J Korean Soc Echocardiogr.
1996 Jul;4(1):34-46. 10.4250/jkse.1996.4.1.34.
A Comparative Study of the echocardiographic Methods Assessing Severity of Stenosis in Pateints with mitral Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2410404
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jkse.1996.4.1.34
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Determination of mitral valve area (MVA) in patients with mitral stenosis is very important in clinical practice. Therefore, the ability to assess accurately MVA by noninvasive technique is of great meaning to the management of patients with mitral stenosis. Echo-Doppler(ED) method was derived from the study of fluid dynamics that the flow volume is proportional to orifice area, velocity of flow which shows period requird by the flow. It has been proposed recently that measuring the flow convergence region proximal to an orifice by Doppler flow mapping can be used to derive cardiac output or flow rate proximal to stenotic orifices and therefore to calculate their areas by the continuity equation (area=flow rate/velocity). Applying these methods in mitral stenosis would provide a unique way of validating the underlying concept because the predicted areas could be compared with those measured directly by planimetry and pressure half-time method. Valve resistance has been proposed as an alternative hemodynamic indicator, but initially this index was not used because it was unlikely to remain constant at different flow rates. Recently valve resistance provided a better indices of hemodynamic obstruction than mitral valve area, and these indices usually estimated by invasive method, but it is able to calculate from Doppler echocardiography and compared to the results of invasive method.
METHODS
The mitral inflow volume can be obtained by estimating the stroke volume (SV) by Teichholz's method from M-mode echocardiogram of the left ventricle, and the mean diastolic velocity(MDV) and diastolic filling period (DFP) by mitral inflow continuous-wave Dopler echocardiogram. Therefore, Echo-Doppler method is MVA=SV/MDV×DFP. Doppler color flow recordings of mitral inflow were obtained from the apex, and the radius of the proximal flow convergence region was measured at its peak diastolic value from the calculated assuming uniform radial flow convergence toward the orifice, modified by a factor that accounted for the inflow funnel angle formed by the mitral leaflets. Mitral valve area was then calculated as peak flow rate divided by peak velocity by continuous-wave Doppler. To Compare the stenotic indices from noninvasive method and invasive method, cardiac catheterization was performed.
RESULTS
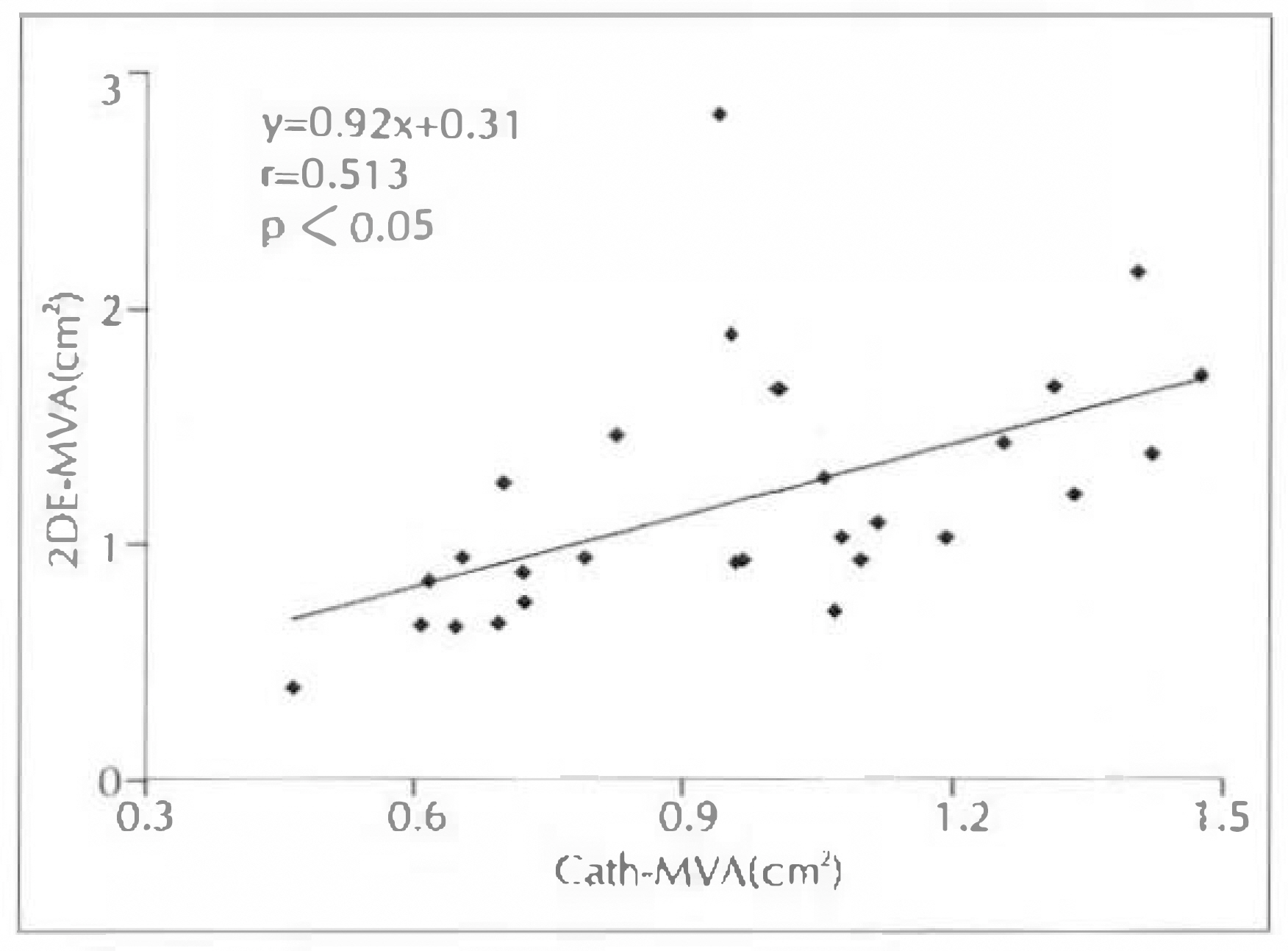
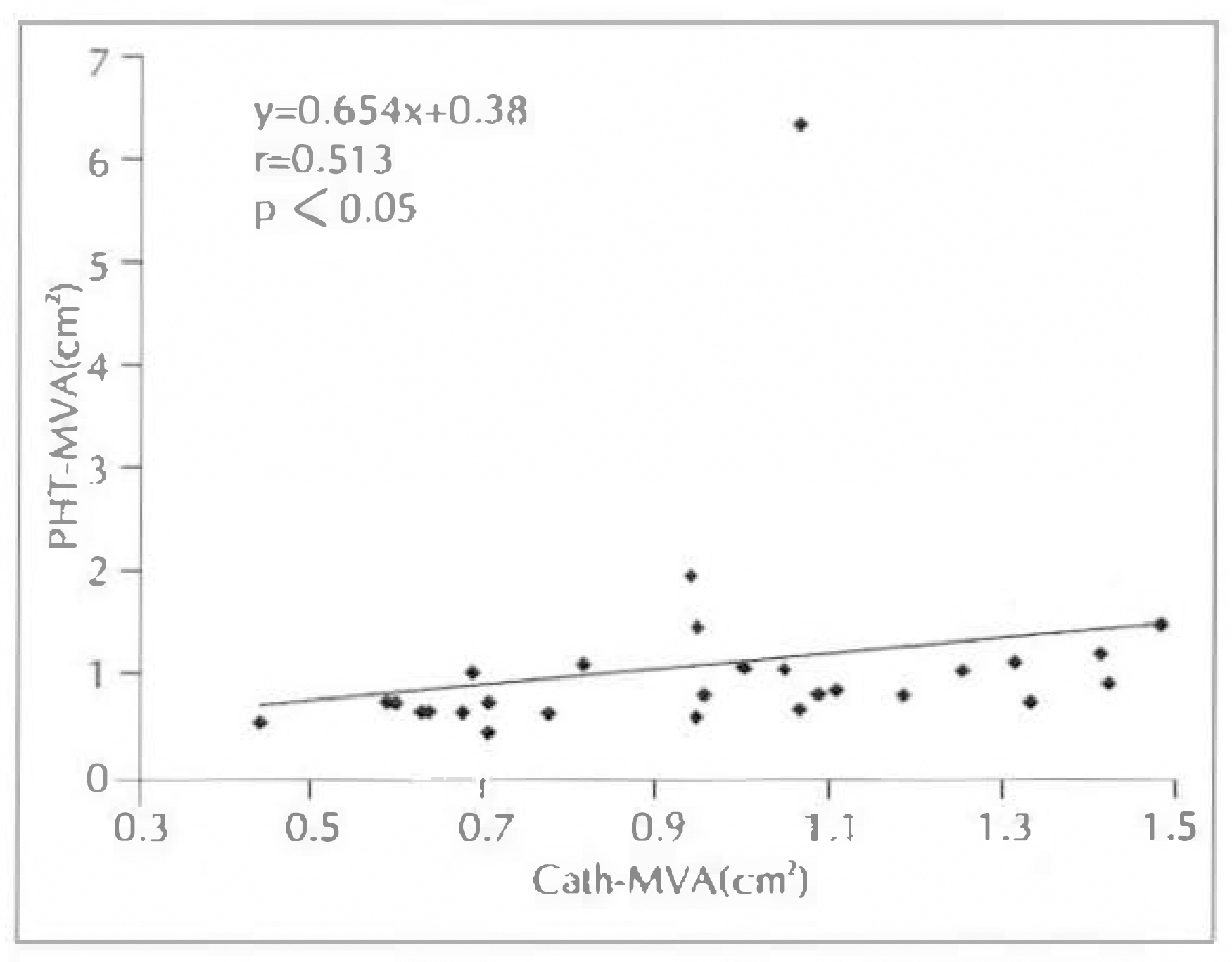
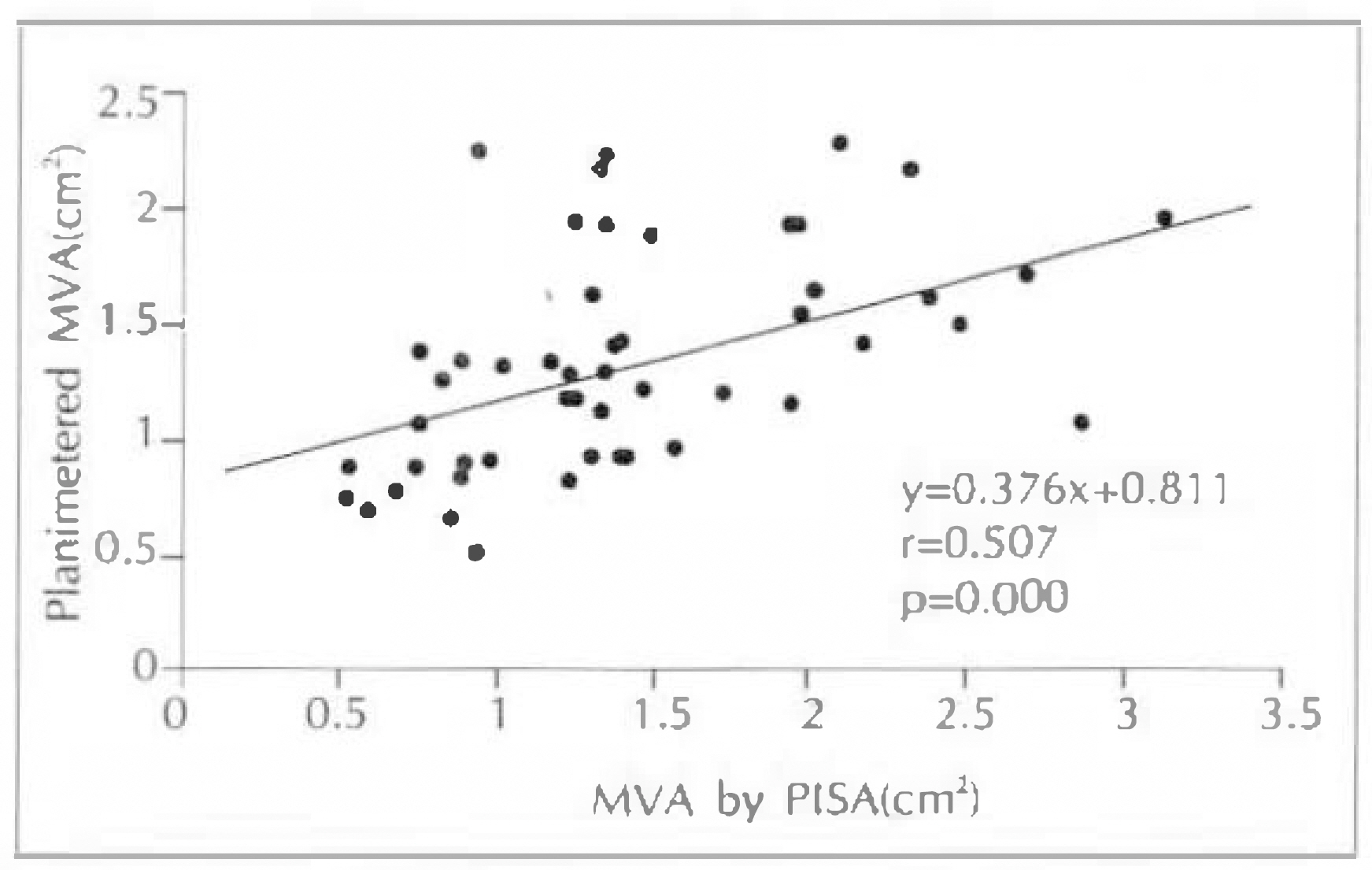
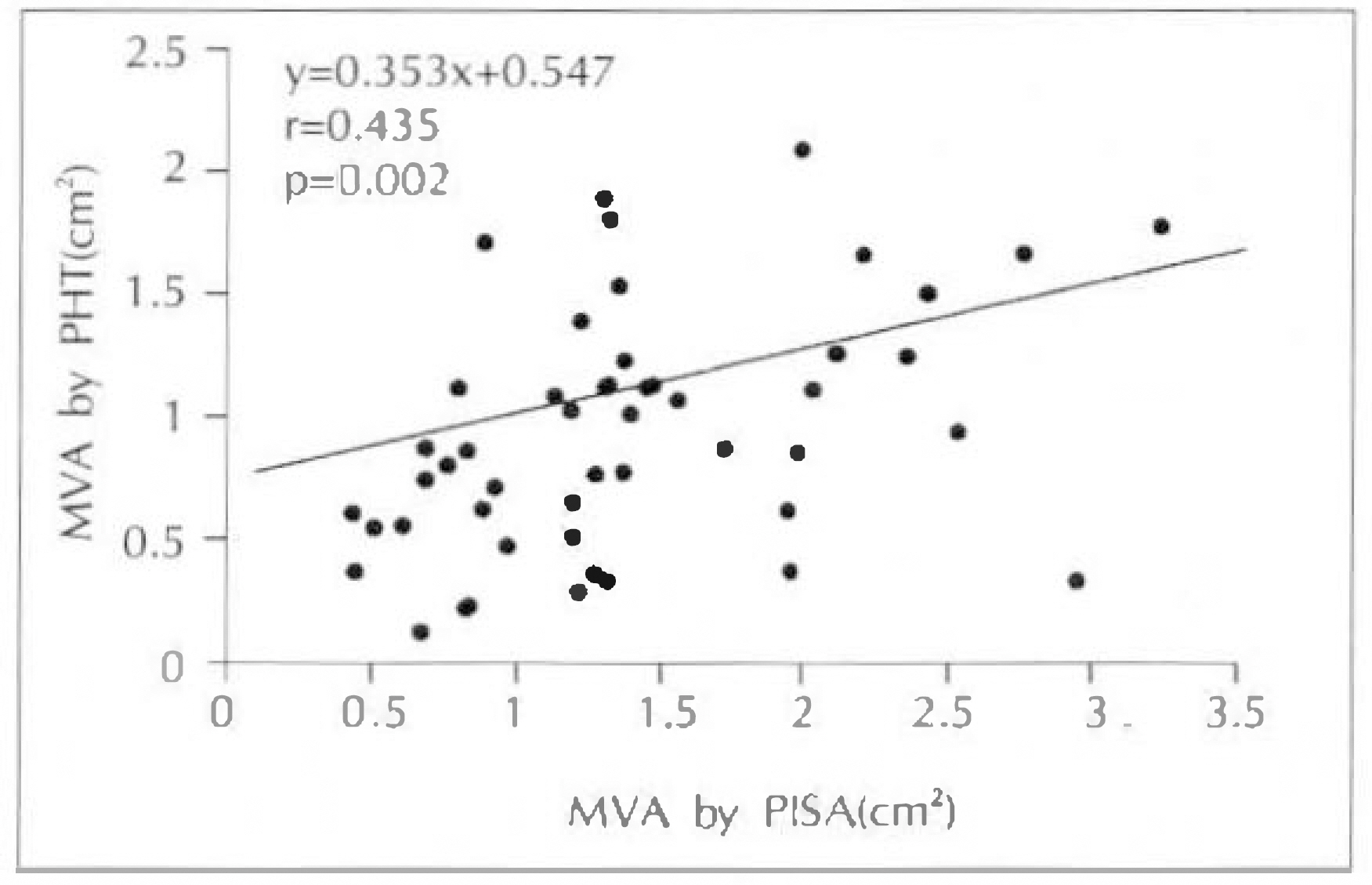
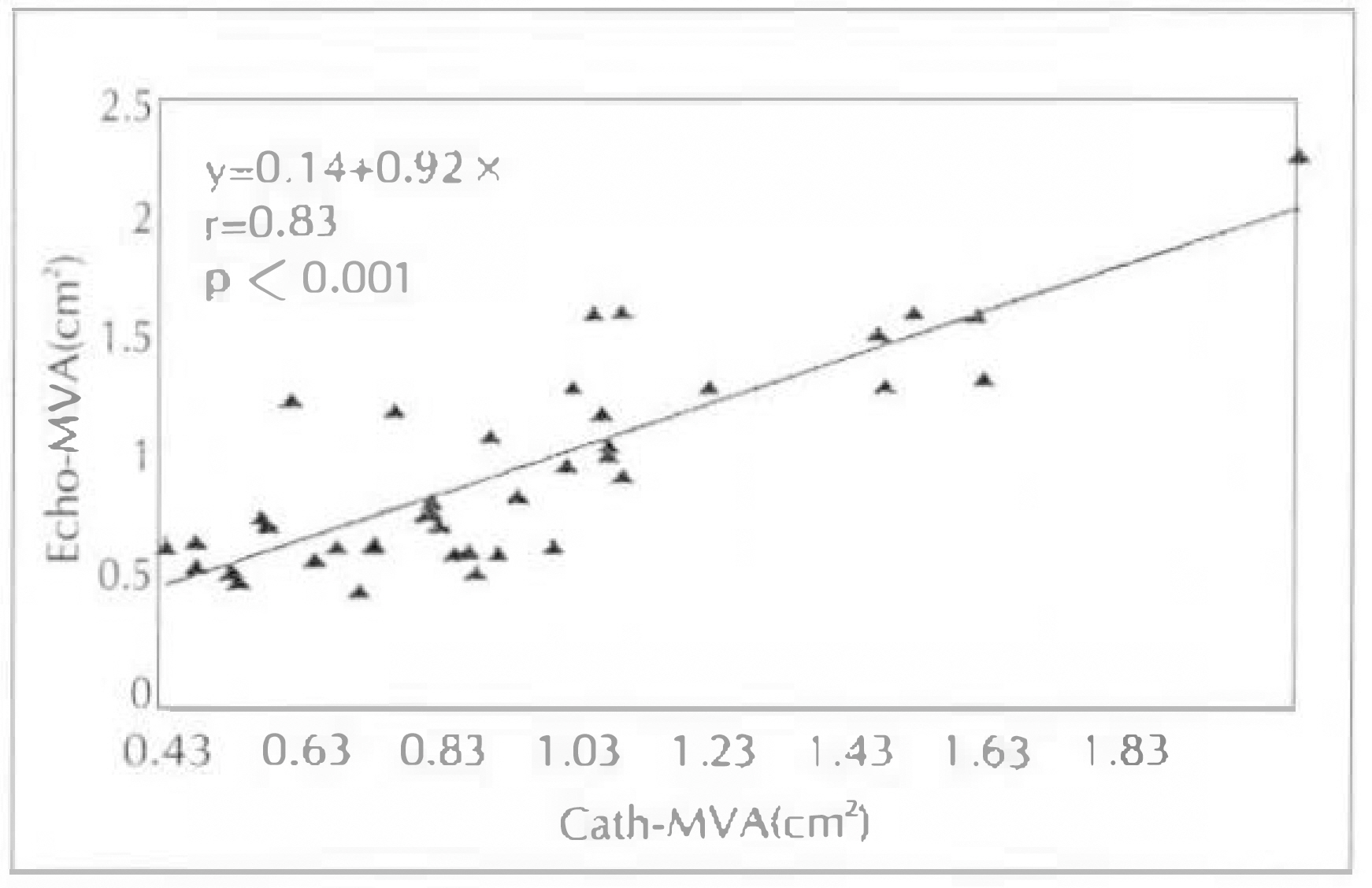
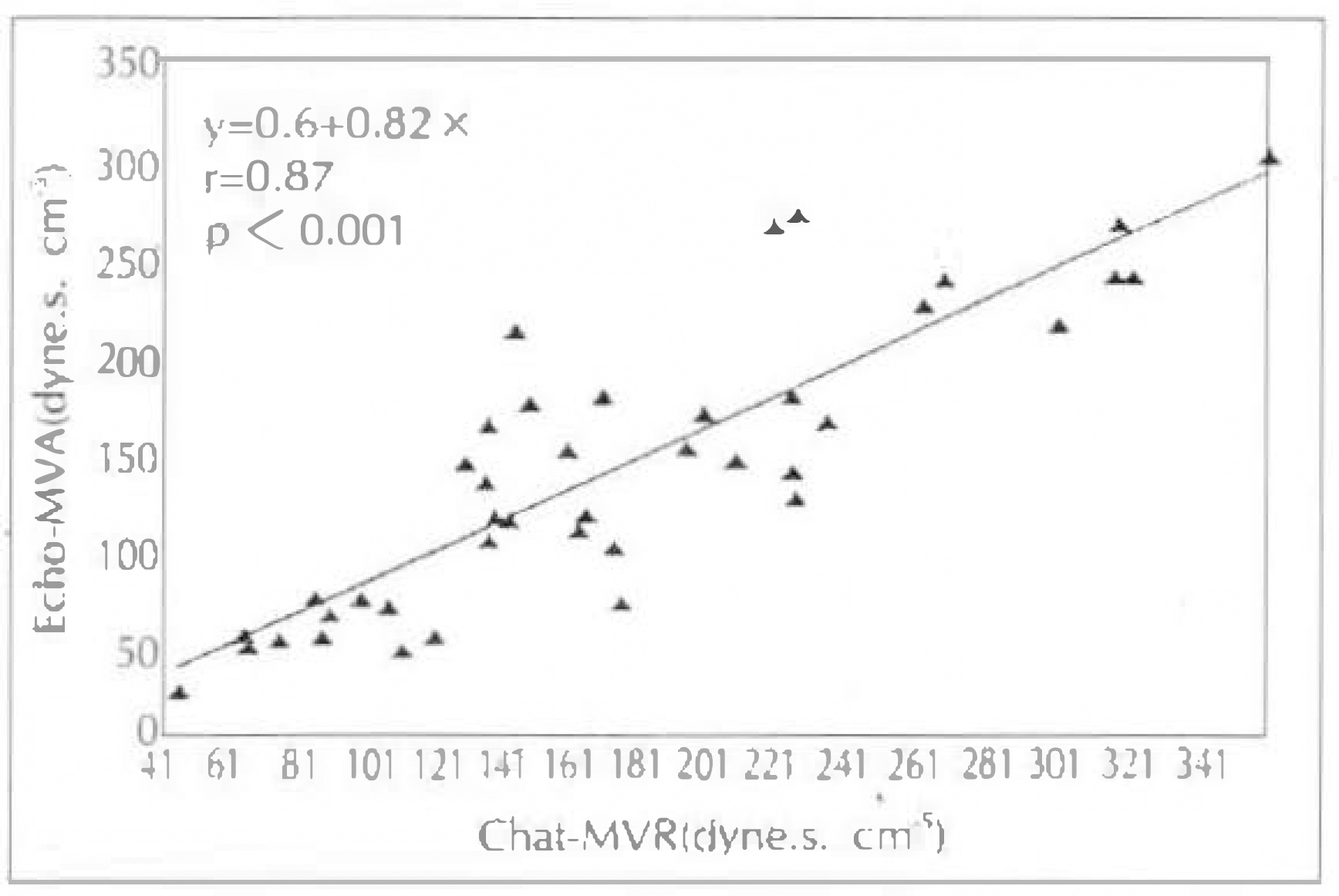
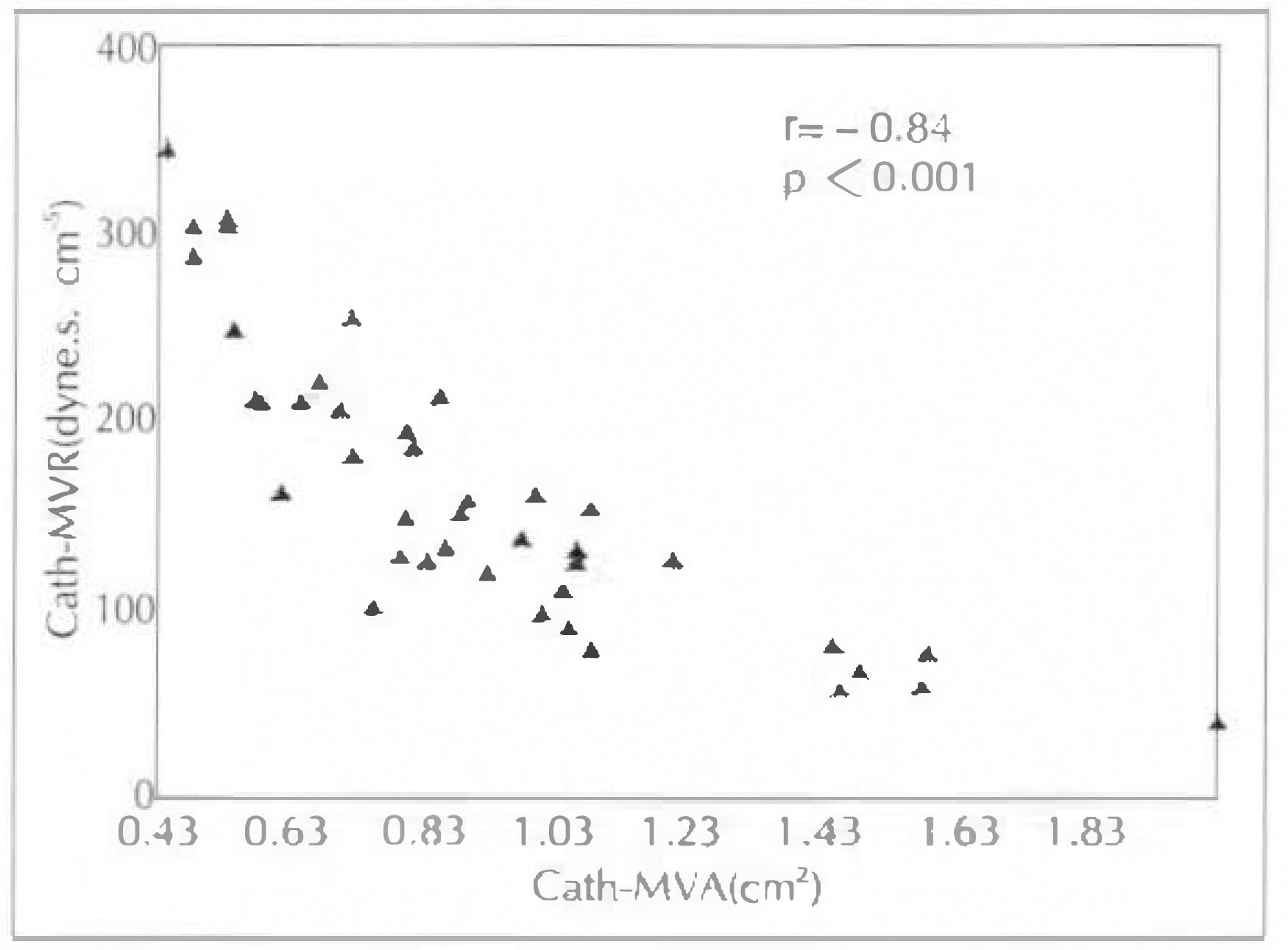
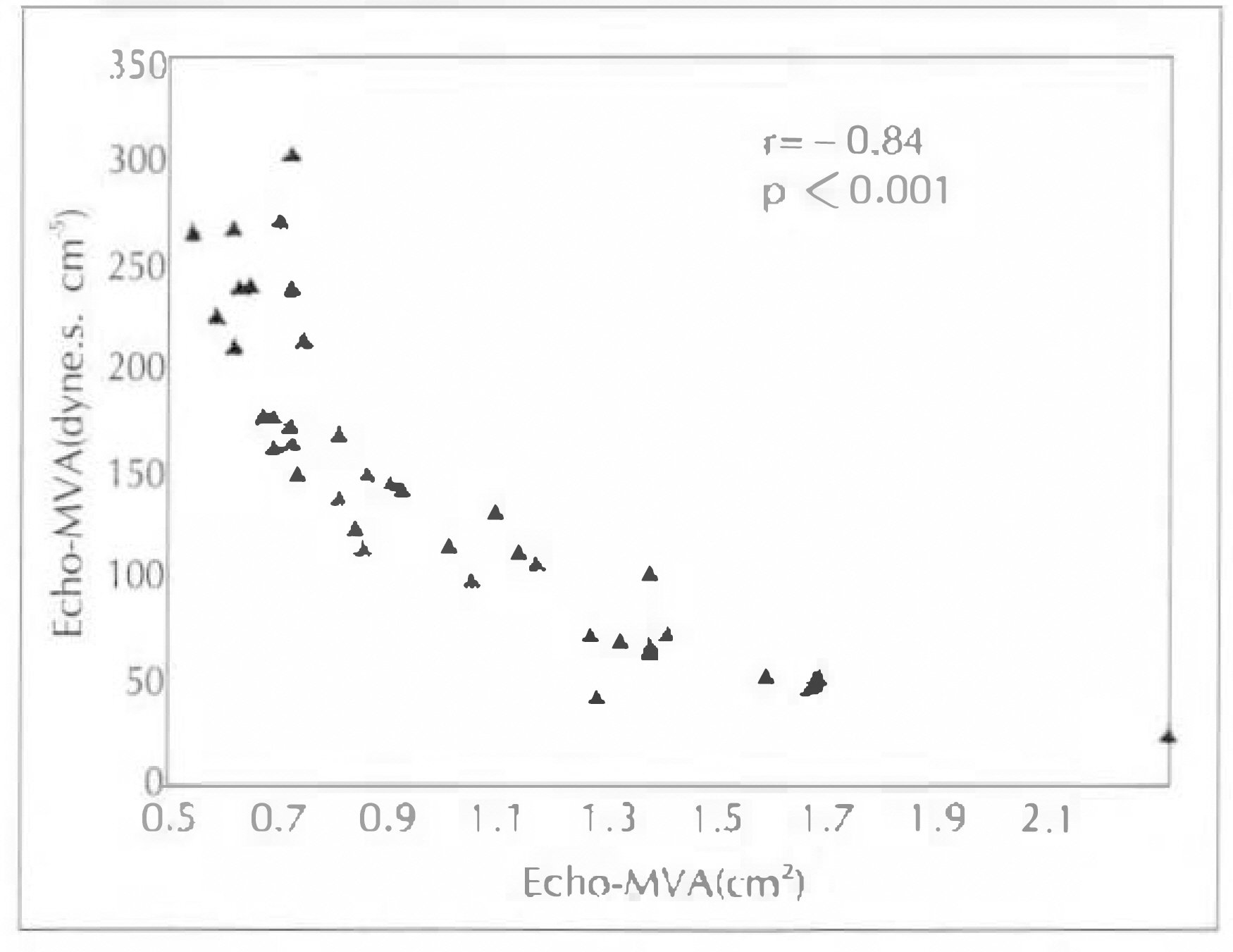
1) ED-MVA of these 28 patients with mitral stenosis correlated well at a coeffitient of 0.867 than PHT-MVA(r=0.513) or 2DE(r=0.513) in comparison with Cath-MVA. 2) Excluding 4 patients with mitral regurgitation, the ED-MVA of 24 patients with isolated mitral stenosis showed a better correlation with r=0.944 than with PHT-MVA(r=0.642) or 2DE-MVA(r=0.647) in comparison with Cath-MVA. 3) MVA determined by PISA method were correlated with planimetry method on 2DE(r=0.51, p < 0.001). 4) MVA determined by PISA method were correlated with PTH method(r=0.44, p=0.002). 5) Agreement with planimetrymethod was similar for 26 patients with mitral regurgitation and 24 without it, as well as for 34 in atrial fibrillation. 6) The correlation coefficient of mitral valve area and mitral valve resistance between echocardiography(r=0.87) and cardiac catheterization(r=0.82) showed positive correlation(p < 0.001). 7) Linear regression analysis showed a negative correlation of mitral valve resistance and Gorlin mitral valve area between echocardiography (r=−0.84) and cardiac catheterization(r=−0.84).
CONCLUSION
Echocardiographic evaluation of mitral valve stenosis by planimetry, pressur half-time method, Echo-Doppler method, PISA method, and mitral valve resistance were useful noninvasive methods in assessing the severity of mitral stenosis. In mitral stenosis patients with mitral regurgitation and/or aortic regurgitation, PISA and mitral valve resistance methods were also reliable. In conclusion, these results suggested that the echocardiographic methods could be sufficient for assessing the severity of mitral stenosis without the necessity of invasive technique.
MeSH Terms
-
Aortic Valve Insufficiency
Atrial Fibrillation
Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac Catheters
Cardiac Output
Clothing
Constriction, Pathologic*
Echocardiography*
Echocardiography, Doppler
Heart Ventricles
Hemodynamics
Humans
Hydrodynamics
Linear Models
Methods*
Mitral Valve
Mitral Valve Insufficiency
Mitral Valve Stenosis*
Radius
Stroke Volume
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). Braunwald E. Valvular heart disease. Braunwald E, editor. Heart disease: A Text book of cardiovascular Medicine. 4th ed.Philadelphia WB Saunders;1992.2). Gorlin R, Gorlin SG. Hydraulic formula for calculation of the area of stenosis mitral valve, other cardiac valves and central circulator shunts. Am Heart J. 41:1–29. 1951.3). Cohn MV, Gorlin R. Modified orifice equation for the calculation of mitral valve area. Am Heart J. 85:839–40. 1972.4). Nichol PM, Gilbert BW, Kisslo JA. Two-dimensional echocardiographic assessment of mitral stenosis. Circulation. 55:120–8. 1977.
Article5). Wann LS, Weymann AE, Feigenbaum H, Dill JC, Johnston KW, Eggleton RC. Determination of mitral valve area by cross-sectional echocardiography. Ann Intern Med. 88:337–41. 1978.
Article6). Martin RP, Rakowski H, Kleimal JH, Beaver W, London E, Popp RL. Reliability and reproducibility of two-dimensional echocardiographic measurement of stenotic mitral valve area. Am J Cardiol. 43:560–8. 1979.7). Smith MD, Handshoe R, Handshole S, Kwan OL, DeMaria AN. Comparative accuracy of two-dimensional echocardiography and Doppler pressure half-time method in assessing severity of mitral stenosis in patients with and without prior commissurotomy. Circulation. 73:100–7. 1986.8). Hatle L, Brubakk A, Trornsdal A, Angelsen B. Noninvasive assessment of pressure drop in mitral stenosis by Doppler ultrasound. Breart J. 40:131–40. 1978.
Article9). Halte L, Angelsen B, Tromsdal A. Noninvasive assessment of atrioventricular pressure half-time by Doppler ultrasound. Circulation. 60:1096–104. 1979.
Article10). Nakatani S, Masuyama T, Kodama K, Kitabatake A, Fujii K, Kamada T. Value and limitation of Doppler echocardiography in the quantification of stenotic mitral valve area: comparison of the pressure-half time and the continuity equation methods. Circulation. 77:78–85. 1988.11). Flachskampf FA, Weymann AE, Gillan L, Chun-Ming L, Abascal VM, Thomas JD. Aortic regurgitation shortens Doppler pressure half-time in mitral stenosis: clinical evidence, in vitro simulation and theoretic analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 16:396–404. 1990.
Article12). Karp K, Teien D, Bjerle P, Eriksson P. Reassessment of valve area determinations in mitral stenosis by the pressure half-time method: Impact of left ventricular stiffness and peak diastolic pressure difference. J Am Coll Cardiol. 13:594–9. 1989.
Article13). Yoshida K, Yoshikava J, Yamaura Y, Hozumi T, Shakudo M, Akasaka T, Kato H. Value of acceleration flows and regurgitant jet direction by color Doppler flow mapping in the evaluation of mitral valve prolapse. Circulation. 81:879–885. 1990.
Article14). Yoshida K, Yoshikawa J, Yamamura Y, Hozumi T, Akasaka T, Iutaya T. Assessment of mitral regurgitation by biplane transesophageal color Doppler flow mapping Circulation. 82:1121–26. 1990.15). Bargiggia GS, Bertucci C, Raisaro A, Setta S, Angoli L, Recusani F, Gallati M, Tronconi L. Quantitative assessment of mitral regurgitation by color Doppler analysis of flow convergence region: Usefulness of continuity equation. Proceedings of the Sixth International Congress on Cardiac Doppler. p. 140. 1988.16). Bargiggia GS, Raisaro A, Bertucci C, Bramucci E, Recusani F, Montemartini C. Color Doppler analysis of proximal flow convergence region in patient with mitral regurgitation. Cardiovascular Imaging. 2:137–141. 1990.17). Gardin J. Doppler color flow “proximal isovelocity surface area(PISA)”: An alternative method for estimating volume flow across narrowed orifice regurgitant valves and intracardiac shunt lesion. Echocardiography. 9:39–42. 1992.18). Giesler M, Scaugch M. Color Doppler determination of regurgitant flow: from proximal isovelocity surface areas to proximal velocity profiles. Echocardiography. 9:51–62. 1992.19). Utsunomiya T, Ogawa T, Patel D. Doppler color flow mapping of the “proximal isovelocity surface area. A new method for measuring volume flow across an orifice. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 4:338–348. 1991.20). Rouse H. Fluid Mechanics for Hydraulic Engineers. New York: Dover Publications Inc.;p. 83–95. 1961.21). Utsunomiya T, Doshi R, Patel D, Mehta K, Nguyen D, Henry WL, Gardin JM. Calculation of volume flow rate by the proximal isovelocity surface area method: Simplified approach using color Doppler zero baseline shift. J Am Coll Cardiol. 22:277–82. 1993.
Article22). Utsunomiya T, Doshi R, Patel D, Nguren D, Mehta K, Gardin J. Regurgitant volume estimation in patient with mitral regurgitation initial studies using the color Doppler proximal isovelocity surface area method. Echocardiography. 9:63–70. 1992.23). Cohen MV, Gorlin R. Modified orifice equation for the calculation of mitral valve area. Am Heart J. 84:839–43. 1972.
Article24). Teichholz LE, Krelen T, Herman MV, Gorlin R. Problems in echocardiographic volume determinations, echocardiographic correlations inthe presence of asynergy. Am J Cardiol. 37:7–13. 1976.25). Rodriguez L, Thomas JD, Monterrosos V, Weymann AE, Harrigan P, Mueller LN, Levine RA. Validation of the proximal flow convergence method: Calculation of orifice area in patients with mitral stenosis. Circulation. 88:1157–1165. 1993.
Article26). Gorlin R. The mechanism of the signs and symptoms of mitral valve disease. Br Heart J. 16:375–42. 1954.
Article27). Selzer A, Cohe W. Natural history of mitral stenosis: A view. Circulation. 45:878–84. 1972.28). Shiu MF, Crowther A, Jenkins BS. Echocardiographic and exercise evaluation of results of mitral valvulotomy operations. Br Heart J. 41:139–45. 1979.29). Thomas RD, Das M, Ionescu MI. Echocardiographic pattern of posterior mitral valve leaflet movement after mitral valve repair. Br Heart J. 41:399–404. 1979.
Article30). Weyman AE, Wann LS, Rogers WE. Five year experience in correlating cross-sectional echocardiographic assessment on the mitral valve area with hemodynamic area determination. Am J Cardiol. 43:386–97. 1979.31). Smith MD, Handshoe R, Handshoe S, Kwan OL, De Maria AN. Comparative accuracy of two-dimentional echocardiography and Doppler pressure half-time method in assessing severity of mitral stenosis in patient with and without prior commisurotomy. Circulation. 73:100–7. 1988.32). 박종훈 성 언 한. 송요판!삭 절 한 에 서 Doppler 선 초 음파도같 이용한 확장기압력 경 사 및 숭요판구 연 척 에 관한 관 장 순한기. 16:225–232. 1986. 16:225–232. 1986.33). Libanoff AJ, Rodbard S. Atrioventricular pressure half time, measure of mitral orifice area. Circulation. 38:144–50. 1986.34). Tuillez C, Theroux P, Bourassa MG. Pulse Doppler ecocardiographic study of mitral stenosis. Circulation. 61:381–7. 1980.35). Fredmann CS, Pearson AC, Labovitz AJ, Kern MJ. Comparison of hemodynamic pressure half-time method and Gorlin formula with Doppler and echocardiographic determinations of mitral valve area in patients with combined mitral stenosis and regurgitation. Am Heart J. 119:121. 1990.36). Thomas JD, wilkins GT, Choong CYP, et al. Inaccuracy of mitral pressure half-time immediately after percutaneous mitral valvulotomy; dependence on transmitral gradient and left atrial and ventricular compliance. Circulation. 78:980–93. 1988.37). Chen C, Wang Y, Guo B, Lin Y. Reliability of the Doppler pressure half-time method for assessing effects of percutaneous mitral balloon valvuloplasty. J Am Coll Cardiol. 13:1309–13. 1987.
Article38). Henry WL, Kastl DJ. Echocardiographic evaluation of patients with mitral stenosis. Am J Med. 62:813–8. 1977.39). Askenazi J, Carlson CJ, Alpert JS, Dexter L. Mitral valve area in combined mitral stenosis and regurgitation. Circulation. 54:480–3. 1976.
Article40). Bryg RJ, Williams GA, Labovitz AJ, Aker U, Kennedy HL. Effect of atrial fibrillation and mitral regurgitation on calculated mitral valve area in mitral stenosis. Am J Cardiol. 57:634–8. 1986.
Article41). Henry WL, Griffith JM, Michaelis LL, Mc Intosh CL, Morrow AG, Epstein SE. Measurement of mitral orifice area in patients with mitral valve disease by real-time two-dimentional echocardiography. Circulation. 51:827–31. 1975.42). Hammermeister KE, Murray JA and Blackmon Jr. Revision of Gorlin constant for circulation of mitral valve area from left heart pressure. Br Heart J. 35:392–6. 1973.43). Libanoff AL, Rodbard S. Evaluation of the severity of mitral stenosis and regurgitation. Circulation. 33:218–26. 1966.
Article44). Martin RP, Rakowski H, Kleiman JH. Reliability and reproducibility of two dimentional echocardiographic measurement of the stenotic mitral valve orifice area. Am J Cardiol. 43:560–8. 1979.45). Holen J, Aaslid R, Landmark , Simonsen S. Determination of pressure gradient in mitral stenosis with non-invasive ultrasound Doppler technique. Acta Med Scand. 199:455–60. 1976.46). Holen J, Aaslid R, Landmark , Simosen S. Determination of effective orifice area in mitral stenosis from non-invasive ultrasound Doppler data and mitral flow rate. Acta Med Scand. 201:83–8. 1977.
Article47). Recusani F, Bargiggia GS, Yoganathan AP, Raisaro A, Valdes-Cruz LM, Sung H-W, Bertucci C, Gallati M, Moises VA, Simpson IA, Tronconi L, Sahn DJ. A new method for quantification of regurgitant flow rate using color Doppler flow imaging of the flow convergence region proximal to a discrete orifice: An in vitro study. Circulation. 83:594–604. 1991.
Article48). Utsunomiya T, Ogawa T, Doshi R, et al. Doppler color flow “proximal isovelocity surface area method for estimating volume flow rate. Effects of orifice shape and machine factors. J Am Coll Cardiol. 17:1103. 1991.
Article49). Sahn DJ, Simpson IA, Murillo A, Valdes-Cruz L. Observation of acceleration proximal to restrictive orifices in congenital heart disease: Important clues for the interpretation of Doppler color flow maps. Circulation. 1988; 78(suppl II):II–649. Abstract.50). Moises VA, Maciel BC, Hornberger LK, Murillo-Olivas A, Valdes-Cruz LM, Sahn DJ, Weintraub RG. A new method for noninvasive estimation of ventricular septal defect shunt flow by Doppler color flow mapping: imaging of the laminar flow convergence region on the left septal surface. J Am Coll Cardiol. 18:824–832. 1991.
Article51). 강흥신 · 조 정 휘 깅 권 삼 검 l생 식 · 송 정 상 배종 화. 승£판 폐 쇄 부신증환자에 서 색 채 도플러 심 초유파도의 근위부 등속 표떤척 (PISA) 방 법 윤 이 용한 역 류 혈 액 량 측정 한국심 초음파학회 지. 2(/):41–52. 1994.52). Reinaldo W, Beyer , Alfonso Olmas, Ruban F. Mitral valve resistance as a hemodynamic indicator in mitral stenosis. Am J Cardiol. 69:775–82. 1992.53). Lincolon E, Ford , Ted Feldman Y, Christopher C, John D. Carroll: Hemodynamic resistance as a measure of functional impairment on aortic valvular stenosis. Circulation Research. 66:1–6. 1990.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Echocardiographic Indices of the Severity in Patients with Mitral Stenosis
- Noninvasive Evaluation of Rheumatic Tricuspid Stenosis with Doppler and 2 Dimensional Echocardiography
- Echocardiographic Study on the Mitral Valvular Heart Diseases
- A Giant Left Atrium in Rheumatic Mitral Stenosis
- Indices for Assessing the Dynamic Severity of Mitral Stenosis