Ann Surg Treat Res.
2018 Jul;95(1):45-53. 10.4174/astr.2018.95.1.45.
Intraoperative management of liver transplant recipients having severe renal dysfunction: results of 42 cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. gskim@skku.edu
- 3Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2414452
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2018.95.1.45
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Whereas continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) has been utilized during liver transplantation (LT), there was a lack of evidence to support this practice. We investigated the adverse events at the perioperative periods in recipients of LT who received preoperative CRRT without intraoperative CRRT.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed medical records of adult patients (age ≥ 18 years) who received LT between December 2009 and May 2015. Perioperative data were collected from the recipients, who received preoperative CRRT until immediately before LT, because of refractory renal dysfunction.
RESULTS
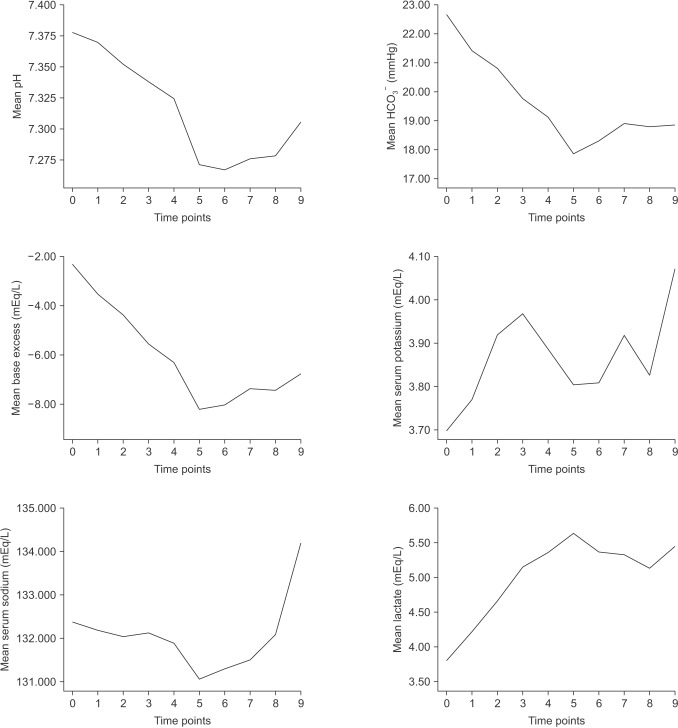
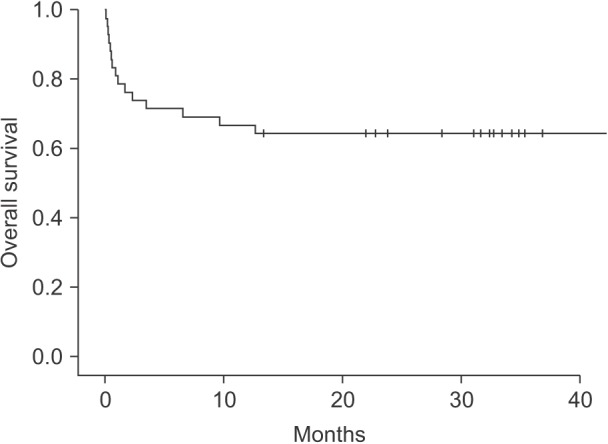
Of 706 recipients, 42 recipients received preoperative CRRT. The mean (standard deviation) Model for end-stage liver disease score were 49.6 (13.4). Twenty-six point two percent (26.2%) of recipients experienced the serum potassium > 4.5 mEq/L before reperfusion and treated with regular insulin. Thirty-eight point one percent (38.1%) of recipients were managed with sodium bicarbonate because of acidosis (base excess <−10 mEq/L throughout LT). All patients finished their operations without medically uncontrolled complications such as severe hyperkalemia (serum potassium > 5.5 mEq/L), refractory acidosis, or critical arrhythmias. Mortality was 19% at 30 day and 33.3% at 1 year.
CONCLUSION
Although intraoperative CRRT was not used in recipients with severe preoperative renal dysfunction, LT was safely performed. Our experience raises a question about the need for intraoperative CRRT.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lau C, Mar t, Bunnapradist S. Management of renal dysfunction in patients receiving a liver transplant. Clin Liver Dis. 2011; 15:807–820. PMID: 22032530.
Article2. Matuszkiewicz-Rowińska J, Wieliczko M, Małyszko J. Renal replacement therapy before, during, and after orthotopic liver transplantation. Ann Transplant. 2013; 18:248–255. PMID: 23792528.
Article3. Ikegami T, Shirabe K, Soejima Y, Taketomi A, Yoshizumi T, Uchiyama H, et al. The impact of renal replacement therapy before or after living donor liver transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2012; 26:143–148. PMID: 21447144.
Article4. Nadim MK, Annanthapanyasut W, Matsuoka L, Appachu K, Boyajian M, Ji L, et al. Intraoperative hemodialysis during liver transplantation: a decade of experience. Liver Transpl. 2014; 20:756–764. PMID: 24634344.
Article5. Parmar A, Bigam D, Meeberg G, Cave D, Townsend DR, Gibney RT, et al. An evaluation of intraoperative renal support during liver transplantation: a matched cohort study. Blood Purif. 2011; 32:238–248. PMID: 21829016.
Article6. Townsend DR, Bagshaw SM, Jacka MJ, Bigam D, Cave D, Gibney RT. Intraoperative renal support during liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2009; 15:73–78. PMID: 19109832.
Article7. Akhoundi A, Singh B, Vela M, Chaudhary S, Monaghan M, Wilson GA, et al. Incidence of adverse events during continuous renal replacement therapy. Blood Purif. 2015; 39:333–339. PMID: 26022612.
Article8. Dawwas MF, Lewsey JD, Watson CJ, Gimson AE. UK, Ireland Liver Transplant Audit. The impact of serum potassium concentration on mortality after liver transplantation: a cohort multicenter study. Transplantation. 2009; 88:402–410. PMID: 19667945.
Article9. Shangraw RE. Metabolic issues in liver transplantation. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 2006; 44:1–20.
Article10. Kamath PS, Kim WR. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group. The model for endstage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology. 2007; 45:797–805. PMID: 17326206.
Article11. Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1964; 1:1–85. PMID: 4950264.12. Bang SR, Ahn HJ, Kim GS, Yang M, Gwak MS, Ko JS, et al. Predictors of high intraoperative blood loss derived by simple and objective method in adult living donor liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2010; 42:4148–4150. PMID: 21168648.
Article13. De Backer D, Biston P, Devriendt J, Madl C, Chochrad D, et al. Comparison of dopamine and norepinephrine in the treatment of shock. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:779–789. PMID: 20200382.
Article14. De Backer D, Creteur J, Silva E, Vincent JL. Effects of dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine on the splanchnic circulation in septic shock: which is best? Crit Care Med. 2003; 31:1659–1667. PMID: 12794401.
Article15. Russell JA, Walley KR, Singer J, Gordon AC, Hébert PC, Cooper DJ, et al. Vasopressin versus norepinephrine infusion in patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:877–887. PMID: 18305265.
Article16. Gonwa TA, McBride MA, Anderson K, Mai ML, Wadei H, Ahsan N. Continued influence of preoperative renal function on outcome of orthotopic liver transplant (OLTX) in the US: where will MELD lead us? Am J Transplant. 2006; 6:2651–2659. PMID: 16939515.
Article17. Gonwa TA, Mai ML, Melton LB, Hays SR, Goldstein RM, Levy MF, et al. Renal replacement therapy and orthotopic l iver transplant ation: the role of continuous veno-venous hemodialysis. Transplantation. 2001; 71:1424–1428. PMID: 11391230.18. Salord F, Bailly MP, Gaussorgues P, Workineh S, Pouyet M, Robert D. Continuous arteriovenous haemodialysis during emergency hepatic retransplantation: two case reports. Intensive Care Med. 1990; 16:330–331. PMID: 2212260.
Article19. Douthitt L, Bezinover D, Uemura T, Kadry Z, Shah RA, Ghahramani N, et al. Perioperative use of continuous renal replacement therapy for orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2012; 44:1314–1317. PMID: 22664007.
Article20. Vitin A, Muczynski K, Bakthavatsalam R, Martay K, Dembo G, Metzner J. Treatment of severe lactic acidosis during the preanhepatic stage of liver transplant surgery with intraoperative hemodialysis. J Clin Anesth. 2010; 22:466–472. PMID: 20868970.
Article21. Sedra AH, Strum E. The role of intraoperative hemodialysis in liver transplant patients. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2011; 16:323–325. PMID: 21543980.
Article22. Bellomo R, Harris C, Kang Y, Daniel E, Fung JJ, Bronsther O. Combined veno-venous bypass and high volume hemofiltration during orthotopic liver transplantation. ASAIO J. 1993; 39:954–956. PMID: 8123934.
Article23. Agopian VG, Dhillon A, Baber J, Kaldas FM, Zarrinpar A, Farmer DG, et al. Liver transplantation in recipients receiving renal replacement therapy: outcomes analysis and the role of intraoperative hemodialysis. Am J Transplant. 2014; 14:1638–1647. PMID: 24854341.
Article24. Gruber M, Breu A, Frauendorf M, Seyfried T, Hansen E. Washing of banked blood by three different blood salvage devices. Transfusion. 2013; 53:1001–1009. PMID: 22897672.
Article25. Vraets A, Lin Y, Callum JL. Transfusion-associated hyperkalemia. Transfus Med Rev. 2011; 25:184–196. PMID: 21498041.
Article26. Glanemann M, Langrehr J, Kaisers U, Schenk R, Müller A, Stange B, et al. Postoperative tracheal extubation after orthotopic liver transplantation. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2001; 45:333–339. PMID: 11207470.
Article27. Snowden CP, Hughes T, Rose J, Roberts DR. Pulmonary edema in patients after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2000; 6:466–470. PMID: 10915170.
Article28. Lin YH, Cai ZS, Jiang Y, Lü LZ, Zhang XJ, Cai QC. Perioperative risk factors for pulmonary complications after liver transplantation. J Int Med Res. 2010; 38:1845–1855. PMID: 21309501.
Article29. Feltracco P, Carollo C, Barbieri S, Pettenuzzo T, Ori C. Early respiratory complications after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:9271–9281. PMID: 24409054.
Article30. Wi W, Hahm TS, Kim GS. A case series on simultaneous l iver and kidney transplantation: do we need intraoperative renal replacement therapy? Korean J Anesthesiol. 2017; 70:467–476. PMID: 28794844.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case series on simultaneous liver and kidney transplantation: do we need intraoperative renal replacement therapy?
- The Risk Factors and Natural History of Chronic Kidney Disease in Liver Transplant Recipients
- Super-fast-track discharge of liver transplant recipients
- Association between early allograft dysfunction and requirement of renal replacement therapy in liver transplant recipients
- Malignancy in Renal Transplant Recipients