J Vet Sci.
2016 Dec;17(4):569-576. 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.4.569.
Improvement of pregnancy rate by intrauterine administration of dexamethasone and recombinant human leukemia inhibitory factor at the time of embryo transfer in cattle
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Dentistry and Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul 03080, Korea.
- 2ETbiotech Ltd., Damyang 57344, Korea.
- 3Department of Theriogenology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 05029, Korea. jipark84@konkuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2412614
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2016.17.4.569
Abstract
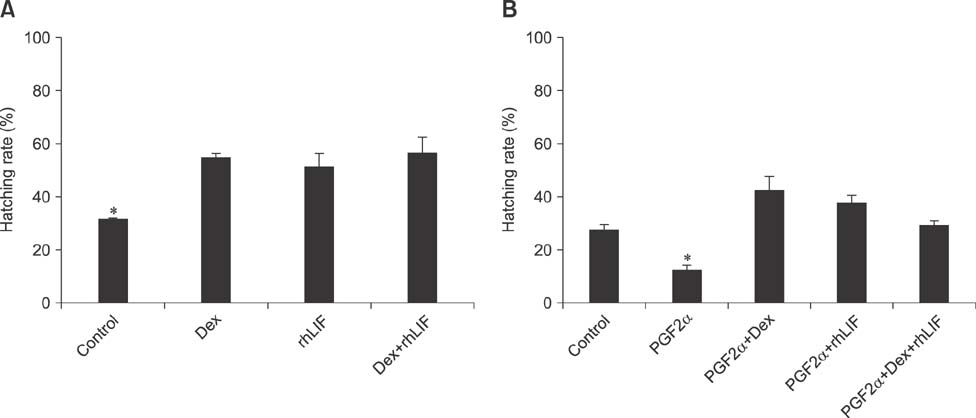
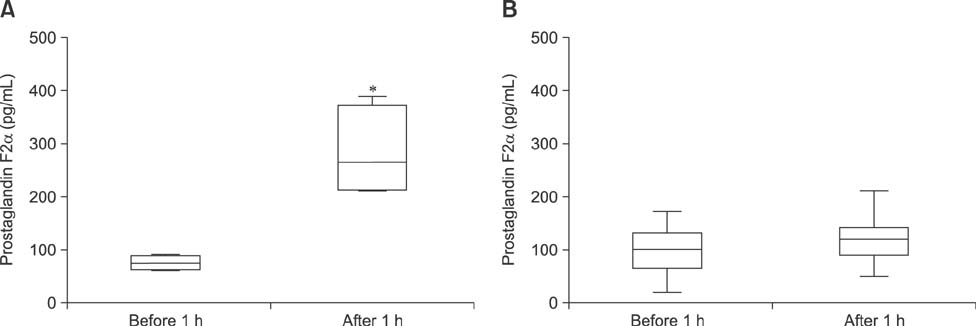
- Bovine embryos (day 5) were cultured to day 10 with or without 100 ng/mL PGF2α in medium supplemented with control; 100 nM Dex; 1,000 U/mL recombinant human leukemia inhibitory factor (rhLIF); or Dex+rhLIF. Although the rates to development to the blastocyst were not significantly different among groups, the hatching rate after additional culture with Dex +/or rhLIF was significantly higher in all supplemented groups than the control (p < 0.05). In the presence of PGF2α, the hatching rate was significantly restored in all supplemented groups relative to the group treated with only PGF2α and the control (p < 0.05). Embryo transfer (ET) was performed with blastocysts (day 7). PGF2α levels of control recipient cows were significantly higher in the circulatory blood samples collected 60 min after ET than in samples collected 60 min before ET (p < 0.005), and were decreased in cows injected with loading medium supplemented with Dex+rhLIF (p < 0.005). Pregnancy rate was significantly higher in the ET group that received supplemented embryo-loading medium than in the non-supplemented control (p < 0.05). The intrauterine administration of Dex and rhLIF at ET prevented increased PGF2α in circulatory blood and resulted in enhanced pregnancy rate.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. al-Hozab A, Menino AR Jr. Lack of effect of hormones and inducers of intracellular messengers on plasminogen activator production by bovine embryos in vitro. J Reprod Fertil. 1992; 96:79–90.
Article2. Al Naib A, Mamo S, O'Gormana GM, Lonergana P, Swalesb A, Fair T. Regulation of non-classical major histocompatability complex class I mRNA expression in bovine embryos. J Reprod Immunol. 2011; 91:31–40.
Article3. Andersen CY. Possible new mechanism of cortisol action in female reproductive organs: physiological implications of the free hormone hypothesis. J Endocrinol. 2002; 173:211–217.
Article4. Bamberger AM, Jenatschke S, Schulte HM, Löning T, Bamberger MC. Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) stimulates the human HLA-G promoter in JEG3 choriocarcinoma cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000; 85:3932–3936.
Article5. Chaudhari N, Talwar P, Parimisetty A, Lefebvre d'Hellencourt C, Ravanan P. A molecular web: endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014; 8:213.
Article6. Dorniak P, Bazer FW, Spencer TE. Physiology and Endocrinology Symposium: biological role of interferon tau in endometrial function and conceptus elongation. J Anim Sci. 2013; 91:1627–1638.
Article7. Eswari S, Sai Kumar G, Sharma GT. Expression of mRNA encoding leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and its receptor (LIFRβ) in buffalo preimplantation embryos produced in vitro: markers of successful embryo implantation. Zygote. 2013; 21:203–213.
Article8. Geary TW, Ansotegui RP, MacNeil MD, Roberts AJ, Waterman RC. Effects of flunixin meglumine on pregnancy establishment in beef cattle. J Anim Sci. 2010; 88:943–949.
Article9. González R, Ruiz-León Y, Gomendio M, Roldan ERS. The effect of glucocorticoids on mouse oocyte in vitro maturation and subsequent fertilization and embryo development. Toxicol In Vitro. 2010; 24:108–115.
Article10. Goppelt Struebe M. Molecular mechanisms involved in the regulation of prostaglandin biosynthesis by glucocorticoids. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997; 53:1389–1395.
Article11. Gough NM, Williams RL. The pleiotrophic actions of leukemia inhibitory factor. Cancer Cells. 1989; 1:77–80.12. Guzeloglu A, Erdem H, Saribay MK, Thatcher WW, Tekeli T. Effect of the administration of flunixin meglumine on pregnancy rates in Holstein heifers. Vet Rec. 2007; 160:404–406.
Article13. Han YM, Lee ES, Mogoe T, Lee KK, Fukui Y. Effect of human leukemia inhibitory factor on in vitro development of IVF-derived bovine morulae and blastocysts. Theriogenology. 1995; 44:507–516.
Article14. Hasler JF. Forty years of embryo transfer in cattle: a review focusing on the journal Theriogenology, the growth of the industry in North America, and personal reminisces. Theriogenology. 2014; 81:152–169.
Article15. Heuwieser W, Iwersen M, Goetze L. Efficacy of carprofen on conception rates in lactating dairy cows after subcutaneous or intrauterine administration at the time of breeding. J Dairy Sci. 2011; 94:146–151.
Article16. Hillier SG, Tetsuka M. An anti-inflammatory role for glucocorticoids in the ovaries? J Reprod Immunol. 1998; 39:21–27.
Article17. International Embryo Transfer Society. Stringfellow DA, Seidel SM, editors. International Embryo Transfer Society. Manual of the International Embryo Transfer Society: a procedural guide and general information for the use of embryo transfer technology emphasizing sanitary procedures. Savoy: Manchester;1998. p. 103–134.18. Kask K, Malmgren L, Odensvik K. Prostaglandin F2 alpha metabolite levels following an embryo transfer procedure in the mare. Acta Vet Scand. 1995; 36:145–147.
Article19. Krisher RL, Prather RS. A role for the Warburg effect in preimplantation embryo development: metabolic modification to support rapid cell proliferation. Mol Reprod Dev. 2012; 79:311–320.
Article20. Malazdrewich C, Thumbikat P, Abrahamsen MS, Maheswaran SK. Pharmacological inhibition of Mannheimia haemolytica lipopolysaccharide and leukotoxin-induced cytokine expression in bovine alveolar macrophages. Microb Pathog. 2004; 36:159–169.
Article21. Maurer PR, Beier HM. Uterine proteins and development in vitro of rabbit preimplantation embryos. J Reprod Fertil. 1976; 48:33–41.
Article22. Okuda K, Miyamoto Y, Skarzynski DJ. Regulation of endometrial prostaglandin F2α synthesis during luteolysis and early pregnancy in cattle. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2002; 23:255–264.
Article23. Oshima K, Watanabe H, Yoshihara K, Kojima T, Dochi O, Takenouchi N, Fukushima M, Komatsu M. Gene expression of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSF) in bovine endometrium during early pregnancy. Theriogenology. 2003; 60:1217–1226.
Article24. Santana PPB, Carvalho CMF, da Costa NN, Silva TVG, Ramos PCA, Cordeiro MS, Santos SSD, Khayat AS, Ohashi OM, Miranda MS. Effect of dexamethasone on development of in vitro-produced bovine embryos. Theriogenology. 2014; 82:10–16.
Article25. Sasson R, Shinder V, Dantes A, Land A, Amsterdam A. Activation of multiple signal transduction pathways by glucocorticoids: protection of ovarian follicular cells against apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003; 311:1047–1056.
Article26. Scenna FN, Edwards JL, Rohrbach NR, Hockett ME, Saxton AM, Schrick FN. Detrimental effects of prostaglandin F2α on preimplantation bovine embryos. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2004; 73:215–226.
Article27. Scenna FN, Hockett ME, Townsa TM, Saxton AM, Rohrbach NR, Wehrman ME, Schrick FN. Influence of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor administered at embryo transfer on pregnancy rates of recipient cows. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005; 78:38–45.
Article28. Seals RC, Lemaster JW, Hopkins FM, Schrick FN. Effects of elevated concentrations of prostaglandin F2α on pregnancy rates in progestogen supplemented cattle. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 1998; 56:377–389.
Article29. Shido F, Ito T, Nomura S, Yamamoto E, Sumigama S, Ino K, Itakura A, Hattori A, Tsujimoto M, Mizutani S, Kikkawa F. Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase-1 mediates leukemia inhibitory factor-induced cell surface human leukocyte antigen-G expression in JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cells. Endocrinology. 2006; 147:1780–1788.
Article30. Sirisathien S, Hernandez-Fonseca HJ, Bosch P, Hollet BR, Lott JD, Brackett BG. Effect of leukemia inhibitory factor on bovine embryos produced in vitro under chemically defined conditions. Theriogenology. 2003; 59:1751–1763.
Article31. Soto P, Natzke RP, Hansen PJ. Identification of possible mediators of embryonic mortality caused by mastitis: actions of lipopolysaccharide, prostaglandin F2α, and the nitric oxide generator, sodium nitroprusside dihydrate, on oocyte maturation and embryonic development in cattle. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2003; 50:263–272.
Article32. Taverne MAM, Breukelman SP, Perényi Ƶ, Dieleman SJ, Vos PLAM, Jonker HH, de Ruigh L, Van Wagtendonk-de Leeuw JM, Beckers JF. The monitoring of bovine pregnancies derived from transfer of in vitro produced embryos. Reprod Nutr Dev. 2002; 42:613–624.
Article33. Teeling JL, Cunningham C, Newman TA, Perry VH. The effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents on behavioural changes and cytokine production following systemic inflammation: implications for a role of COX-1. Brain Behav Immun. 2010; 24:409–419.
Article34. Van Merris V, Van Wemmel K, Cortvrindt R. In vitro effects of dexamethasone on mouse ovarian function and preimplantation embryo development. Reprod Toxicol. 2007; 23:32–41.
Article35. Velez JS, Randel RD, Neuendorff DA. Effect of uterine manipulation on postpartum fertility and plasma 13,14-dihydro-15-keto-prostaglandin F2α in Brahman cows and first-calf heifers. Theriogenology. 1991; 36:987–998.
Article36. Waldenström U, Hellberg D, Nilsson S. Low-dose aspirin in a short regimen as standard treatment in in vitro fertilization: a randomized, prospective study. Fertil Steril. 2004; 81:1560–1564.
Article37. Wang M. The role of glucocorticoid action in the pathophysiology of the metabolic syndrome. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2005; 2:3.38. Wann RA, Randel RD. Effect of uterine manipulation 35 days after parturition on plasma concentrations of 13,14-dihydro-15-keto prostaglandin F2α in multiparous and primiparous Brahman cows. J Anim Sci. 1990; 68:1389–1394.
Article39. Yang JG, Chen WY, Li PS. Effects of glucocorticoids on maturation of pig oocytes and their subsequent fertilizing capacity in vitro. Biol Reprod. 1999; 60:929–936.
Article40. Yamashita S, Abe H, Itoh T, Satoh T, Hoshi H. A serum-free culture system for efficient in vitro production of bovine blastocysts with improved viability after freezing and thawing. Cytotechnology. 1999; 31:123–131.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of Heterotopic Pregnancy following in vitro fertilization: transcervical evacuation with preserved intrauterine pregnancy
- A Case of Combined Interstitial and Intrauterine Pregnancy as Fifth Ectopic Pregnancies after In Vitro Fertilization and Embryo Transfer in Bilateral Salpingectomy patient
- Combined intrauterine and intraligamentary full term pregnancy after in vitro fertilization & embryo transfer
- Role of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor in the Effect of Co-Culture on Preimplantation Embryo Develpement
- A Case of Primary Ovarian Pregnancy after In Vitro Fertilization and Embryo Transfer