Korean J Ophthalmol.
2018 Jun;32(3):234-240. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0104.
Use of the Bispectral Index to Predict Eye Position of Children during General Anesthesia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. mingming8@naver.com
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2412803
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0104
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To assess the relationship between eye position and anesthesia depth using the bispectral index (BIS) value, a parameter derived from electroencephalography data.
METHODS
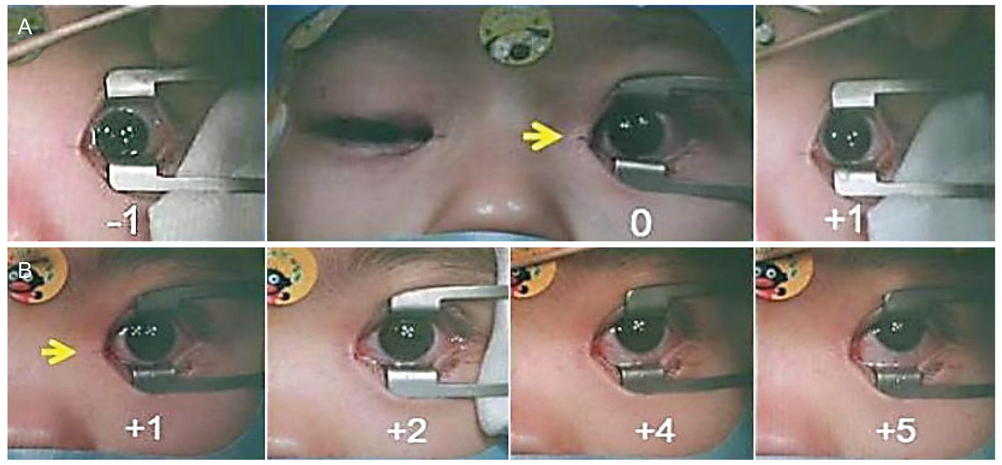
We investigated the relationship between BIS value and eye position in 32 children who underwent surgery for epiblepharon under general anesthesia. BIS values were recorded continuously throughout the procedure (from induction to awakening). Eye positions were video-recorded and analyzed after surgery. The vertical position of each eye was scored according to its height in relation to the medial canthus. An eye position in which the upper eyelid covered one-third of the cornea was defined as a significant ocular elevation.
RESULTS
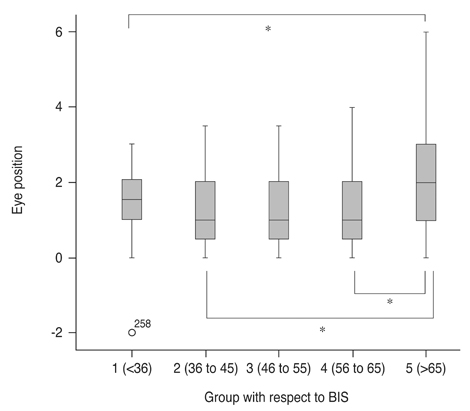
The BIS value correlated inversely with the end-tidal concentration of each anesthetic agent, whereas it correlated positively with the eye elevation score (eye position = 0.014 × BIS + 0.699, p = 0.011). The mean eye position score was significantly greater in patients whose BIS values were over 65. Eleven patients (34.4%) had significant ocular elevation; their mean concurrent BIS value was 61.6. Two of these patients had elevation during surgery and 9 had elevation during emergence from anesthesia.
CONCLUSIONS
We found that high BIS values were correlated with low levels of anesthetic concentration and high eye position, suggesting that BIS monitoring may be useful for predicting eye position during anesthesia. Particular attention must be given to eye position during ophthalmic surgery. Anesthesia depth can be maintained by assuring that the BIS value remains below 65.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. von Noorden GK, Campos EC. Classification of neuromuscular anomalies of the eyes. In : von Noorden GK, Campos EC, editors. Binocular vision and ocular motility: theory and management of strabismus. 6th ed. St. Louis: CV Mosby;2002. p. 110–128.2. Rossiter JD, Wood M, Lockwood A, Lewis K. Operating conditions for ocular surgery under general anaesthesia: an eccentric problem. Eye (Lond). 2006; 20:55–58.
Article3. Snow JD. On the inhalation of the vapour of ether in surgical operations. Br J Anaesth. 1953; 25:253–267.
Article4. Guedel AE. Inhalation anaesthesia: a fundamental guide. 1st ed. Macmillan: New York;1937. p. 63–64.5. Sebel PS, Lang E, Rampil IJ, et al. A multicenter study of bispectral electroencephalogram analysis for monitoring anesthetic effect. Anesth Analg. 1997; 84:891–899.
Article6. McCann ME, Bacsik J, Davidson A, et al. The correlation of bispectral index with endtidal sevoflurane concentration and haemodynamic parameters in preschoolers. Paediatr Anaesth. 2002; 12:519–525.
Article7. Denman WT, Swanson EL, Rosow D, et al. Pediatric evaluation of the bispectral index (BIS) monitor and correlation of BIS with end-tidal sevoflurane concentration in infants and children. Anesth Analg. 2000; 90:872–877.
Article8. Davidson AJ, McCann ME, Devavaram P, et al. The differences in the bispectral index between infants and children during emergence from anesthesia after circumcision surgery. Anesth Analg. 2001; 93:326–330.
Article9. Ganesh A, Watcha MF. Bispectral index monitoring in pediatric anesthesia. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2004; 17:229–234.
Article10. Apt L, Isenberg S. Eye position of strabismus patients under general anesthesia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1977; 84:574–579.
Article11. Romano P, Gabriel L. Intraoperative adjustment of eye muscle surgery: correction based on eye position during general anesthesia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985; 103:351–353.12. Castanera de Molina A, Giner Munoz ML. Ocular alignment under general anesthesia in congenital esotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1991; 28:278–282.
Article13. Cheeseman JF, Merry AF, Pawley MD, et al. The effect of time of day on the duration of neuromuscular blockade elicited by rocuronium. Anaesthesia. 2007; 62:1114–1120.
Article14. Kevin LG, Cunningham AJ, Bolger C. Comparison of ocular microtremor and bispectral index during sevoflurane anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2002; 89:551–555.15. Deletis V, Urriza J, Ulkatan S, et al. The feasibility of recording blink reflexes under general anesthesia. Muscle Nerve. 2009; 39:642–646.
Article16. Power C, Crowe C, Higgins P, Moriarty DC. Anaesthetic depth at induction. An evaluation using clinical eye signs and EEG polysomnography. Anaesthesia. 1998; 53:736–743.17. Boukadoum AM, Ktonas PY. EOG-based recording and automated detection of sleep rapid eye movements: a critical review, and some recommendations. Psychophysiology. 1986; 23:598–611.
Article18. Collins CC, Carlson MR, Scott AB, Jampolsky A. Extraocular muscle forces in normal human subjects. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981; 20:652–664.19. Harrad RA, Stoddart P. Operating conditions for ocular surgery under general anaesthesia: an eccentric problem. Eye (Lond). 2007; 21:256–257.
Article20. Paez JH, Isenberg S, Apt L. Torsion and elevation under general anesthesia and during voluntary eyelid closure (Bell phenomenon). J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1984; 21:22–24.
Article21. Horiuchi T, Kawaguchi M, Kurita N, et al. The validity of bispectral index values from a dislocated sensor: a comparison with values from a sensor located in the commercially recommended position. Anesth Analg. 2007; 104:857–859.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of beach chair position on bispectral index values during arthroscopic shoulder surgery
- Effect of Nitrous Oxide on Bispectral Index during Sevoflurane Anesthesia
- Interruption of bispectral index monitoring by nerve integrity monitoring during tympanoplasty: A case report
- Pitfall of bispectral index during intraoperative seizure: a case report
- Eye Position of Orthophoric Patients under General Anesthesia