Clin Orthop Surg.
2018 Jun;10(2):216-224. 10.4055/cios.2018.10.2.216.
Sex Differences in Pedobarographic Findings and Relationship between Radiographic and Pedobarographic Measurements in Young Healthy Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Mechanical Engineering, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. oasis100@empal.com
- KMID: 2411748
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.2.216
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Although pedobarographic measurement is increasingly used for clinical and research purposes, relatively few published studies have investigated normative data. This study examined pedobarographic findings in young healthy adults with regard to sex-related differences and correlations among measurement indices.
METHODS
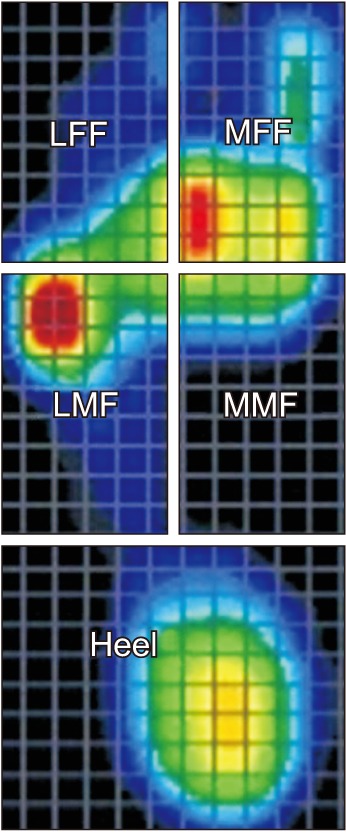
Twenty young healthy adults (mean age, 22.4 years; standard deviation, 1.2 years; and 10 males and 10 females) were included. Weight bearing anteroposterior (AP) and lateral foot radiographs were taken, and dynamic pedobarographic data during treadmill walking and maximum ankle dorsiflexion were obtained. AP talo-first metatarsal angle, naviculocuboid overlap, lateral talo-first metatarsal angle, and plantar soft tissue thickness were measured on foot radiographs. Pedobarographic data including peak pressure and pressure-time integral were measured on five plantar segments: medial forefoot (MFF), lateral forefoot (LFF), medial midfoot (MMF), lateral midfoot (LMF), and heel.
RESULTS
Male and female subjects significantly differed in body mass index (BMI, p < 0.001), AP talo-first metatarsal angle (p = 0.018), soft tissue thickness under the metatarsal head (p = 0.040) and calcaneal tuberosity (p < 0.001), maximum dorsiflexion during stance phase (p = 0.041), peak pressure on the MFF (p = 0.005) and LFF (p = 0.004), and pressure-time integral on the MFF (p = 0.018) and heel (p = 0.001). BMI was significantly correlated with soft tissue thickness under the metatarsal head (r = 0.521, p = 0.018) and calcaneal tuberosity (r = 0.585, p = 0.007), peak pressure on the MFF (r = 0.601, p = 0.005) and LFF (r = 0.487, p = 0.029), pressure-time integral on the heel (r = 0.552, p = 0.012), and total pressure-time integral (r = 0.755, p < 0.001). Maximum dorsiflexion demonstrated significant negative correlations with pressure-time integral on the MFF (r = −0.595, p = 0.007) and total pressure-time integral (r = −0.492, p = 0.032). Pressure-time integral varus/valgus index was significantly correlated with pressuretime integral forefoot/heel index (r = 0.472, p = 0.036).
CONCLUSIONS
Sex-related differences in pedobarographic examination were observed, which could provide useful information in setting appropriate treatment goals and obtaining appropriate control data. The effects of subtalar motion in distributing plantar pressure should be investigated in a future study.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Barn R, Waaijman R, Nollet F, Woodburn J, Bus SA. Predictors of barefoot plantar pressure during walking in patients with diabetes, peripheral neuropathy and a history of ulceration. PLoS One. 2015; 10(2):e0117443. PMID: 25647421.
Article2. Chiu MC, Wu HC, Chang LY. Gait speed and gender effects on center of pressure progression during normal walking. Gait Posture. 2013; 37(1):43–48. PMID: 22824680.
Article3. Duffin AC, Kidd R, Chan A, Donaghue KC. High plantar pressure and callus in diabetic adolescents: incidence and treatment. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2003; 93(3):214–220. PMID: 12756312.4. Pataky Z, Golay A, Faravel L, et al. The impact of callosities on the magnitude and duration of plantar pressure in patients with diabetes mellitus: a callus may cause 18,600 kilograms of excess plantar pressure per day. Diabetes Metab. 2002; 28(5):356–361. PMID: 12461472.5. Pauk J, Daunoraviciene K, Ihnatouski M, Griskevicius J, Raso JV. Analysis of the plantar pressure distribution in children with foot deformities. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2010; 12(1):29–34.6. Salazar-Torres JJ, McDowell BC, Humphreys LD, Duffy CM. Plantar pressures in children with congenital talipes equino varus: a comparison between surgical management and the Ponseti technique. Gait Posture. 2014; 39(1):321–327. PMID: 23973353.7. Sullivan J, Burns J, Adams R, Pappas E, Crosbie J. Plantar heel pain and foot loading during normal walking. Gait Posture. 2015; 41(2):688–693. PMID: 25724260.
Article8. Aliberti S, Costa MS, Passaro AC, Arnone AC, Sacco IC. Medial contact and smaller plantar loads characterize individuals with Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome during stair descent. Phys Ther Sport. 2010; 11(1):30–34. PMID: 20129121.9. Nahas MR, Gawish HM, Tarshoby MM, State OI, Aboelyazid A. Effect of simulated leg length discrepancy on plantar pressure distribution in diabetic patients with neuropathic foot ulceration. J Wound Care. 2011; 20(10):473–477. PMID: 22067885.10. Peyer KE, Brassey CA, Rose KA, Sellers WI. Locomotion pattern and foot pressure adjustments during gentle turns in healthy subjects. J Biomech. 2017; 60:65–71. PMID: 28689681.
Article11. Giancoli DC. Physics: principles with applications. 6th ed. Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ;2004. p. 276.12. Kanatli U, Yetkin H, Simsek A, Besli K, Ozturk A. The relationship of the heel pad compressibility and plantar pressure distribution. Foot Ankle Int. 2001; 22(8):662–665. PMID: 11527028.
Article13. Monteiro M, Gabriel R, Aranha J, Neves e Castro M, Sousa M, Moreira M. Influence of obesity and sarcopenic obesity on plantar pressure of postmenopausal women. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2010; 25(5):461–467.
Article14. Sacco IC, Hamamoto AN, Tonicelli LM, Watari R, Ortega NR, Sartor CD. Abnormalities of plantar pressure distribution in early, intermediate, and late stages of diabetic neuropathy. Gait Posture. 2014; 40(4):570–574. PMID: 25086801.
Article15. Wearing SC, Smeathers JE, Yates B, Urry SR, Dubois P. Bulk compressive properties of the heel fat pad during walking: a pilot investigation in plantar heel pain. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009; 24(4):397–402.
Article16. Burns J, Crosbie J, Hunt A, Ouvrier R. The effect of pes cavus on foot pain and plantar pressure. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2005; 20(9):877–882.
Article17. Lee KM, Chung CY, Park MS, Lee SH, Cho JH, Choi IH. Reliability and validity of radiographic measurements in hindfoot varus and valgus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92(13):2319–2327. PMID: 20926727.
Article18. Riad J, Coleman S, Henley J, Miller F. Reliability of pediobarographs for paediatric foot deformity. J Child Orthop. 2007; 1(5):307–312. PMID: 19308525.
Article19. Kandil OD, Aboelazm SN, Mabrouk MS. Foot biometrics: gender differences in plantar pressure distribution in standing position. Am J Biomed Eng. 2014; 4(1):1–9.20. Wunderlich RE, Cavanagh PR. Gender differences in adult foot shape: implications for shoe design. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001; 33(4):605–611. PMID: 11283437.
Article21. Murphy DF, Beynnon BD, Michelson JD, Vacek PM. Efficacy of plantar loading parameters during gait in terms of reliability, variability, effect of gender and relationship between contact area and plantar pressure. Foot Ankle Int. 2005; 26(2):171–179. PMID: 15737261.
Article22. Putti AB, Arnold GP, Abboud RJ. Foot pressure differences in men and women. Foot Ankle Surg. 2010; 16(1):21–24. PMID: 20152750.
Article23. Putti AB, Arnold GP, Abboud RJ. Differences in foot pressures between Caucasians and Indians. Foot Ankle Surg. 2010; 16(4):195–198. PMID: 21047609.
Article24. Fourchet F, Kelly L, Horobeanu C, Loepelt H, Taiar R, Millet G. High-intensity running and plantar-flexor fatigability and plantar-pressure distribution in adolescent runners. J Athl Train. 2015; 50(2):117–125. PMID: 25531143.
Article25. McCormick CJ, Bonanno DR, Landorf KB. The effect of customised and sham foot orthoses on plantar pressures. J Foot Ankle Res. 2013; 6:19. PMID: 23680496.
Article26. Melvin JM, Preece S, Nester CJ, Howard D. An investigation into plantar pressure measurement protocols for footwear research. Gait Posture. 2014; 40(4):682–687. PMID: 25161007.
Article27. Pataky TC. Correlation between maximum in-shoe plantar pressures and clubhead speed in amateur golfers. J Sports Sci. 2015; 33(2):192–197. PMID: 25010946.
Article28. Xiong S, Goonetilleke RS, Jiang Z. Pressure thresholds of the human foot: measurement reliability and effects of stimulus characteristics. Ergonomics. 2011; 54(3):282–293. PMID: 21390958.
Article29. Macklin K, Healy A, Chockalingam N. The effect of calf muscle stretching exercises on ankle joint dorsiflexion and dynamic foot pressures, force and related temporal parameters. Foot (Edinb). 2012; 22(1):10–17. PMID: 21944945.
Article30. Garcia-Perez JA, Perez-Soriano P, Llana S, Martinez-Nova A, Sanchez-Zuriaga D. Effect of overground vs treadmill running on plantar pressure: influence of fatigue. Gait Posture. 2013; 38(4):929–933. PMID: 23746487.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the Outcomes according to Etiology in the Pediatric Pes Planovalgus after Lateral Column Lengthening: By Radiologic and Pedobarographic Measurements
- Change of In-Shoe Plantar Pressure According to Types of Shoes (Flat Shoes, Running Shoes, and High Heels)
- Differences in Electrocardiography Findings Between the Healthy Elderly and Young Adults
- Diagnostic Availability of Pedobarography and Correlation of Radiographic and Pedobarographic Measurements in Pediatric Flexible Flatfoot
- Association between dietary intake, body measurements, and urinary bone resorption markers in young adults with osteopenia and osteoporosis: a cross-sectional study