J Korean Soc Echocardiogr.
1994 Dec;2(2):215-219. 10.4250/jkse.1994.2.2.215.
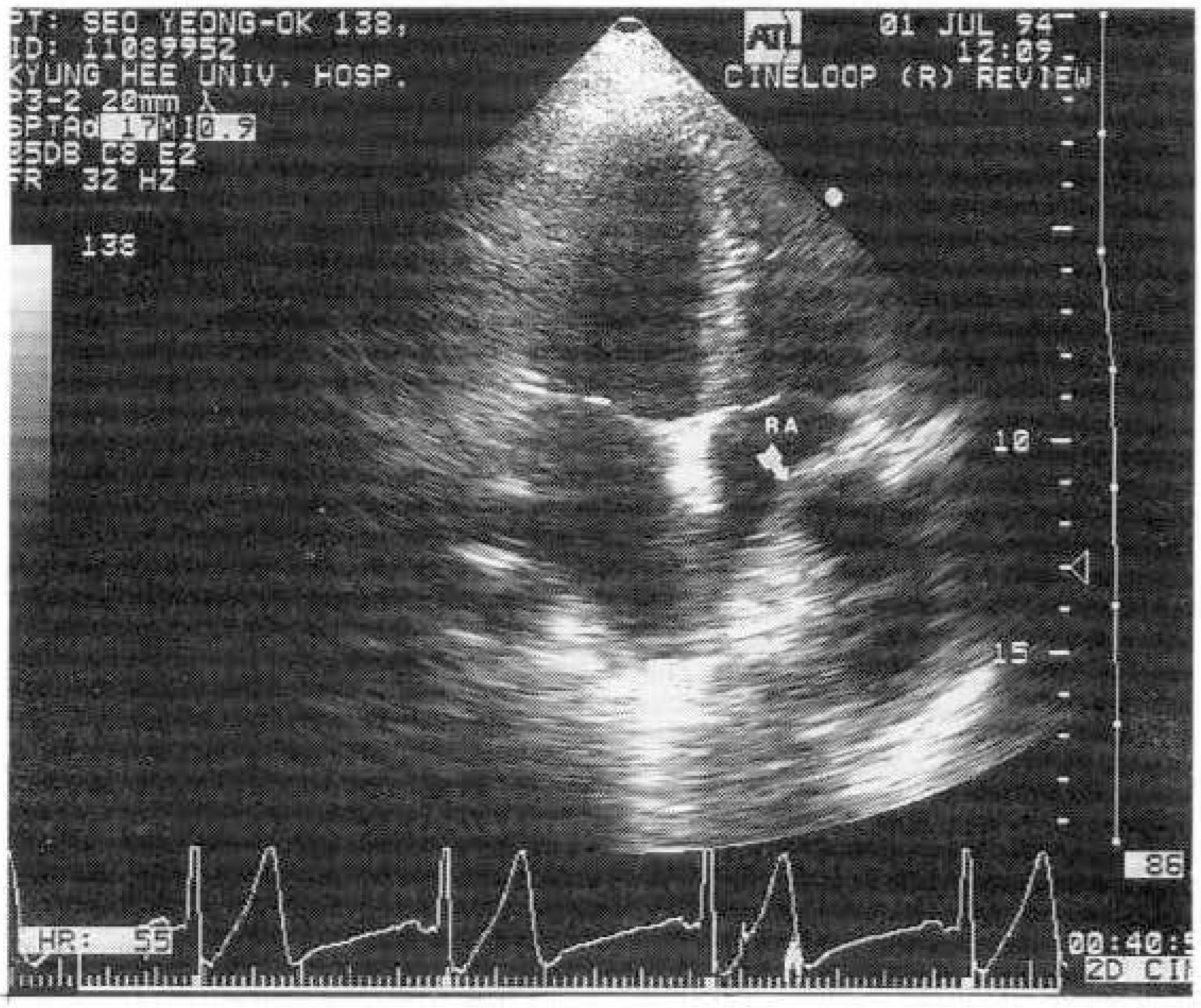
Four Cases of Cystic Nature Adjacent to Right Atrial Wall by Two-Dimensional Echocardiography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2410451
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jkse.1994.2.2.215
Abstract
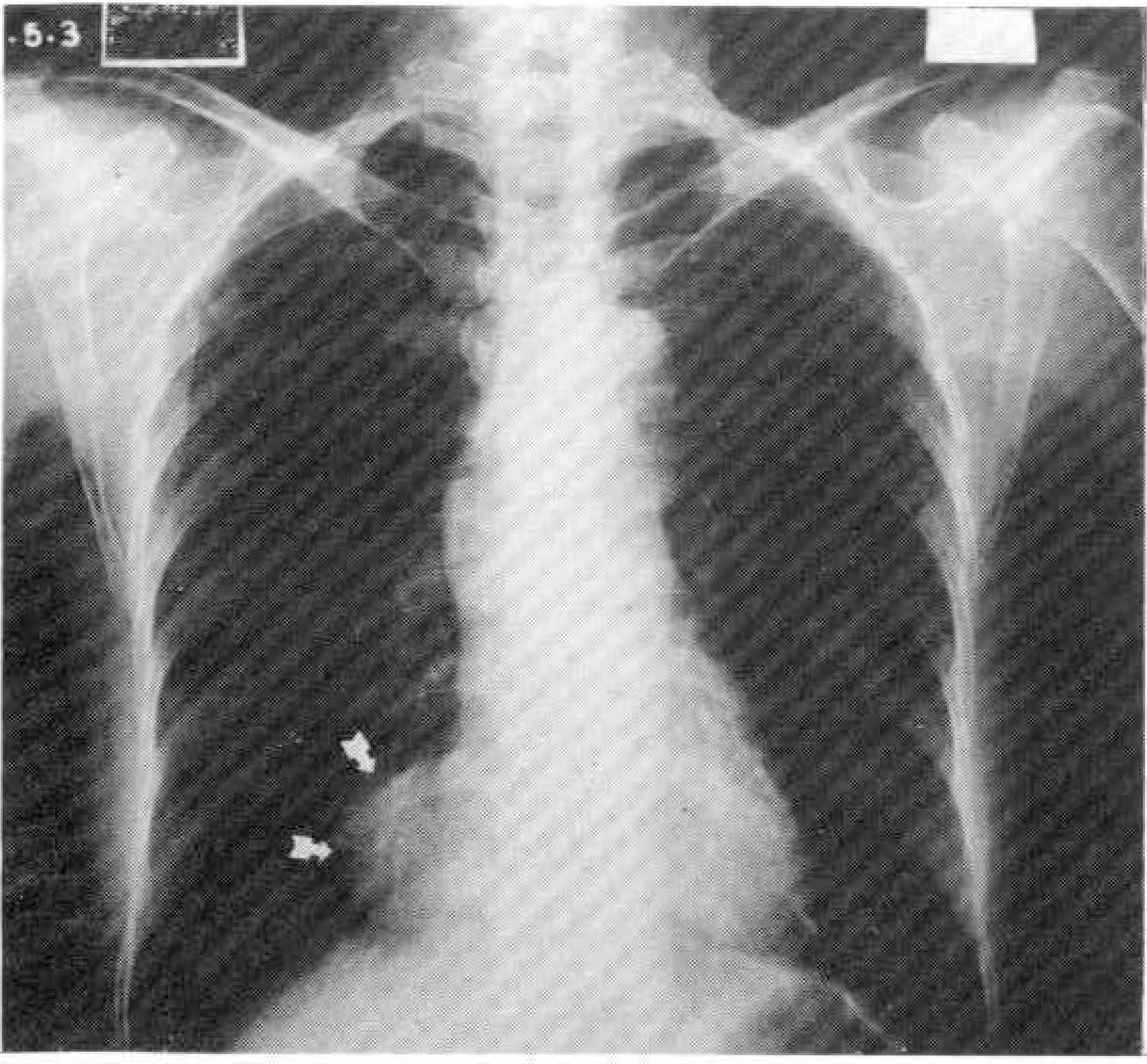
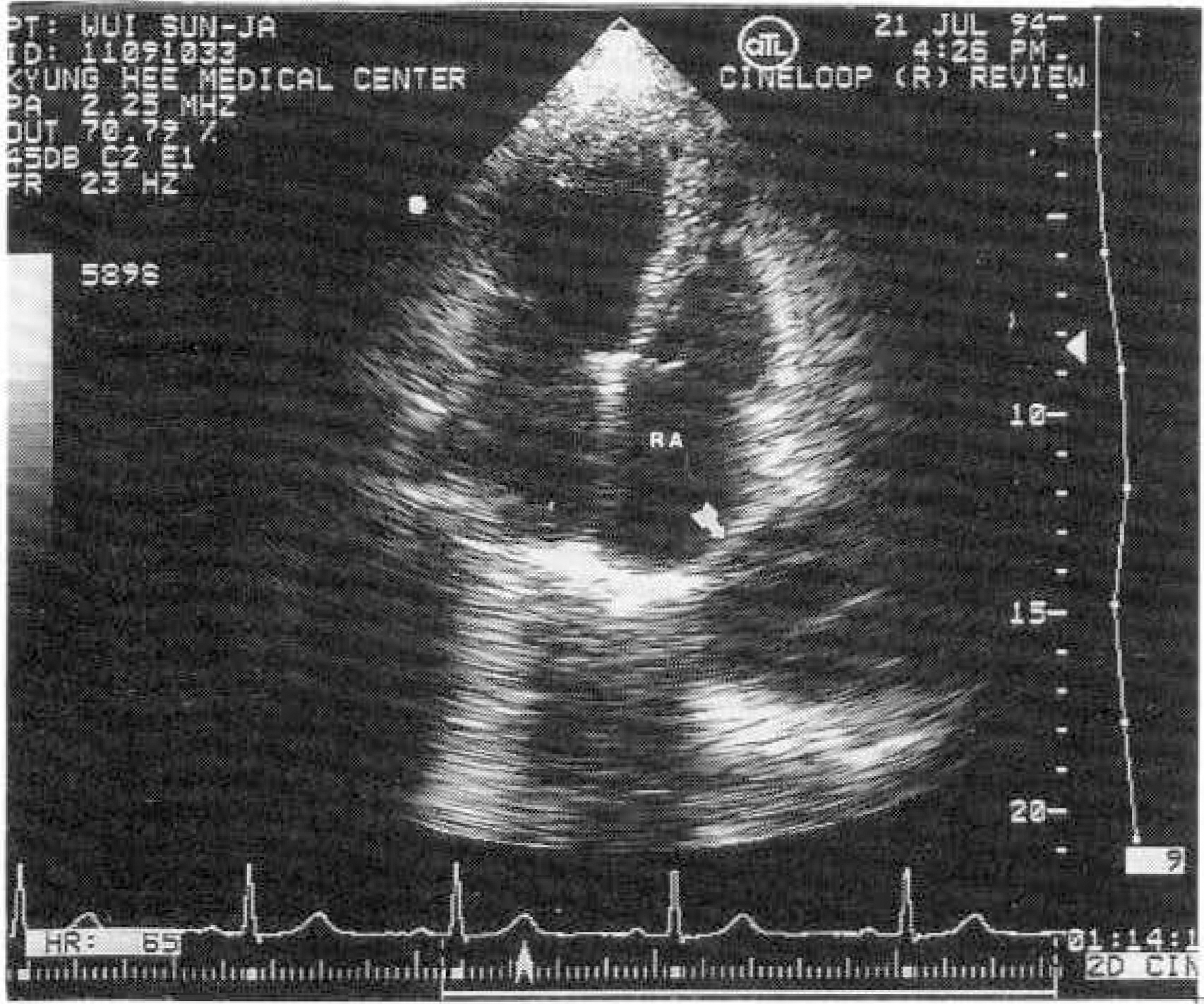
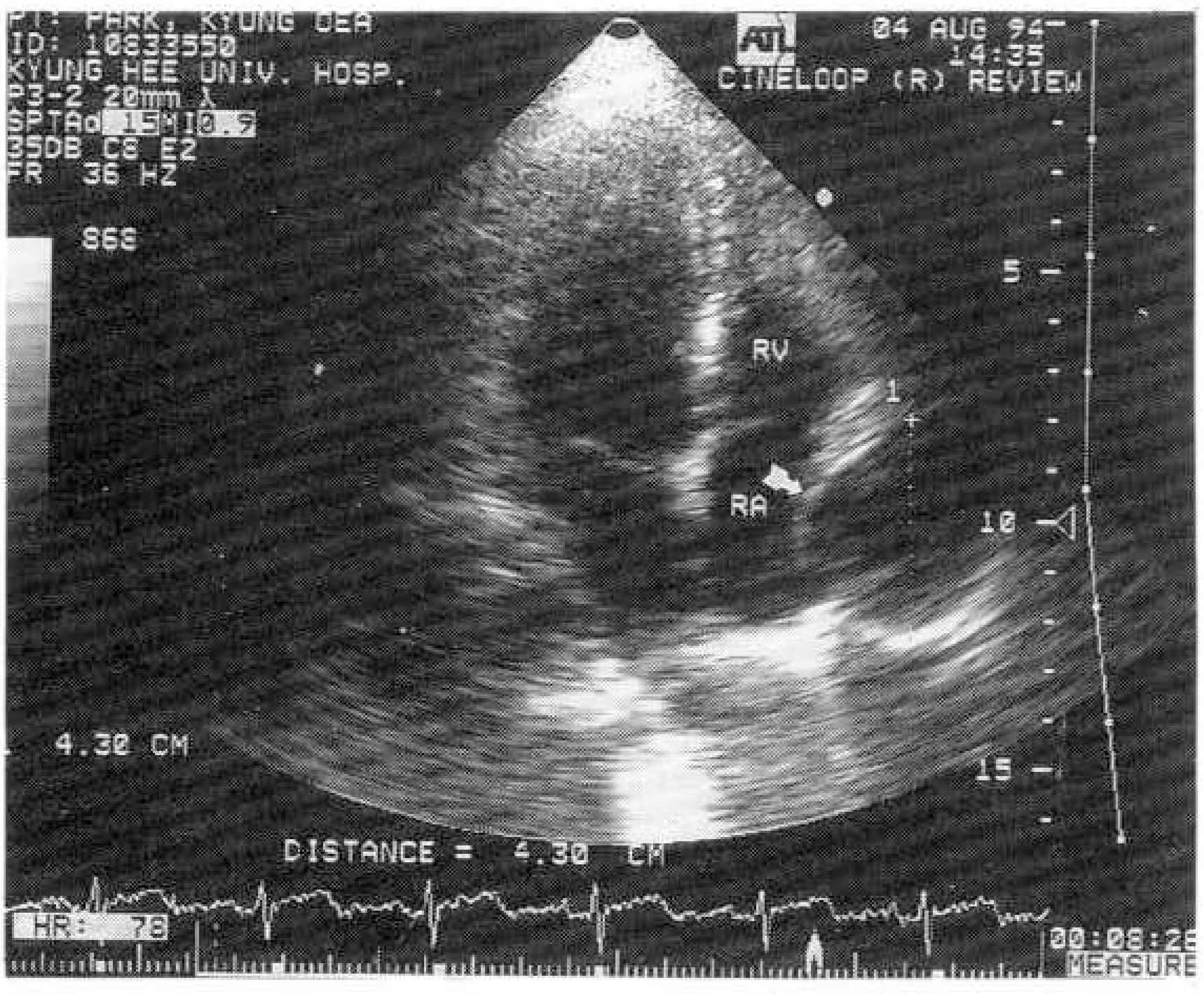
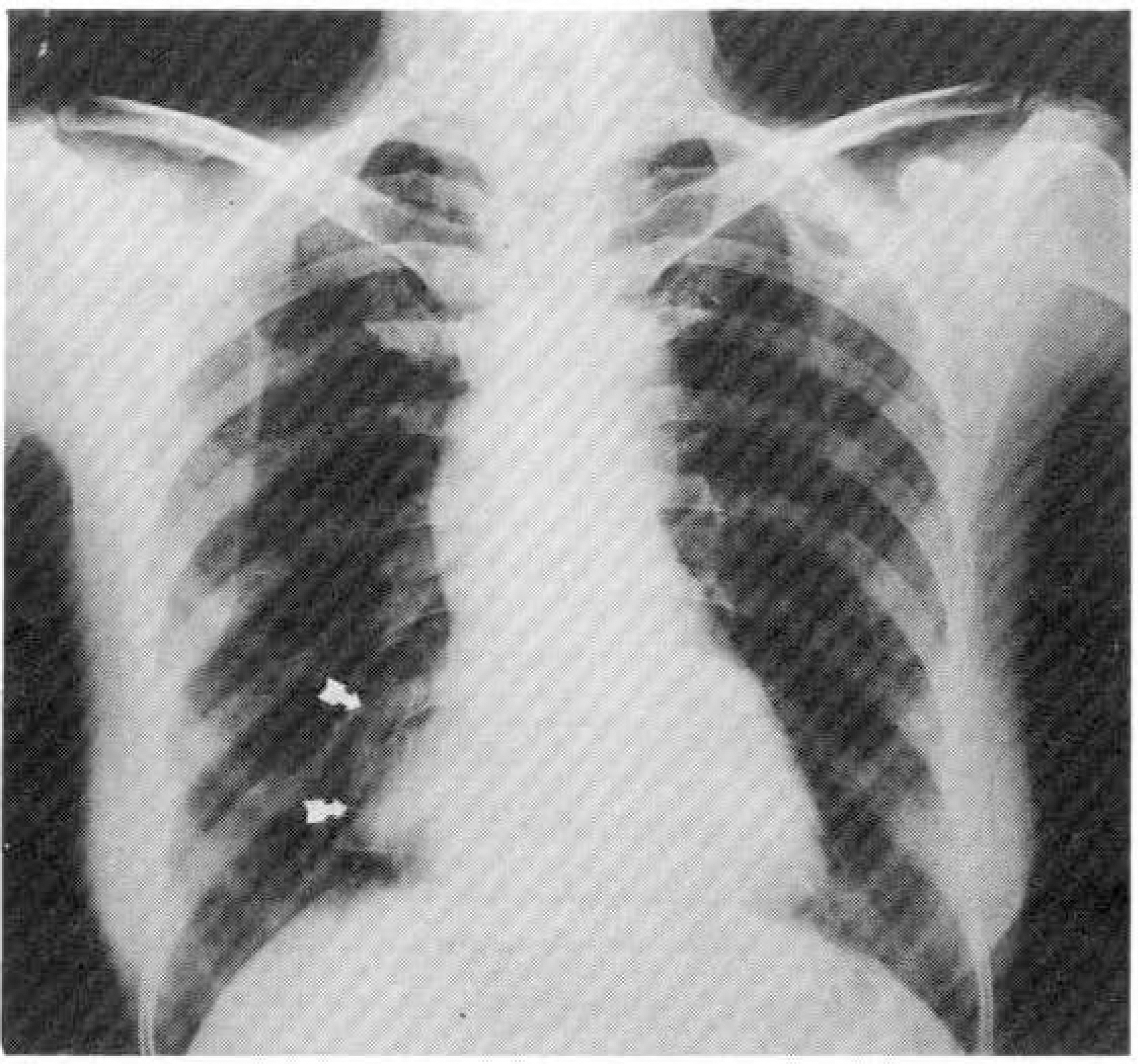
- Two-dimensional echocardiography is a simple, noninvasive method of evaluating cardiac strucures and pericardiac structures. The diagnosis of pericarial cyst is strongly suggested by the prominent roentgenographic appearance of a round, sharply demarcated mass along the right cardiac silhouette in an asymptomatic patient. Two-dimensional echocardiography is also useful method for diagnosing pericardial cyst, but differential diagnosis is difficult when other mass revealed echo-lucent cystic nature is located adjacent to the right atrial wall. We report the similar two-dimensional echcardiography findings located adjacent to the right atrial wall which are diagnosed different disease entity each oter. We suggest that two-dimensional echocardiography helps diagnosis of mass adjacent to the right atrial wall and may need more extensive investigation for accurate differential diagnosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Popp RI, Fowles R, Coltart J, Martin RP. Cardiac anatomy viwed systemically with two-dimensional echocardiography. Chest. 75:579. 1979.2). Cloez JL, Neimann JL, Chivoret G, Danchin N, Bruntz JF, Godenir JP, Faivre G. Echocardiographic rediscovery of an anatomical structure: The Chiari network. Apropos of 16 cases. Arch Mal Coeur. 76:1284. 1983.3). Hynes JK, Tajik AJ, Osborn MJ, et al. Two-dimensional echocardiographic diagnosis of pericardial cyst. Mayo Clin Proc. 58:60. 1983.4). De Roover P, Maisin J, Lacquet A. Congenital pleuropericardial cysts. Thorax. 18:146–150. 1963.
Article5). Unverferth DV, Wooley CF. The differential diagnosis of pericardiac lesions: pericardial cysts. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 5:31–40. 1979.6). Feigin DS, Fenoglio JJ, McAllister HA, Madewell JE. Pericardial cysts: a radiographic-pathologic correlation and review. Radiology. 125:15–20. 1977.7). Kruger SR, Michaud J, Cannom DS. Spontaneous resolution of a pericardial cysts. Am Heart J. 109:1390. 1985.8). Klatt EC, Yune HY. Diagnosis and treatment of pericardial cysts. Radiology. 104:541. 1972.
Article9). Felner JM, Fleming WH, Franch RH. Echocardiographic identification of a pericardial cyst. Chest. 68:386–387. 1975.
Article10). Pugatch RD, Braver JH, Robbins AH, Faling LJ. CT diagnosis of pericardial cysts. AJR. 131:515–516. 1978.
Article11). Modic MT, Janicki PC. Computed tomography of mass lesions of the right cardiophrenic angle. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 4:521–526. 1980.
Article12). Moncada R, Baker M, Salinas M, Demos TC, Churchill R, Love L, Reynes C, Hale D, Candoso M, Pifarre R, Gunnar RM. Diagnostic role of computed tomography in pericardial heart disease: cogenital defects, thickening, neoplasms, and effusions. Am Heart J. 103:263–282. 1982.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Horseshoe-like Shaped Atrial Septal Defects Confirmed on Three-Dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography
- The role of transesophageal three-dimensional echocardiography in the measurement of dynamic changes of atrial septal defect
- Comprehensive understanding of atrial septal defects by imaging studies for successful transcatheter closure
- Coronary Neovascularity and Fistula Formation in Left Atrial Thrombosis
- A Case of Atrial Septal Aneurysm Associated with Atrial Septal Defect