Investig Clin Urol.
2018 May;59(3):200-205. 10.4111/icu.2018.59.3.200.
Relative to open surgery, minimally-invasive renal and ureteral pediatric surgery offers no improvement in 30-day complications, yet requires longer operative time: Data from the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Pediatrics
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, NC, USA. ahester@wakehealth.edu
- KMID: 2410594
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2018.59.3.200
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Performance of minimally-invasive surgery (MIS) is increasing relative to open surgery. We sought to compare the contemporary rates of short-term complications of open versus laparoscopic renal and ureteral surgery in pediatric patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective cross-sectional analysis of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Pediatrics database was performed of all cases in 2014 identified using CPT procedure codes for nephrectomy, partial nephrectomy (PN), ureteroneocystostomy (UNC), and pyeloplasty, and reviewed for postoperative complications. Univariate analysis was performed to determine 30-day complications, with comparison between open and MIS approaches. Receiver operator curve (ROC) analysis was performed to determine differences in body surface area (BSA) and age for open versus MIS.
RESULTS
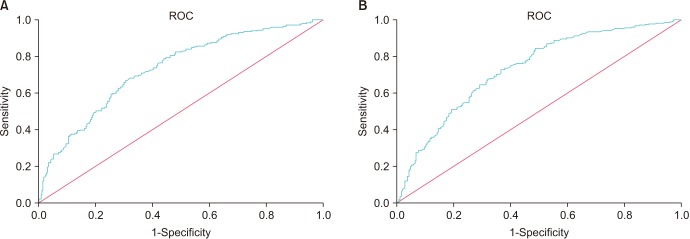
Review identified 207 nephrectomies, 72 PN, 920 UNC, and 625 pyeloplasties. MIS was associated with older age and larger BSA except for cases of UNC. Apart from PN, operative durations were longer with MIS. However, only PN was associated with significantly longer length of hospital stay (LOS). There was no difference in incidence of all other 30-day complications. When evaluating BSA via ROC, the area under the curve (AUC) was found to be 0.730 and was significant. Children with a BSA greater than 0.408 m2 were more likely to have MIS (sensitivity, 66.9%; specificity, 69.3%). Regarding age, the AUC was 0.732. Children older than 637.5 days were more likely to have MIS (sensitivity, 72.8%; specificity, 63.3%).
CONCLUSIONS
Pediatric MIS is associated with longer operative time for nephrectomy, but shorter LOS following PN. Surgical approach was not associated with difference in short-term complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tejwani R, Young BJ, Wang HS, Wolf S, Purves JT, Wiener JS, et al. Open versus minimally invasive surgical approaches in pediatric urology: trends in utilization and complications. J Pediatr Urol. 2017; 13:283.e1–283.e9. PMID: 28344019.
Article2. American College of Surgeons. Pediatric national surgical quality improvement program [Internet]. Chicago, IL: American College of Surgeons;2009. cited 2017 Nov 14. Available from: http://www.pediatric.acsnsqip.org/.
Article3. Raval MV, Dillon PW, Bruny JL, Ko CY, Hall BL, Moss RL, et al. American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Pediatric: a phase 1 report. J Am Coll Surg. 2011; 212:1–11. PMID: 21036076.
Article4. Roxbury CR, Yang J, Salazar J, Shah RK, Boss EF. Safety and postoperative adverse events in pediatric otologic surgery: analysis of American College of Surgeons NSQIP-P 30-Day outcomes. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; 152:790–795. PMID: 25805641.
Article5. Tahiri Y, Fischer JP, Wink JD, Paine KM, Paliga JT, Bartlett SP, et al. Analysis of risk factors associated with 30-day readmissions following pediatric plastic surgery: a review of 5376 procedures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015; 135:521–529. PMID: 25357160.
Article6. Blackwood BP, Gause CD, Harris JC, Theodorou CM, Helenowski I, Lautz T, et al. Overweight and obese pediatric patients have an increased risk of developing a surgical site infection. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2017; 18:491–497. PMID: 28009537.
Article7. Sherrod BA, Arynchyna AA, Johnston JM, Rozzelle CJ, Blount JP, Oakes WJ, et al. Risk factors for surgical site infection following nonshunt pediatric neurosurgery: a review of 9296 procedures from a national database and comparison with a single-center experience. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2017; 19:407–420. PMID: 28186476.
Article8. Basques BA, Lukasiewicz AM, Samuel AM, Webb ML, Bohl DD, Smith BG, et al. Which pediatric orthopaedic procedures have the greatest risk of adverse outcomes. J Pediatr Orthop. 2017; 37:429–434. PMID: 26558959.
Article9. Tejwani R, Wang HS, Young BJ, Greene NH, Wolf S, Wiener JS, et al. Increased pediatric sub-specialization is associated with decreased surgical complication rates for inpatient pediatric urology procedures. J Pediatr Urol. 2016; 12:388.e1–388.e7. PMID: 27363329.
Article10. Chu DI, Canning DA, Tasian GE. Race and 30-day morbidity in pediatric urologic surgery. Pediatrics. 2016; 138:e20154574. PMID: 27317576.
Article11. Preece J, Asti L, Ambeba E, McLeod DJ. Peri-operative transfusion risk in classic bladder exstrophy closure: results from a national database review. J Pediatr Urol. 2016; 12:208.e1–208.e6. PMID: 27282549.
Article12. McLeod DJ, Asti L, Mahida JB, Deans KJ, Minneci PC. Preoperative risk assessment in children undergoing major urologic surgery. J Pediatr Urol. 2016; 12:26.e1–26.e7. PMID: 26683111.
Article13. Song SH, Kim KS. Current status of robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery in pediatric urology. Korean J Urol. 2014; 55:499–504. PMID: 25132942.
Article14. Yu HY, Hevelone ND, Lipsitz SR, Kowalczyk KJ, Hu JC. Use, costs and comparative effectiveness of robotic assisted, laparoscopic and open urological surgery. J Urol. 2012; 187:1392–1398. PMID: 22341274.
Article15. Wang HH, Tejwani R, Cannon GM Jr, Gargollo PC, Wiener JS, Routh JC. Open versus minimally invasive ureteroneocystostomy: a population-level analysis. J Pediatr Urol. 2016; 12:232.e1–232.e6. PMID: 27140001.
Article16. McNamara ER, Kurtz MP, Schaeffer AJ, Logvinenko T, Nelson CP. 30-Day morbidity after augmentation enterocystoplasty and appendicovesicostomy: a NSQIP pediatric analysis. J Pediatr Urol. 2015; 11:209.e1–209.e6. PMID: 26049255.
Article17. Wang HH, Tejwani R, Zhang H, Wiener JS, Routh JC. Hospital surgical volume and associated postoperative complications of pediatric urological surgery in the United States. J Urol. 2015; 194:506–511. PMID: 25640646.
Article18. Kurtz MP, McNamara ER, Schaeffer AJ, Logvinenko T, Nelson CP. Association of BMI and pediatric urologic postoperative events: results from pediatric NSQIP. J Pediatr Urol. 2015; 11:224.e1–224.e6. PMID: 26139160.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Comparison with Traditional Open Surgery
- Minimally Invasive Surgery vs. Open Surgery for Infectious Spondylodiscitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Establishment of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Program
- Current Issues in Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy
- Changing Trend of Rectal Prolapse Surgery in the Era of the Minimally Invasive Surgery