J Vet Sci.
2017 Jun;18(2):209-216. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.2.209.
Efficacy evaluation of commercial disinfectants by using Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium as a test organism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Gimcheon 39660, Korea.
- 2College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 05029, Korea. nojamaji@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2412574
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.2.209
Abstract
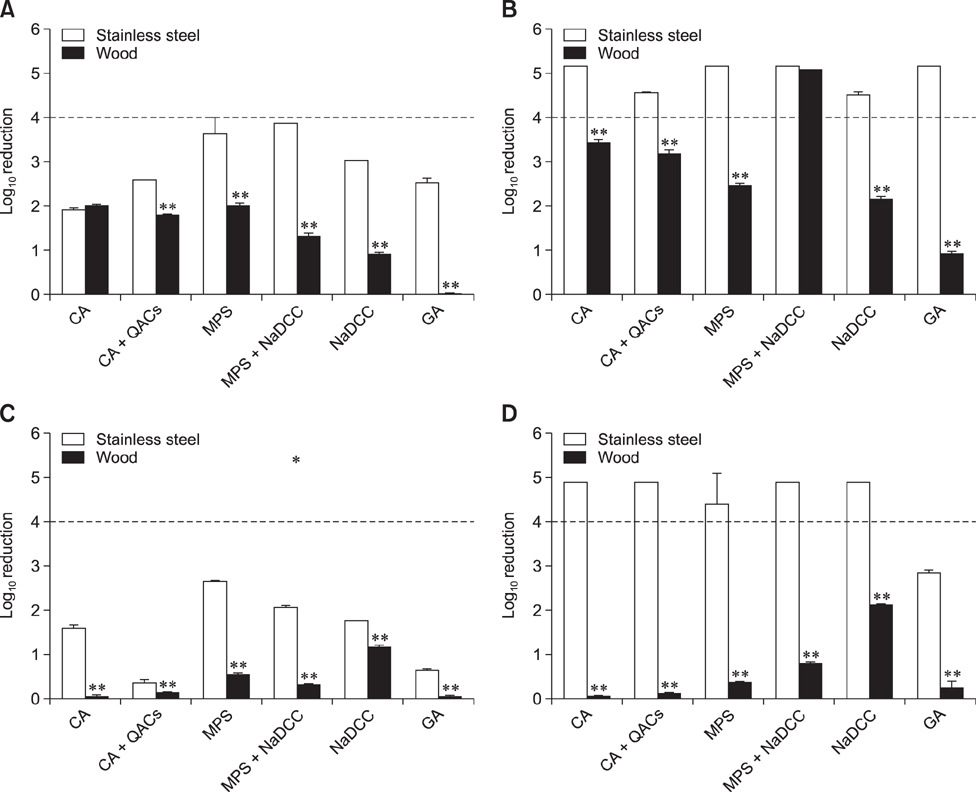
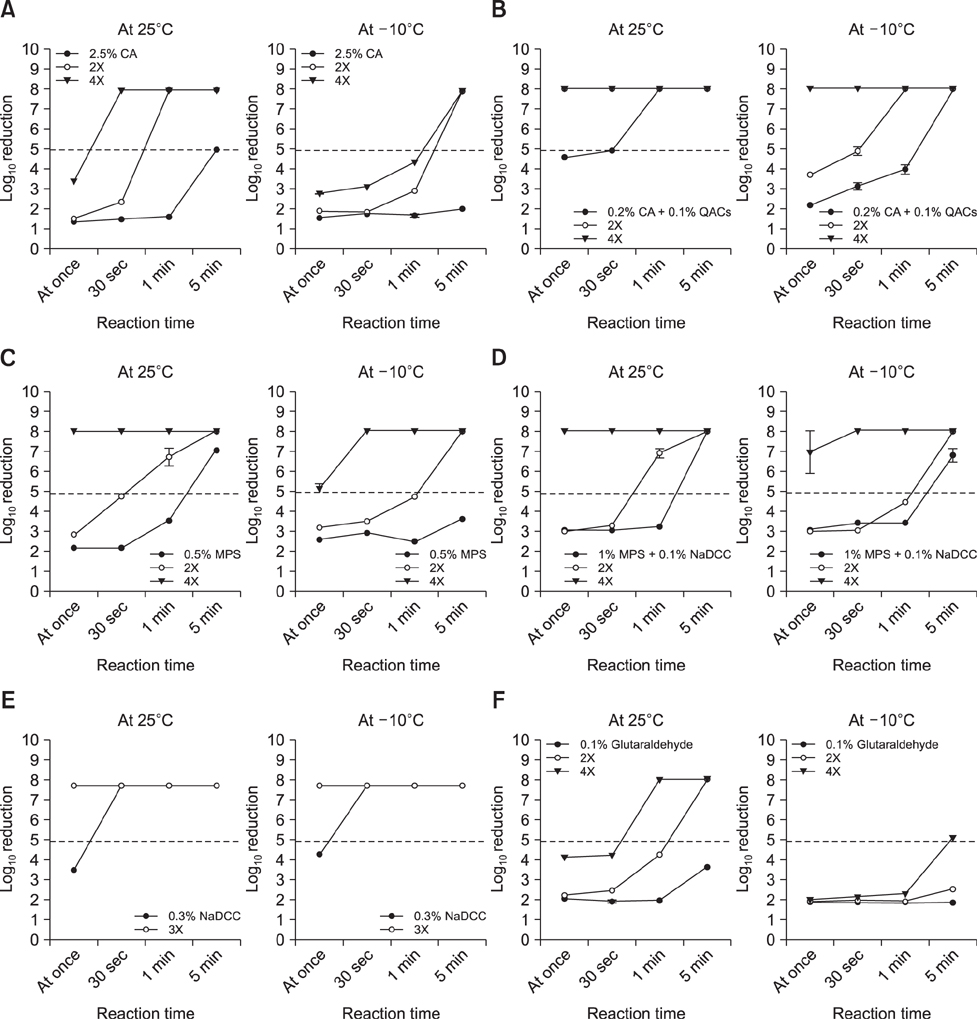
- The efficacies of six commercial disinfectants were evaluated by using Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium under simulated natural conditions such as sub-zero temperature, short disinfecting time, and surface type (uneven or smooth). We used a suspensionmodel test to determine the disinfecting efficacy under varying contact times (1, 5, 10, and 30 min) and temperatures (25℃, 4℃, 0℃, and −10℃). The bactericidal effect according to surface structure was measured by using a carriermodel test at 25℃ and −10℃. The effective concentrations of each disinfectant were fixed to give a disinfecting effect within a short time (< 1 min) at 25℃ and −10℃. The suspension model results revealed that bactericidal efficacy significantly dropped at low temperature for most of the disinfectants used; a sodium dichloroisocyanurate product showed the strongest efficacy. In the carrier test, bacterial load on a wooden surface was more difficult to remove than that on a stainless-steel surface. The results show that commercial disinfectant products vary in their disinfecting efficacy, which is affected by several field factors including temperature, contact time, and carrier material. Environmental conditions and surface type for disinfection should be considered prior to selecting an optimal disinfectant in the field.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency (KR). Biocides Efficacy Test against Bacteria. Notice 2013-34 (Mar. 23 2013).2. Carling PC, Wormser GP. Antisepsis, disinfection and sterilization: types, action and resistance by Gerald E. McDonnell Wahington, DC: American Society for Microbiology Press, 2007. 378 pp., illustrated. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 45:1251–1252.
Article3. Carrique-Mas JJ, Marin C, Breslin M, McLaren I, Davies R. A comparison of the efficacy of cleaning and disinfection methods in eliminating Salmonella spp. from commercial egg laying houses. Avian Pathol. 2009; 38:419–424.
Article4. De Benedictis P, Beato MS, Capua I. Inactivation of avian influenza viruses by chemical agents and physical conditions: a review. Zoonoses Public Health. 2007; 54:51–68.
Article5. Gradel KO, Sayers AR, Davies RH. Surface disinfection tests with Salmonella and a putative indicator bacterium, mimicking worst-case scenarios in poultry houses. Poult Sci. 2004; 83:1636–1643.
Article6. Hiramatsu R, Matsumoto M, Sakae K, Miyazaki Y. Ability of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. to survive in a desiccation model system and in dry foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005; 71:6657–6663.
Article7. Kang S, Jang A, Lee SO, Min JS, Kim IS, Lee M. Effect of organic acids on microbial populations and Salmonella typhimurium in pork loins. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2003; 16:96–99.
Article8. Koleci X, Quinn PJ, Çela M, Malaj Z. The place of disinfection in the control of infectious diseases. Albanian J Nat Tech Sci. 2007; 12:139–156.9. Kuda T, Iwase T, Yuphakhun C, Takahashi H, Koyanagi T, Kimura B. Surfactant-disinfectant resistance of Salmonella and Staphylococcus adhered and dried on surfaces with egg compounds. Food Microbiol. 2011; 28:920–925.
Article10. Marin C, Hernandiz A, Lainez M. Biofilm development capacity of Salmonella strains isolated in poultry risk factors and their resistance against disinfectants. Poult Sci. 2009; 88:424–431.
Article11. McLaren I, Wales A, Breslin M, Davies R. Evaluation of commonly-used farm disinfectants in wet and dry models of Salmonella farm contamination. Avian Pathol. 2011; 40:33–42.
Article12. Møretrø T, Heir E, Nesse LL, Vestby LK, Langsrud S. Control of Salmonella in food related environments by chemical disinfection. Food Res Int. 2012; 45:532–544.
Article13. Møretrø T, Midtgaard ES, Nesse LL, Langsrud S. Susceptibility of Salmonella isolated from fish feed factories to disinfectants and air-drying at surfaces. Vet Microbiol. 2003; 94:207–217.
Article14. Møretrø T, Vestby LK, Nesse LL, Storheim SE, Kotlarz K, Langsrud S. Evaluation of efficacy of disinfectants against Salmonella from the feed industry. J Appl Microbiol. 2009; 106:1005–1012.
Article15. Payne JB, Kroger EC, Watkins SE. Evaluation of disinfectant efficacy when applied to the floor of poultry grow-out facilities. J Appl Poult Res. 2005; 14:322–329.
Article16. Pinto F, Maillard JY, Denyer SP. Effect of surfactants, temperature, and sonication on the virucidal activity of polyhexamethylene biguanide against the bacteriophage MS2. Am J Infect Control. 2010; 38:393–398.
Article17. Preller L, Heederik D, Boleij JSM, Vogelzang PFJ, Tielen MJM. Lung function and chronic respiratory symptoms of pig farmers: focus on exposure to endotoxins and ammonia and use of disinfectants. Occup Environ Med. 1995; 52:654–660.
Article18. Sattar SA, Springthorpe VS, Adegbunrin O, Abu Zafer A, Busa M. A disc-based quantitative carrier test method to assess the virucidal activity of chemical germicides. J Virol Methods. 2003; 112:3–12.
Article19. Shah DH, Zhou XH, Addwebi T, Davis MA, Orfe L, Call DR, Guard J, Besser TE. Cell invasion of poultry-associated Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis isolates is associated with pathogenicity, motility and proteins secreted by the type III secretion system. Microbiology. 2011; 157:1428–1445.
Article20. Stringfellow K, Anderson P, Caldwell D, Lee J, Byrd J, McReynolds J, Carey J, Nisbet D, Farnell M. Evaluation of disinfectants commonly used by the commercial poultry industry under simulated field conditions. Poult Sci. 2009; 88:1151–1155.
Article21. Tuladhar E, Hazeleger WC, Koopmans M, Zwietering MH, Beumer RR, Duizer E. Residual viral and bacterial contamination of surfaces after cleaning and disinfection. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012; 78:7769–7775.
Article22. Uesugi AR, Danyluk MD, Harris LJ. Survival of Salmonella enteritidis phage type 30 on inoculated almonds stored at –20, 4, 23, and 30℃. J Food Prot. 2006; 69:1851–1857.
Article23. Wales A, Breslin M, Davies R. Assessment of cleaning and disinfection in Salmonella-contaminated poultry layer houses using qualitative and semi-quantitative culture techniques. Vet Microbiol. 2006; 116:283–293.
Article24. Wong HS, Townsend KM, Fenwick SG, Maker G, Trengove RD, O'Handley RM. Comparative susceptibility of Salmonella Typhimurium biofilms of different ages to disinfectants. Biofouling. 2010; 26:859–864.
Article25. Yilmaz A, Heffels-Redmann U, Redmann T. Evaluation of the virucidal efficacy of two chemical disinfectants against avian influenza virus A at different temperatures. Arch Geflügelk. 2004; 68:50–56.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Salmonella Serovars from Foodborne and Waterborne Diseases in Korea, 1998-2007: Total Isolates Decreasing Versus Rare Serovars Emerging
- Modulation of Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immunity Against Avian Influenza and Newcastle Disease Vaccines by Oral Administration of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Expressing Chicken Interleukin-18
- Prevalence of Specific Clone of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Clones in the Swine Population of Kyungpook Province During 1998 to 2000
- Characteristics of Epidemic Multidrugresistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium DT104 Strains First Isolated in Korea
- Protection Against Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum, and Salmonella Enteritidis Infection in Layer Chickens Conferred by a Live Attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium Strain