Trichophyton rubrum: A Novel Approach of Bee Venom Study for Possible Emerging Antifungal Agent
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. g9563009@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2414682
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.2.202
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Bee venom (BV) has been widely investigated for potential medical uses. Recent inadvertent uses of BV based products have shown to mitigate signs of fungal infections. However, the component mediating the antifungal effect has not been identified.
OBJECTIVE
This investigation compares bee venom in its whole and partial forms to evaluate the possible component responsible for the antifungal effect.
METHODS
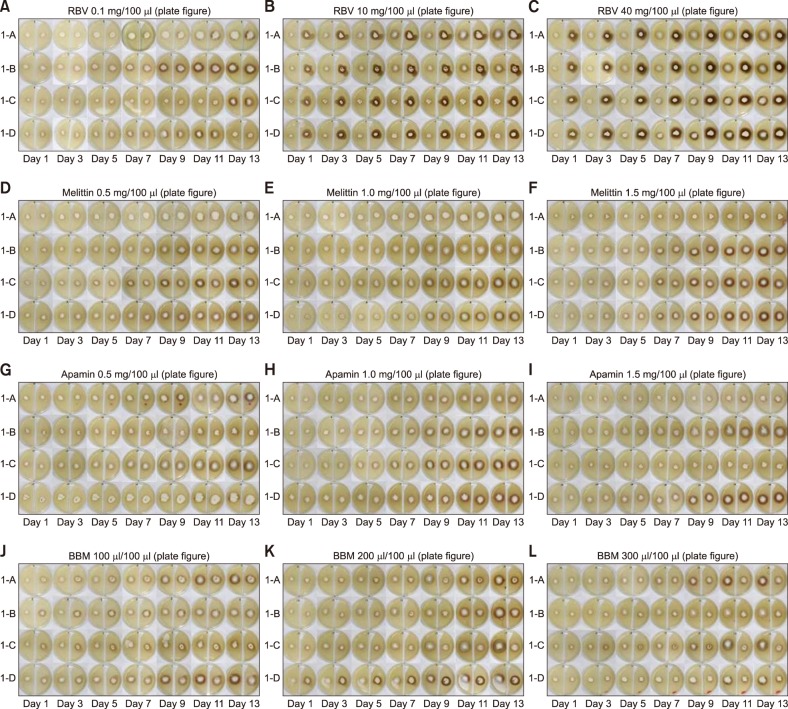
Forty-eight plates inoculated with Trichophyton rubrum were allocated into four groups. The groups were treated with raw BV (RBV), melittin, apamin and BV based mist (BBM) respectively and each group was further allocated accordingly to three different concentrations. The areas were measured every other day for 14 days to evaluate the kinetic changes of the colonies.
RESULTS
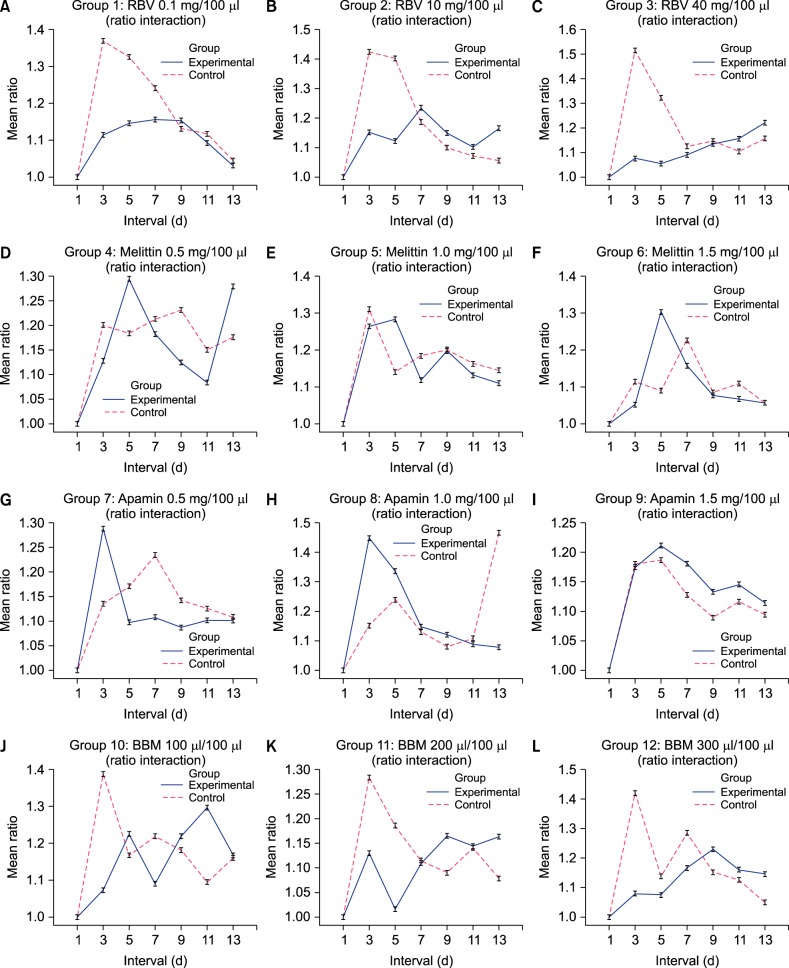
The interactions of ratio differences over interval were confirmed in groups treated with RBV and BBM. In RBV, the level of differences were achieved in groups treated with 10 mg/100 µl (p=0.026) and 40 mg/100 µl (p=0.000). The mean difference of ratio in groups treated with RBV was evident in day 3 and day 5. The groups that were treated with melittin or apamin did not show any significant interaction. In BBM groups, the significant levels of ratio differences over time intervals were achieved in groups treated with 200 µl/100 µl (p=0.000) and 300 µl/100 µl (p=0.030).
CONCLUSION
The the bee venom in its whole form delivered a significant level of inhibition and we concluded that the venom in separated forms are not effective. Moreover, BV based products may exert as potential antifungal therapeutics.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yu AR, Kim JJ, Park GS, Oh SM, Han CS, Lee MY. The antifungal activity of bee venom against dermatophytes. J Appl Biol Chem. 2012; 55:7–11.
Article2. Kwon YB, Lee JD, Lee HJ, Han HJ, Mar WC, Kang SK, et al. Bee venom injection into an acupuncture point reduces arthritis associated edema and nociceptive responses. Pain. 2001; 90:271–280. PMID: 11207399.
Article3. Kim KS, Choi US, Lee SD, Kim KH, Chung KH, Chang YC, et al. Effect of bee venom on aromatase expression and activity in leukaemic FLG 29.1 and primary osteoblastic cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005; 99:245–252. PMID: 15894134.
Article4. Peng XL, Gao XL, Chen J, Huang X, Chen HS. Effects of intravenous Injections Paederiae and Stauntonia on spontaneous pain, hyperalgesia and inflammation induced by cutaneous chemical tissue injury in the rat. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2003; 55:516–524. PMID: 14566397.5. Han SM, Lee KG, Yeo JH, Kweon HY, Kim BS, Kim JM, et al. Antibacterial activity of the honey bee venom against bacterial mastitis pathogens infecting dairy cows. Int J Indust Entomol. 2007; 14:137–142.6. Kwon YB, Lee HJ, Han HJ, Mar WC, Kang SK, Yoon OB, et al. The water-soluble fraction of bee venom produces antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects on rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Life Sci. 2002; 71:191–204. PMID: 12031688.
Article7. Kim HW, Kwon YB, Ham TW, Roh DH, Yoon SY, Lee HJ, et al. Acupoint stimulation using bee venom attenuates formalin-induced pain behavior and spinal cord fos expression in rats. J Vet Med Sci. 2003; 65:349–355. PMID: 12679565.
Article8. Lee SM, Lim J, Lee JD, Choi DY, Lee S. Bee venom treatment for refractory postherpetic neuralgia: a case report. J Altern Complement Med. 2014; 20:212–214. PMID: 24093469.
Article9. Argiolas A, Pisano JJ. Facilitation of phospholipase A2 activity by mastoparans, a new class of mast cell degranulating peptides from wasp venom. J Biol Chem. 1983; 258:13697–13702. PMID: 6643447.
Article10. Akdis CA, Akdis M, Blesken T, Wymann D, Alkan SS, Müller U, et al. Epitope-specific T cell tolerance to phospholipase A2 in bee venom immunotherapy and recovery by IL-2 and IL-15 in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1996; 98:1676–1683. PMID: 8833918.
Article11. Han S, Lee K, Yeo J, Baek H. Determination of major constituents of honeybee venom from Korea. Korean J Apic. 2009; 24:175–178.12. Lee G, Bae H. Anti-Inflammatory applications of melittin, a major component of bee venom: detailed mechanism of action and adverse effects. Molecules. 2016; 21:E616. PMID: 27187328.
Article13. Park C, Lee DG. Melittin induces apoptotic features in Candida albicans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010; 394:170–172. PMID: 20188067.
Article14. An HJ, Kim KH, Lee WR, Kim JY, Lee SJ, Pak SC, et al. Anti-fibrotic effect of natural toxin bee venom on animal model of unilateral ureteral obstruction. Toxins (Basel). 2015; 7:1917–1928. PMID: 26035488.15. Lee SB. Antifungal activity of bee venom and sweet bee venom against clinically isolated Candida albicans. J Pharmacopuncture. 2016; 19:45–50. PMID: 27280049.
Article16. Han SM, Lee KG, Yeol JH, Baek HJ, Park KK. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of honeybee (Apis mellifera) venom against acne-inducing bacteria. J Med Plants Res. 2010; 4:459–464.17. Farghaly DS. Effect of some honey bee and wasp products on some pathogenic bacteria and fungi: in vitro study. Middle East J Appl Sci. 2016; 6:468–473.18. Apisariyakul A, Vanittanakom N, Buddhasukh D. Antifungal activity of turmeric oil extracted from Curcuma longa (Zingiberaceae). J Ethnopharmacol. 1995; 49:163–169. PMID: 8824742.
Article19. Lee MH, Lee KB, Oh SM, Lee BH, Chee HY. Antifungal activities of dieckol isolated from the marine brown alga Ecklonia cava against Trichophyton rubrum. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem. 2010; 53:504–507.
Article20. Arif T, Mandal TK, Dabur R. Natural products: anti-fungal agents derived from plants. In : Tiwari VK, Mishra BB, editors. Opportunity, challenge and scope of natural products in medicinal chemistry. Kerala: Research Signpost;2011. p. 283–311.21. Chee HY, Kim H, Lee MH. In vitro antifungal activity of limonene against Trichophyton rubrum. Mycobiology. 2009; 37:243–246. PMID: 23983542.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Antifungal Activities of Bee Venom Components Against Malassezia Strains
- Bee Venom Therapy for Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Serum sickness reaction with skin involvement induced by bee venom injection therapy
- A Case of Newly Developed Pemphigus Foliaceus and Possible Association with Alternative Bee-Venom Therapy
- A Case of Ischemic Stroke Following Bee Venom Acupuncture