Yonsei Med J.
2018 Jul;59(5):595-601. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.5.595.
A Tumor-Specific Tissue-Penetrating Peptide Enhances the Efficacy of Chemotherapy Drugs in Gastric Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Second Outpatient Department of Chengdu Army Region Authority, Chengdu, China.
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, the 520th Hospital of People's Liberation Army, Mianyang, China.
- 3Sichuan Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China.
- 4Department of Gastroenterology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, the Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China. zhoulin1105@163.com
- KMID: 2412650
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.5.595
Abstract
- PURPOSE
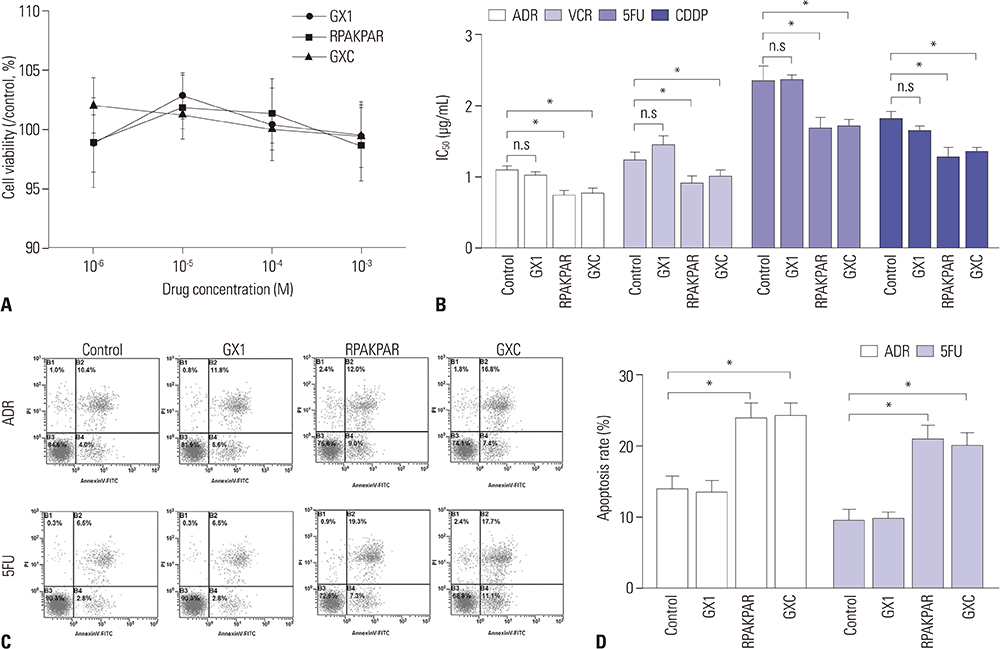
C-end rule (CendR) peptides are found to enhance the penetration of chemotherapeutic agents into tumor cells, while GX1 is a peptide that homes to gastric cancer (GC) vasculature. This study aimed to synthesize a novel peptide GX1-RPAKPAR (GXC) and to explore the effect of GXC on sensitizing GC cells to chemotherapeutic agents.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
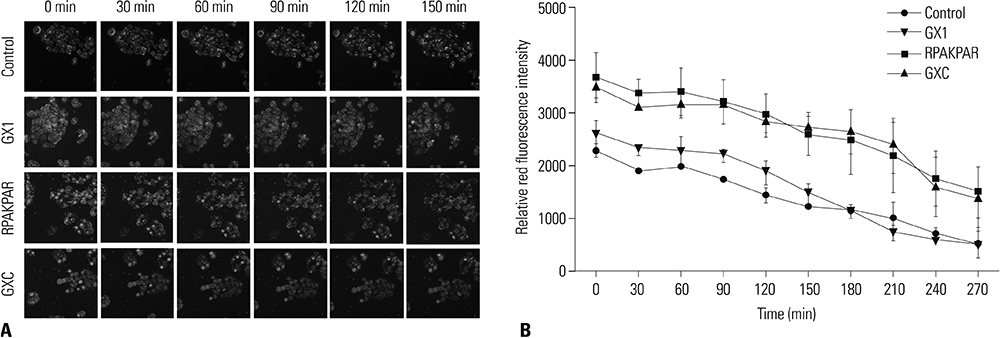
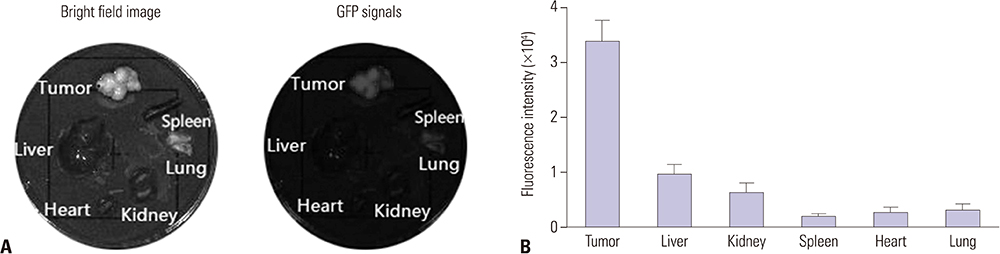
Intracellular Adriamycin concentration analysis was applied to conform whether GXC peptide increases the penetration of chemotherapeutic agents into GC cells in vitro. The effect of GXC peptide on sensitizing GC cells to chemotherapeutics was validated by apoptosis assay and in vitro/vivo drug sensitivity assay. The specificity of GXC to GC tissue was validated by ex vivo fluorescence imaging.
RESULTS
In vitro, administration of GXC significantly increased Adriamycin concentrations inside SGC-7901 cells, and enhanced the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents by decreasing the IC50 value. In vivo, FITC-GXC specifically accumulated in GC tissue. Moreover, systemic co-injection with GXC peptide and Adriamycin statistically improved the therapeutic efficacy in SGC-7901 xenograft models, surprisingly, without obviously increasing side effects.
CONCLUSION
These results demonstrated that co-administration of the novel peptide GXC with chemotherapeutic agents may be a potential way to enhance the efficacy of anticancer drugs in GC treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bray F, Jemal A, Grey N, Ferlay J, Forman D. Global cancer transitions according to the Human Development Index (2008–2030): a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13:790–801.
Article2. Sha H, Zou Z, Xin K, Bian X, Cai X, Lu W, et al. Tumor-penetrating peptide fused EGFR single-domain antibody enhances cancer drug penetration into 3D multicellular spheroids and facilitates effective gastric cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2015; 200:188–200.
Article3. Teesalu T, Sugahara KN, Kotamraju VR, Ruoslahti E. C-end rule peptides mediate neuropilin-1-dependent cell, vascular, and tissue penetration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106:16157–16162.
Article4. Sugahara KN, Teesalu T, Karmali PP, Kotamraju VR, Agemy L, Greenwald DR, et al. Coadministration of a tumor-penetrating peptide enhances the efficacy of cancer drugs. Science. 2010; 328:1031–1035.
Article5. Schmithals C, Köberle V, Korkusuz H, Pleli T, Kakoschky B, Augusto EA, et al. Improving drug penetrability with iRGD leverages the therapeutic response to sorafenib and doxorubicin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015; 75:3147–3154.
Article6. Hui X, Han Y, Liang S, Liu Z, Liu J, Hong L, et al. Specific targeting of the vasculature of gastric cancer by a new tumor-homing peptide CGNSNPKSC. J Control Release. 2008; 131:86–93.
Article7. Chen B, Cao S, Zhang Y, Wang X, Liu J, Hui X, et al. A novel peptide (GX1) homing to gastric cancer vasculature inhibits angiogenesis and cooperates with TNF alpha in anti-tumor therapy. BMC Cell Biol. 2009; 10:63.
Article8. Chen K, Sun X, Niu G, Ma Y, Yap LP, Hui X, et al. Evaluation of 64Cu labeled GX1: a phage display peptide probe for PET imaging of tumor vasculature. Mol Imaging Biol. 2012; 14:96–105.
Article9. Xin J, Zhang X, Liang J, Xia L, Yin J, Nie Y, et al. In vivo gastric cancer targeting and imaging using novel symmetric cyanine dye-conjugated GX1 peptide probes. Bioconjug Chem. 2013; 24:1134–1143.
Article10. Green M, Loewenstein PM. Autonomous functional domains of chemically synthesized human immunodeficiency virus tat transactivator protein. Cell. 1988; 55:1179–1188.
Article11. Oliveira EA, Faintuch BL. Radiolabeling and biological evaluation of the GX1 and RGD-GX1 peptide sequence for angiogenesis targeting. Nucl Med Biol. 2015; 42:123–130.
Article12. Xiong D, Liu Z, Bian T, Li J, Huang W, Jing P, et al. GX1-mediated anionic liposomes carrying adenoviral vectors for enhanced inhibition of gastric cancer vascular endothelial cells. Int J Pharm. 2015; 496:699–708.
Article13. Frankel AD, Pabo CO. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988; 55:1189–1193.
Article14. Elliott G, O'Hare P. Intercellular trafficking and protein delivery by a herpesvirus structural protein. Cell. 1997; 88:223–233.
Article15. Morris MC, Deshayes S, Heitz F, Divita G. Cell-penetrating peptides: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics. Biol Cell. 2008; 100:201–217.
Article16. Arap W, Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E. Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science. 1998; 279:377–380.
Article17. Aird WC. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res. 2007; 100:158–173.18. Arap W, Haedicke W, Bernasconi M, Kain R, Rajotte D, Krajewski S, et al. Targeting the prostate for destruction through a vascular address. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002; 99:1527–1531.
Article19. Svensen N, Walton JG, Bradley M. Peptides for cell-selective drug delivery. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012; 33:186–192.
Article20. Sugahara KN, Teesalu T, Karmali PP, Kotamraju VR, Agemy L, Girard OM, et al. Tissue-penetrating delivery of compounds and nanoparticles into tumors. Cancer Cell. 2009; 16:510–520.
Article21. Du Y, Zhang Q, Jing L, Liang X, Chi C, Li Y, et al. GX1-conjugated poly(lactic acid) nanoparticles encapsulating Endostar for improved in vivo anticolorectal cancer treatment. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015; 10:3791–3802.
Article22. Mantis C, Kandela I, Aird F. Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology. Replication study: coadministration of a tumor-penetrating peptide enhances the efficacy of cancer drugs. Elife. 2017; 6:e17584.
Article23. Baker M, Dolgin E. Cancer reproducibility project releases first results. Nature. 2017; 541:269–270.
Article24. Staton CA, Kumar I, Reed MW, Brown NJ. Neuropilins in physiological and pathological angiogenesis. J Pathol. 2007; 212:237–248.
Article25. Jia H, Bagherzadeh A, Hartzoulakis B, Jarvis A, Löhr M, Shaikh S, et al. Characterization of a bicyclic peptide neuropilin-1 (NP-1) antagonist (EG3287) reveals importance of vascular endothelial growth factor exon 8 for NP-1 binding and role of NP-1 in KDR signaling. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:13493–13502.
Article26. Pellet-Many C, Frankel P, Jia H, Zachary I. Neuropilins: structure, function and role in disease. Biochem J. 2008; 411:211–226.
Article27. Akagi M, Kawaguchi M, Liu W, McCarty MF, Takeda A, Fan F, et al. Induction of neuropilin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor by epidermal growth factor in human gastric cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2003; 88:796–802.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Preoperative Chemotherapy in Advanced Stomach Cancer (Cons)
- Chemotherapy for Metastatic Gastric Cancer
- Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Asian Patients With Locally Advanced Gastric Cancer
- Efficacy and Safety Profile of TS-1 or TS-1/CDDP in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer
- Update of Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Resected Gastric Cancer