J Korean Soc Echocardiogr.
1995 Dec;3(2):159-167. 10.4250/jkse.1995.3.2.159.
Transesophageal Echocardiography in the Detection of Intracardiac Source of Cerebral Emboli
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Taegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2410418
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jkse.1995.3.2.159
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
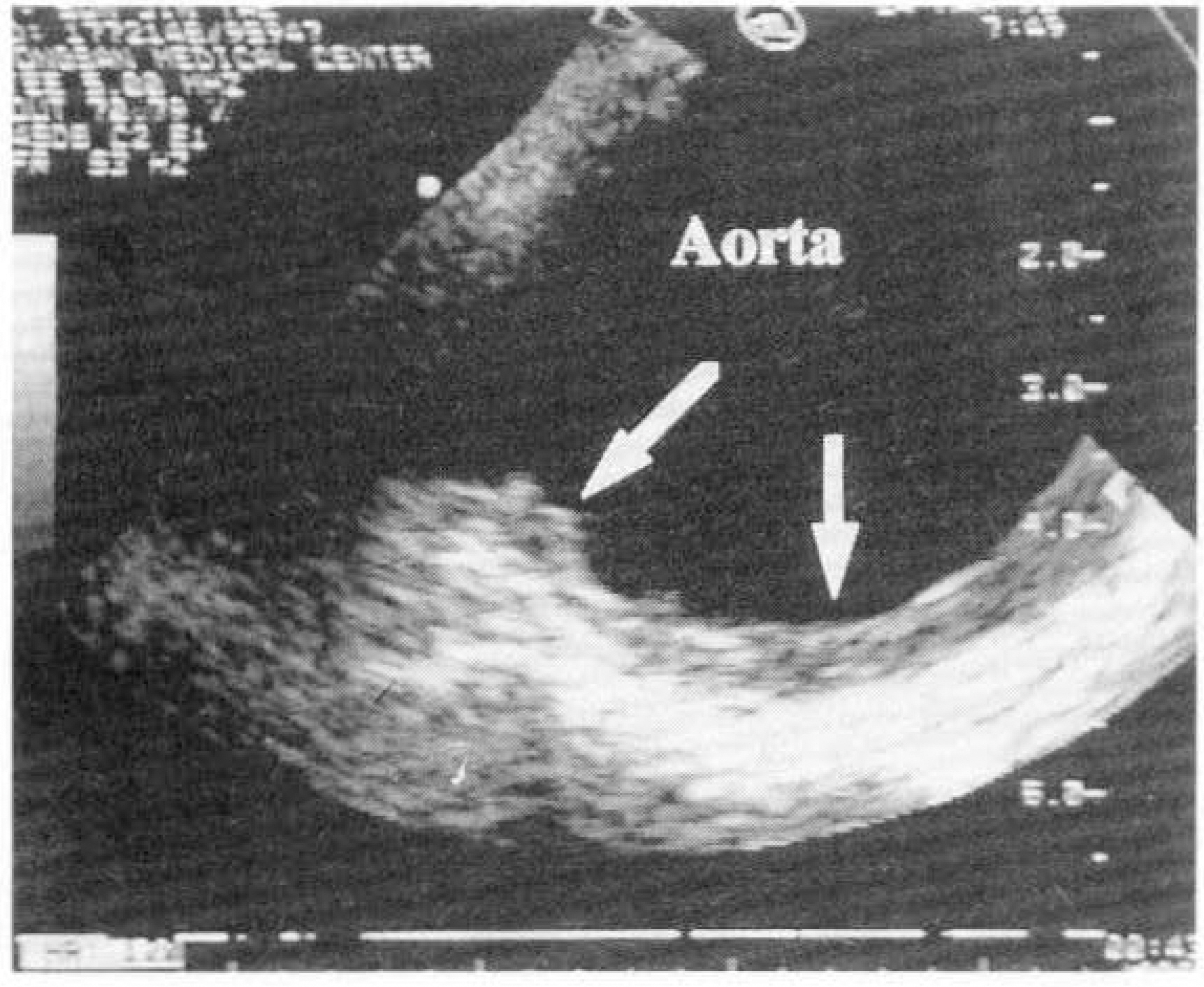
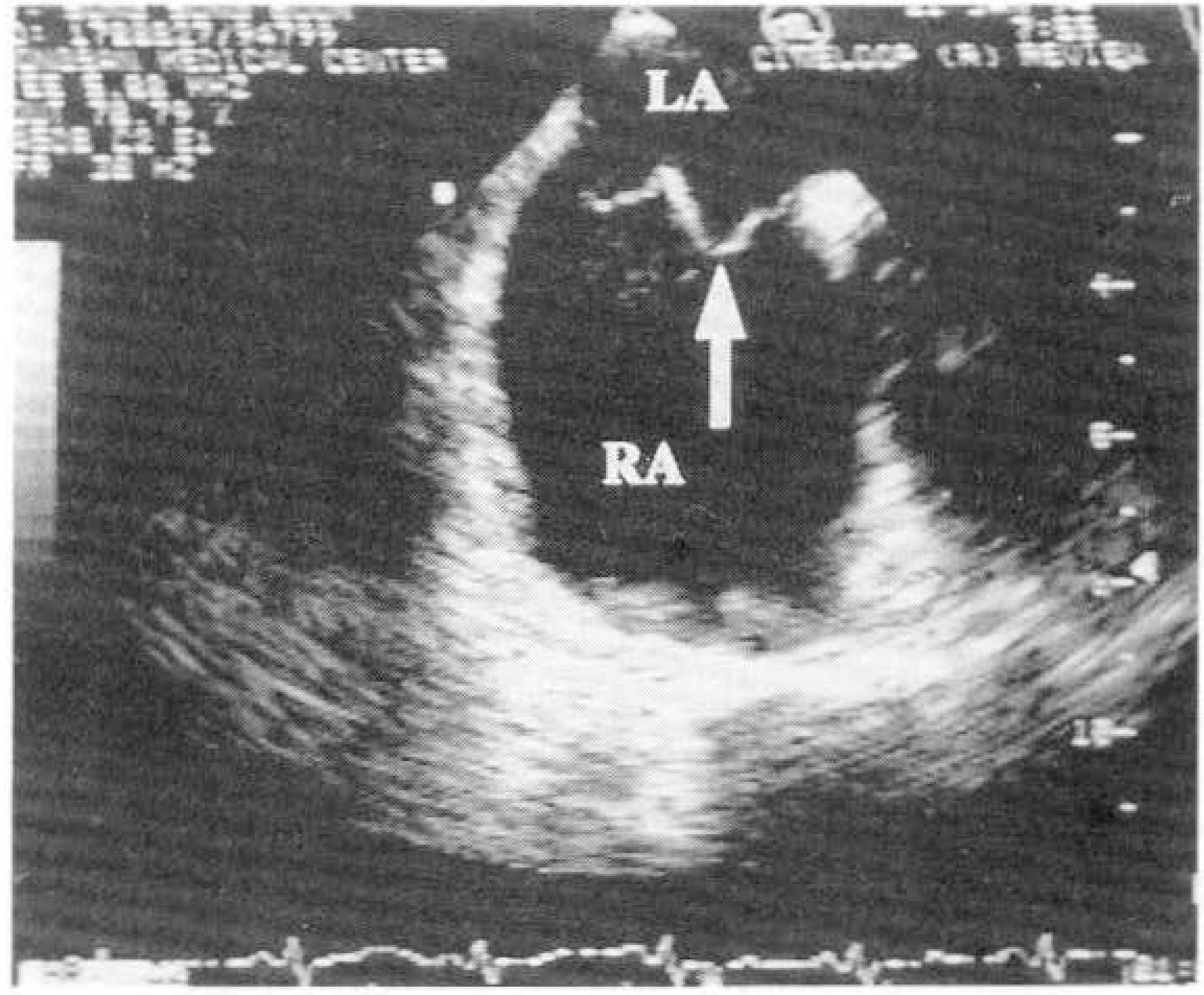
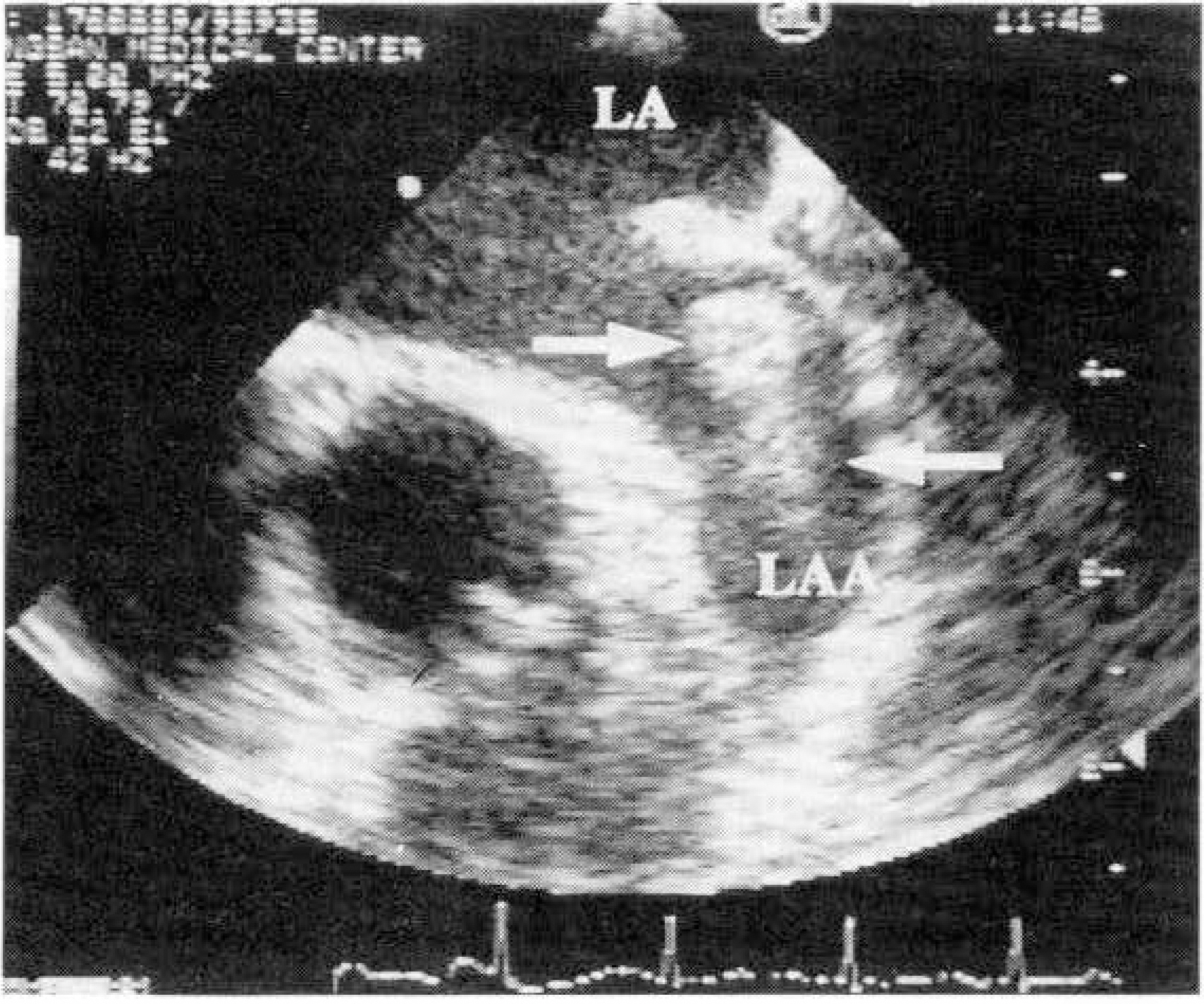
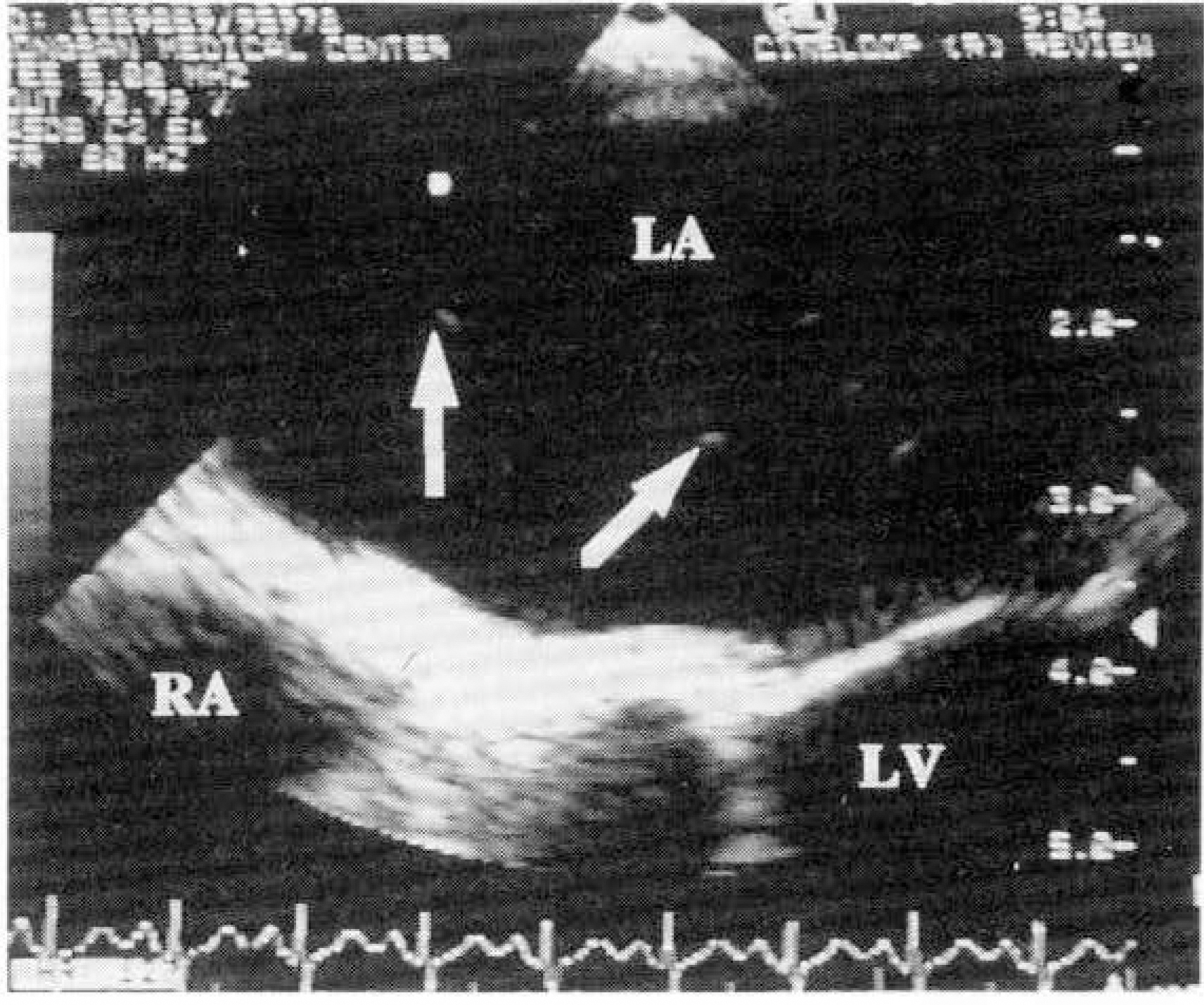
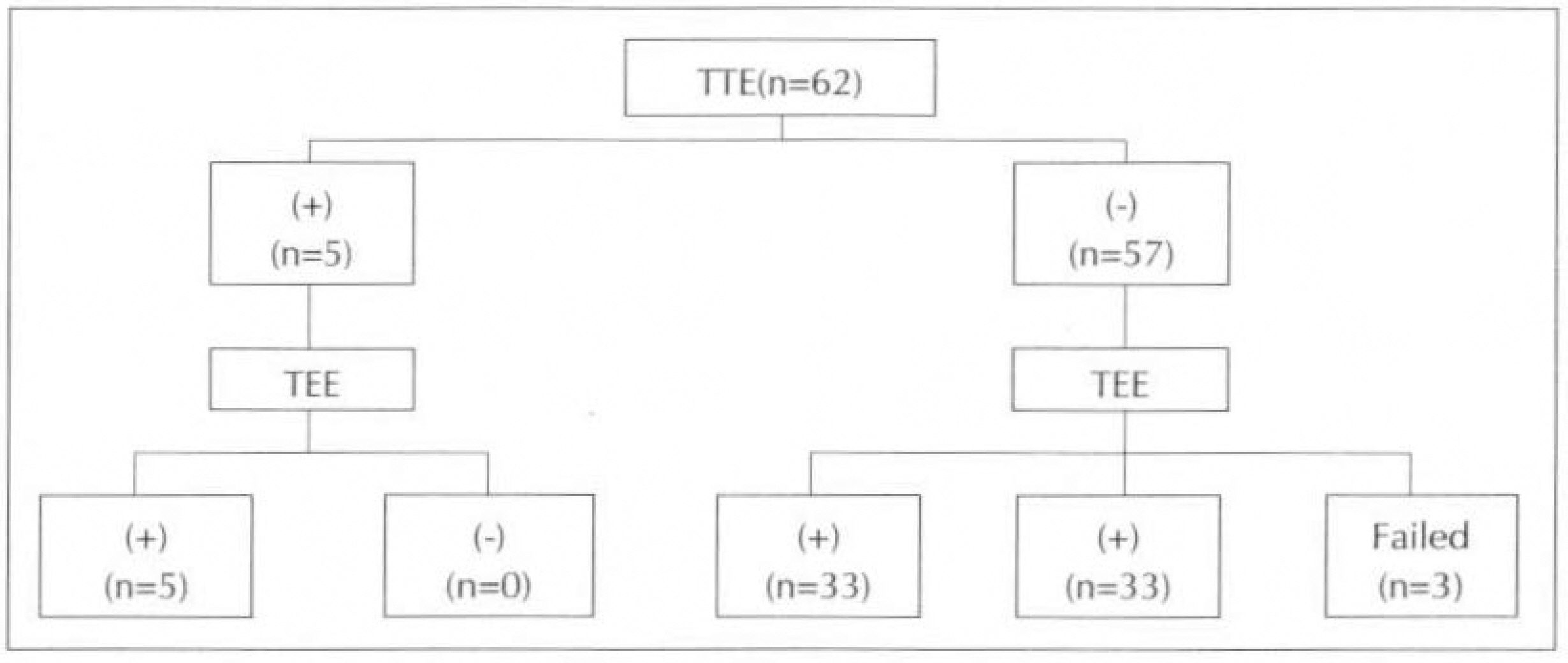
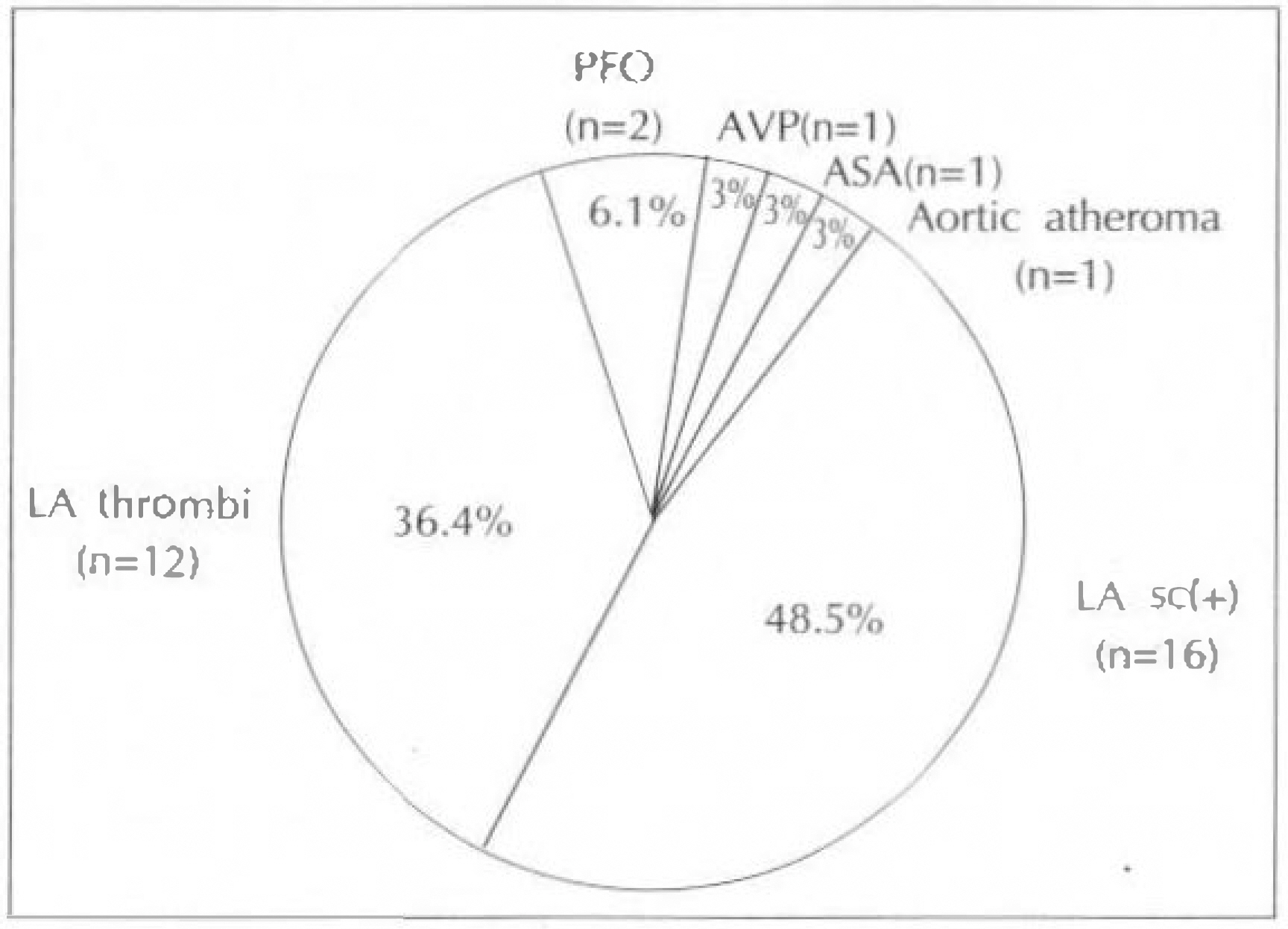
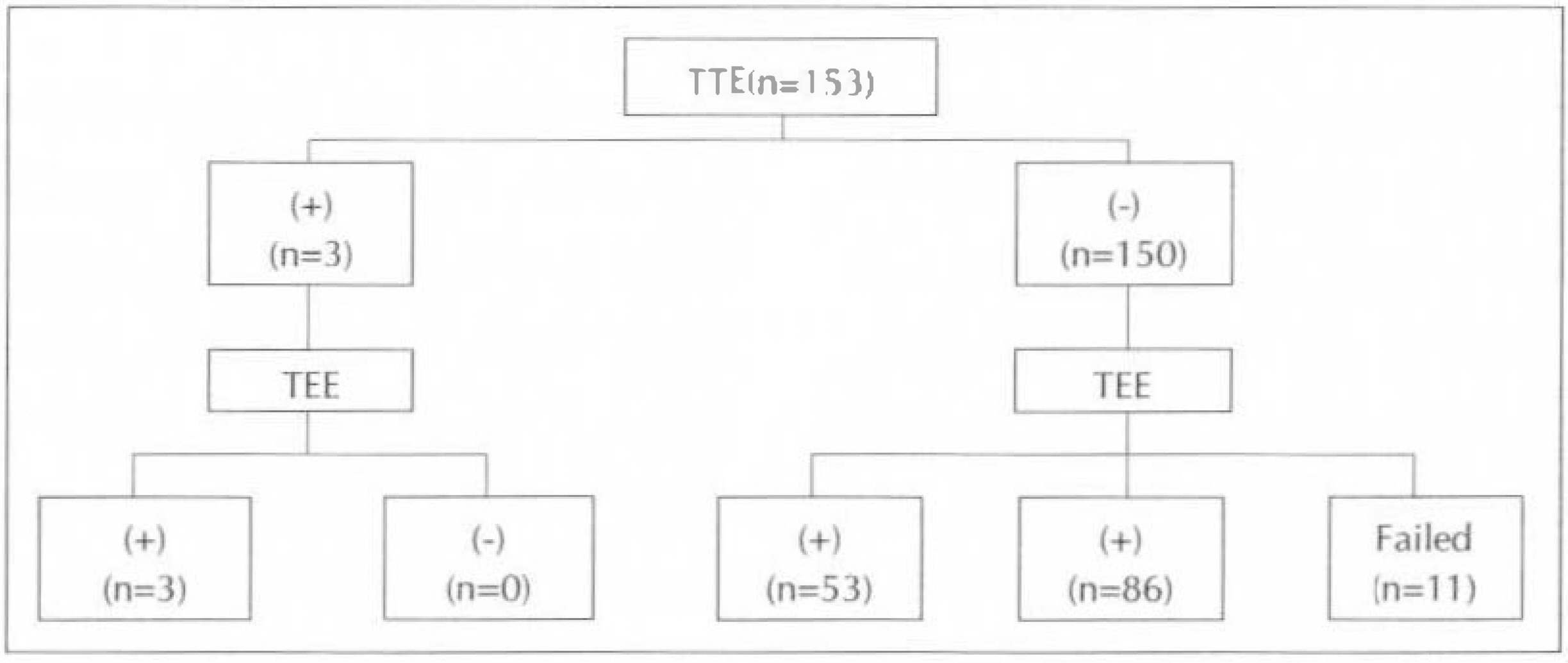
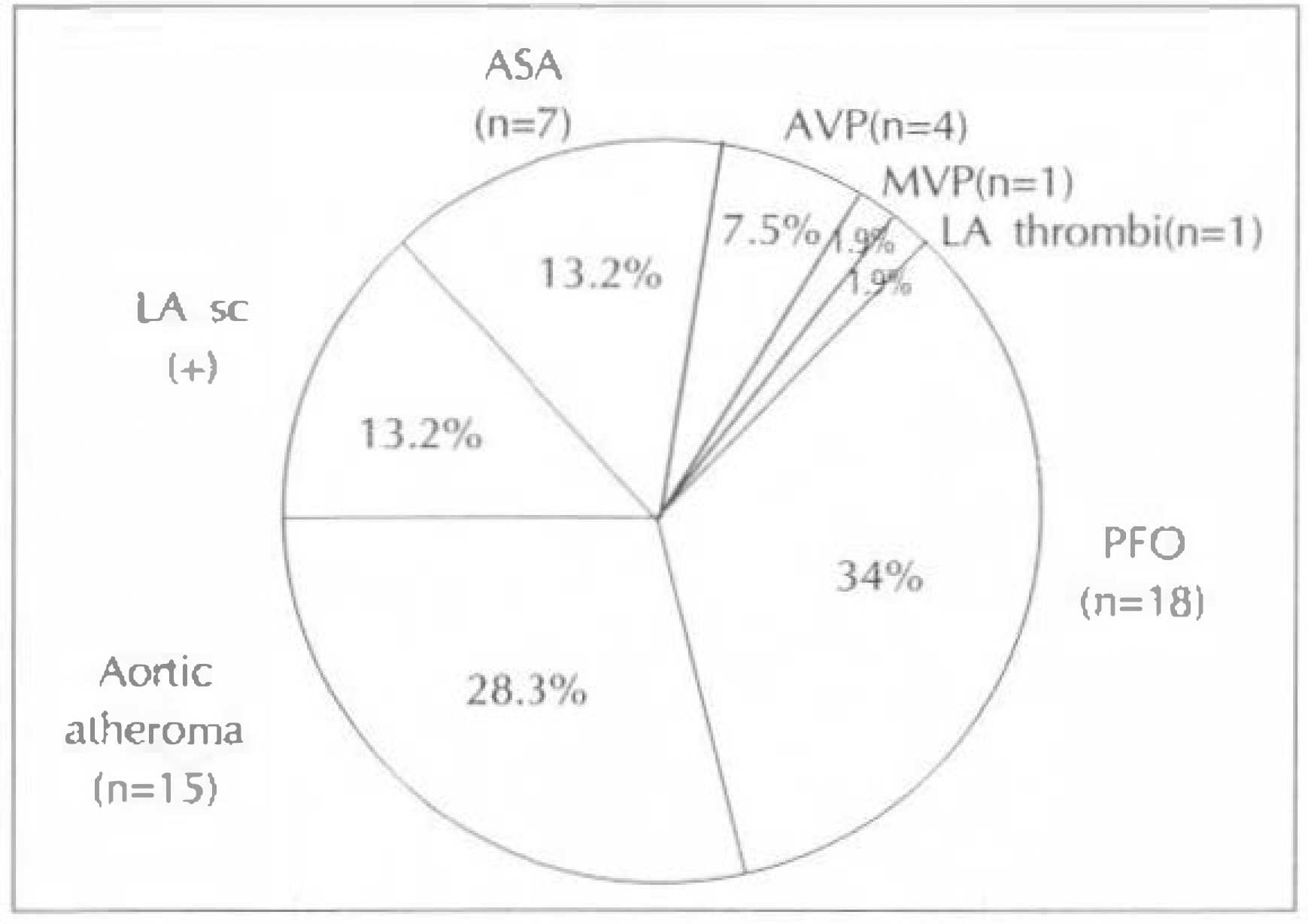
Intracardiac pathology resulting in embloic phenomena is a well-recognized cause of cerebral ischemia and infarction. Recently, the use of transesophageal echocardiography(TEE) has gained wide acceptance because of its superior resolution of basal structures such as the left atrium, left atrial appendage, mitral valvular apparatus, atrial septum, and aorta. The purposes of this study are to evaluate the effectiveness of TEE for detection of intracardiac source of cerebral emboli. METHOD: From 1991 to 1995, 215 patients were included in this study. All patients underwent both transthoracic and transesophageal imaging with saline contrast administration and Doppler color flow imaging. The study group consisted of 132 men and 83 women with a mean age of 51 years(range 15-74). We also reviewed TEE result of all patients according to two groups, which were divided by the presence of clinical cardiac abnormalities. RESULT: 1) TEE identified a potential cardiac source of embolism in 43.7%(94 to 215) of the overall study group compared with only 3.7%(8 to 215) by TTE. 2) Success rate of TEE was 93.5%(201 to 215). 3) Abnormalities noted by TEE included 23 patients with LA spontaneous echo contrast, 20 patients with patient foramen ovale, 16 patients with aortic atheroma, 16 patients with LA thrombi, 8 patients with atrial septal aneurysm, 5 patients with aortic valve prolapse, 4 patients with mitral valve prolapse, and 2 patients with LV thrombi. 4) In the 62 patients with cardiac disease, TEE identified 16 patients with LA spontaneous echo contrast, 12 patients with LA thrombi, 2 patients with patent foramen ovale, 1 patient with aortic atheroma, 1 patient with atrial septal aneurysm and 1 patients with aortic valve prolapse. In the 152 patients with no cardiac disease, TEE identified 18 patients with patent foramen ovale, 15 patients with aortic atheroma, 7 patients with artial septal aneurysm, 7 patients with spontaneous echo contrast, 4 patients with aortic valve prolapse, 1 patient with mitral valve prolapse and 1 patient LA thrombi.
CONCLUSION
TEE was very useful method in investigating potential intracardiac source of cerebral emboli. Thus, the use TEE combined with TTE in patients with unexplained stroke should be recommended.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Toole JF. Cerebrovascular disorders. 4th Ed. p. 246. New York: Raven Press;1990.2). Randall JL, Thomas B, Tiong-Keat Y, Harlen RG, Dennis Choi, Ingela Schnittger. Enhanced detection of intracardiac sources of cerebral emboli by transesophageal echocardiography. Stroke. 22:734.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Enhanced Detection of Inftracardiac Sources of Cerebral Emboli by Transesophageal Echocardiography
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Caused by Tumor Emboli from the Site of
- Transesophageal Echocardiography in the Detection of Intracardiac Embolic Sources in Cerbral Infarction
- Transesophageal Echocardiographic Findings of Ischemic Stroke without Obvious Cardiac Disease
- The Findings of Transesophageal Echocardiography in the Evaluation of the Source of Ischemic Stroke