Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2018 Jun;11(2):102-108. 10.21053/ceo.2017.01277.
Relationship of Vertigo and Postural Instability in Patients With Vestibular Schwannoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ejson@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2412667
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2017.01277
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Growth of vestibular schwannomas (VS) causes progressive vestibular symptoms and postural instability. Since the tumor grows slowly, compensation of decaying vestibular input may decrease subjective symptoms of dizziness. This study aims to estimate the relationship of subjective vestibular symptoms and objective postural instability in patients with VS.
METHODS
A retrospective review of 18 patients newly diagnosed with VS and with subjective vertigo symptoms was performed. The results of vestibular function tests including the sensory organization test (SOT) using computerized dynamic posturography, caloric test, and self-report measures of subjective dizziness handicap (Dizziness Handicap Inventory) and visual analogue scale were compared according to the onset of vertigo symptoms.
RESULTS
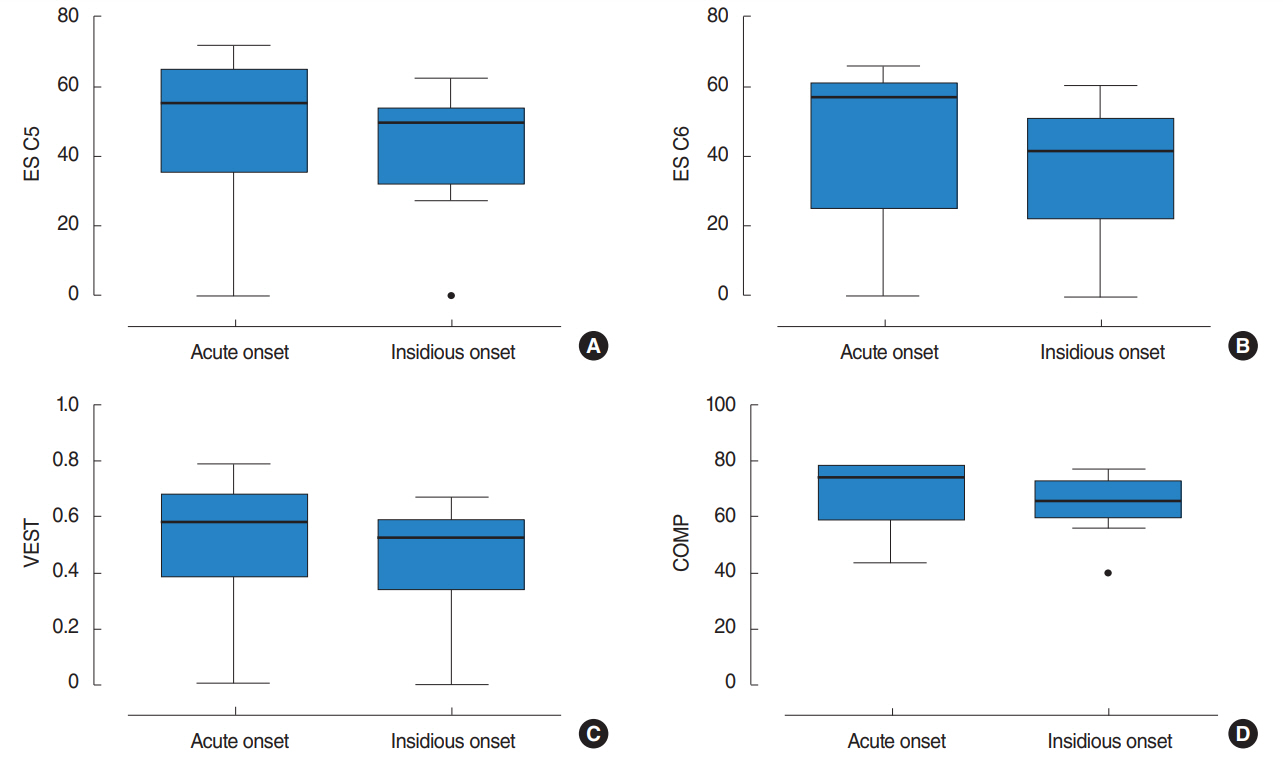
In VS patients, SOT showed decreased equilibrium score for all vestibular function related conditions, condition (C) 5 and 6, and composite (COMP) score. COMP scores were not correlated with visual analogue scale or Dizziness Handicap Inventory scores. Acute onset group included six patients and insidious onset group, 12 patients. Equilibrium scores for C5 and C6, and COMP scores were lower for insidious onset group, but the difference was not statistically significant.
CONCLUSION
Our findings confirmed postural instability is prevalent in VS patients. SOT parameters did not differ significantly between acute onset and insidious onset groups, but increased tumor size and canal weakness were noted in the insidious onset group. Clinicians should consider that postural instability is likely present even in patients who do not complain of acute vertigo, and appropriate counseling should be discussed with the patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kentala E, Pyykko I. Clinical picture of vestibular schwannoma. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2001; Jan. 28(1):15–22.
Article2. Andersen JF, Nilsen KS, Vassbotn FS, Moller P, Myrseth E, Lund-Johansen M, et al. Predictors of vertigo in patients with untreated vestibular schwannoma. Otol Neurotol. 2015; Apr. 36(4):647–52.
Article3. Hoffmann CP, Seigle B, Frere J, Parietti-Winkler C. Dynamical analysis of balance in vestibular schwannoma patients. Gait Posture. 2017; May. 54:236–41.
Article4. Day AS, Wang CT, Chen CN, Young YH. Correlating the cochleovestibular deficits with tumor size of acoustic neuroma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008; Jul. 128(7):756–60.
Article5. Gouveris H, Akkafa S, Lippold R, Mann W. Influence of nerve of origin and tumor size of vestibular schwannoma on dynamic posturography findings. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006; Dec. 126(12):1281–5.
Article6. Gouveris H, Helling K, Victor A, Mann W. Comparison of electronystagmography results with dynamic posturography findings in patients with vestibular schwannoma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007; Aug. 127(8):839–42.
Article7. Morrison GA, Sterkers JM. Unusual presentations of acoustic tumours. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1996; Feb. 21(1):80–3.
Article8. Breivik CN, Nilsen RM, Myrseth E, Finnkirk MK, Lund-Johansen M. Working disability in Norwegian patients with vestibular schwannoma: vertigo predicts future dependence. World Neurosurg. 2013; Dec. 80(6):e301–5.
Article9. Dayal M, Perez-Andujar A, Chuang C, Parsa AT, Barani IJ. Management of vestibular schwannoma: focus on vertigo. CNS Oncol. 2013; Jan. 2(1):99–104.
Article10. Tranter-Entwistle I, Dawes P, Darlington CL, Smith PF, Cutfield N. Video head impulse in comparison to caloric testing in unilateral vestibular schwannoma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016; Nov. 136(11):1110–4.
Article11. Batuecas-Caletrio A, Santa Cruz-Ruiz S, Munoz-Herrera A, Perez-Fernandez N. The map of dizziness in vestibular schwannoma. Laryngoscope. 2015; Dec. 125(12):2784–9.
Article12. Bergenius J, Magnusson M. The relationship between caloric response, oculomotor dysfunction and size of cerebello-pontine angle tumours. Acta Otolaryngol. 1988; Nov-Dec. 106(5-6):361–7.
Article13. Stipkovits EM, Van Dijk JE, Graamans K. Electronystagmographic changes in patients with unilateral vestibular schwannomas in relation to tumor progression and central compensation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1999; Apr. 256(4):173–6.
Article14. Kim HJ, Park SH, Kim JS, Koo JW, Kim CY, Kim YH, et al. Bilaterally abnormal head impulse tests indicate a large cerebellopontine angle tumor. J Clin Neurol. 2016; Jan. 12(1):65–74.
Article15. Monsell EM, Furman JM, Herdman SJ, Konrad HR, Shepard NT. Computerized dynamic platform posturography. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997; Oct. 117(4):394–8.16. Gouveris H, Stripf T, Victor A, Mann W. Dynamic posturography findings predict balance status in vestibular schwannoma patients. Otol Neurotol. 2007; Apr. 28(3):372–5.
Article17. Ribeyre L, Frere J, Gauchard G, Lion A, Perrin P, Spitz E, et al. Preoperative balance control compensation in patients with a vestibular schwannoma: does tumor size matter? Clin Neurophysiol. 2015; Apr. 126(4):787–93.
Article18. Koos WT, Spetzler RF, Bock FW. Microsurgery of cerebellopontine angle tumors. In : Koos WT, Bock FW, Spetzler RF, Ammerman B, editors. Clinical microneurosurgery. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme;1976. p. 91–112.19. Neurocom International Inc. EquiTest system operator’s manual version 8.2. Clackamas: Neurocom International Inc;2004.20. Dilwali S, Landegger LD, Soares VY, Deschler DG, Stankovic KM. Secreted factors from human vestibular schwannomas can cause cochlear damage. Sci Rep. 2015; Dec. 5:18599.
Article21. Yin M, Ishikawa K, Omi E, Saito T, Itasaka Y, Angunsuri N. Small vestibular schwannomas can cause gait instability. Gait Posture. 2011; May. 34(1):25–8.
Article22. Myrseth E, Moller P, Wentzel-Larsen T, Goplen F, Lund-Johansen M. Untreated vestibular schwannomas: vertigo is a powerful predictor for health-related quality of life. Neurosurgery. 2006; Jul. 59(1):67–76.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Vertigo
- Diagnosis and Management of Vestibular Schwannoma: Focus on Dizziness
- Can Postural Instability Respond to Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation in Patients with Parkinson's Disease?
- Vestibular Rehabilitation
- A Case of inferior vestibular schwannoma which was lately diagnosed due to normal hearing level