J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2018 Apr;56(2):161-165. 10.4047/jkap.2018.56.2.161.
Fabrication of palatal lift prosthesis for a patient with palatal defect
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea. ihcc@yuhs.ac
- 2BK21 PLUS Project, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- 3Department of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2410120
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2018.56.2.161
Abstract
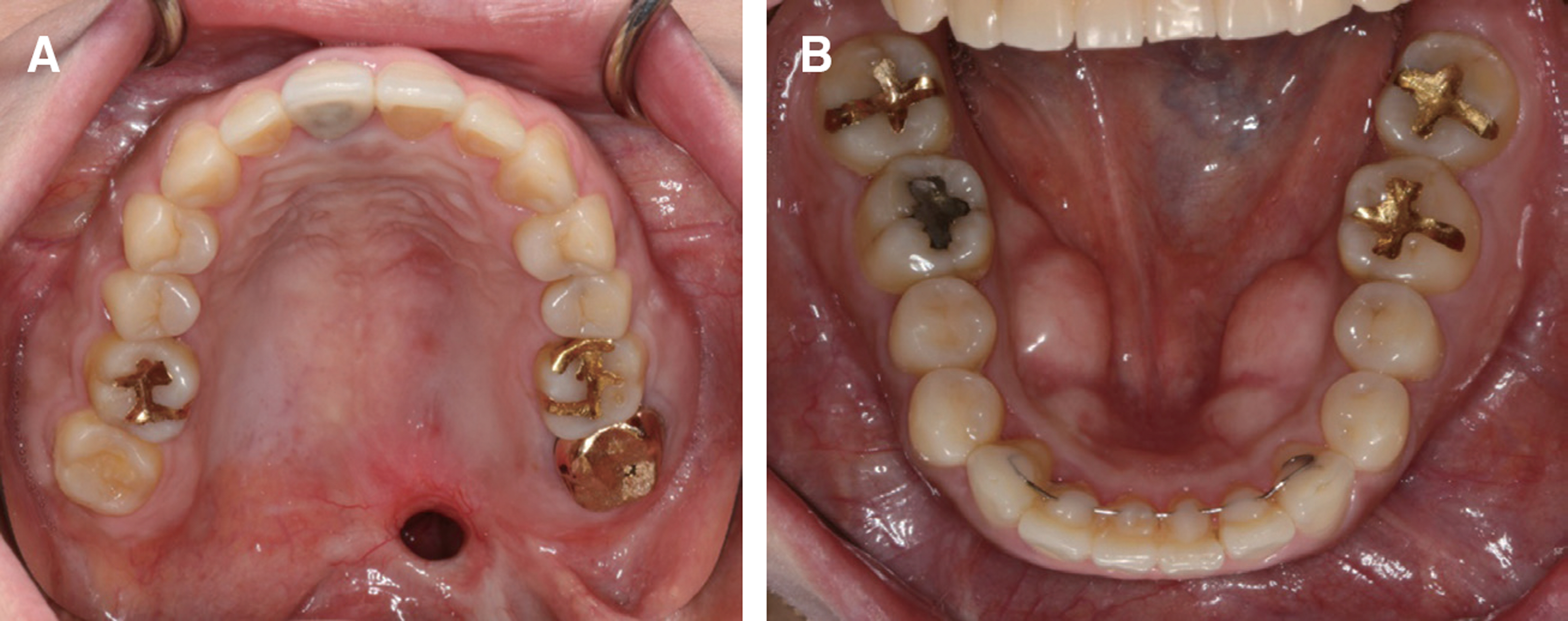
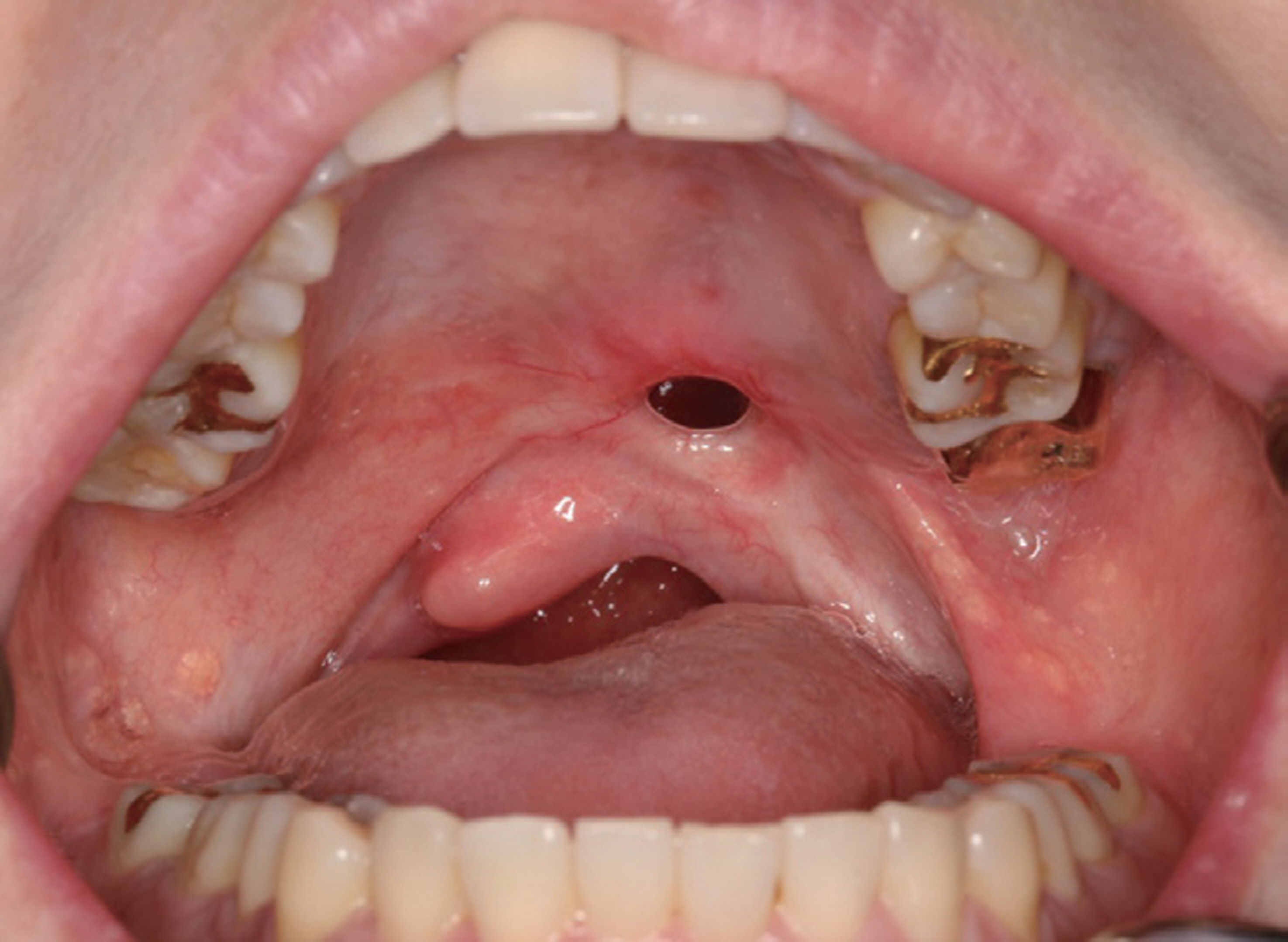
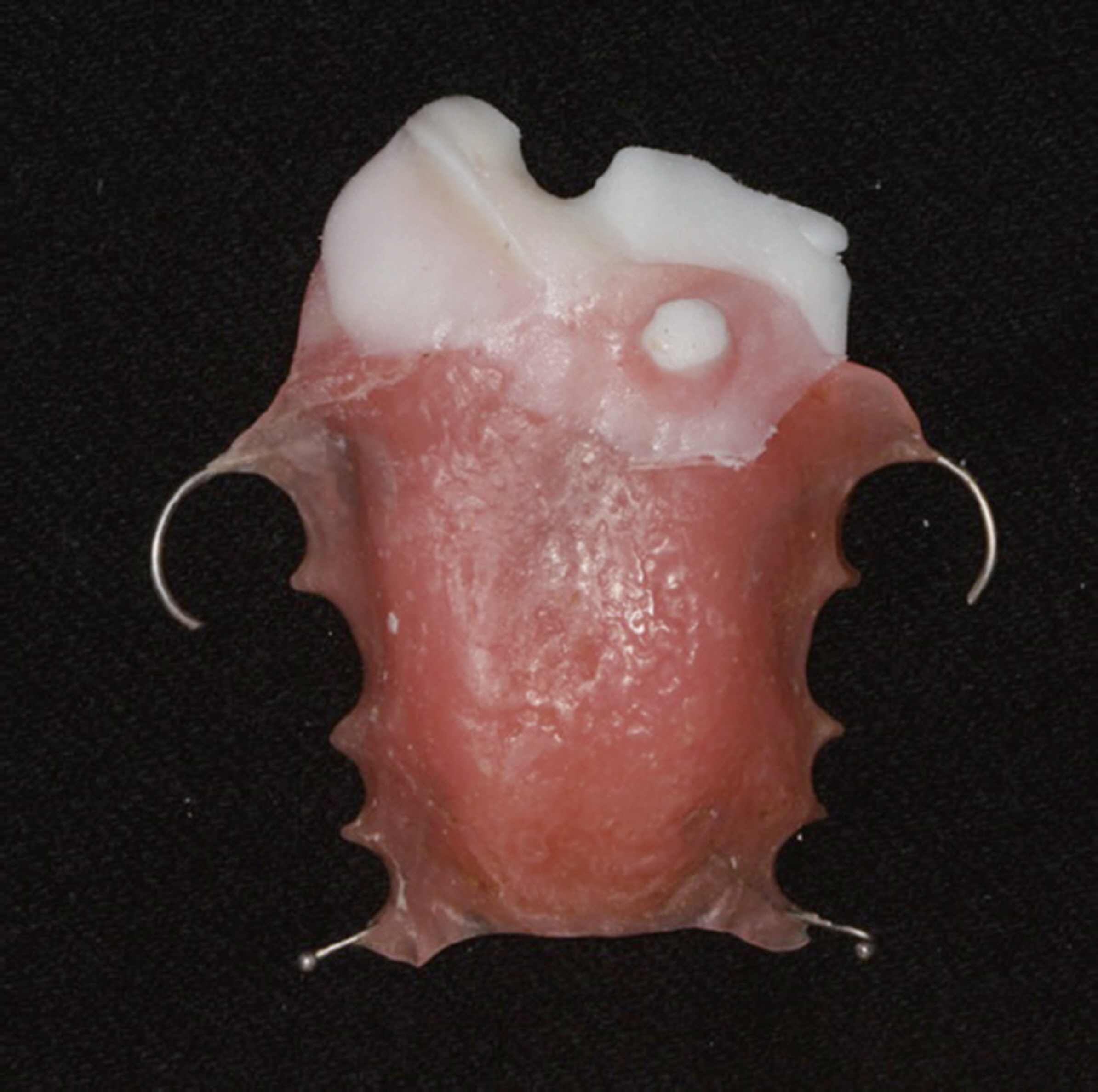
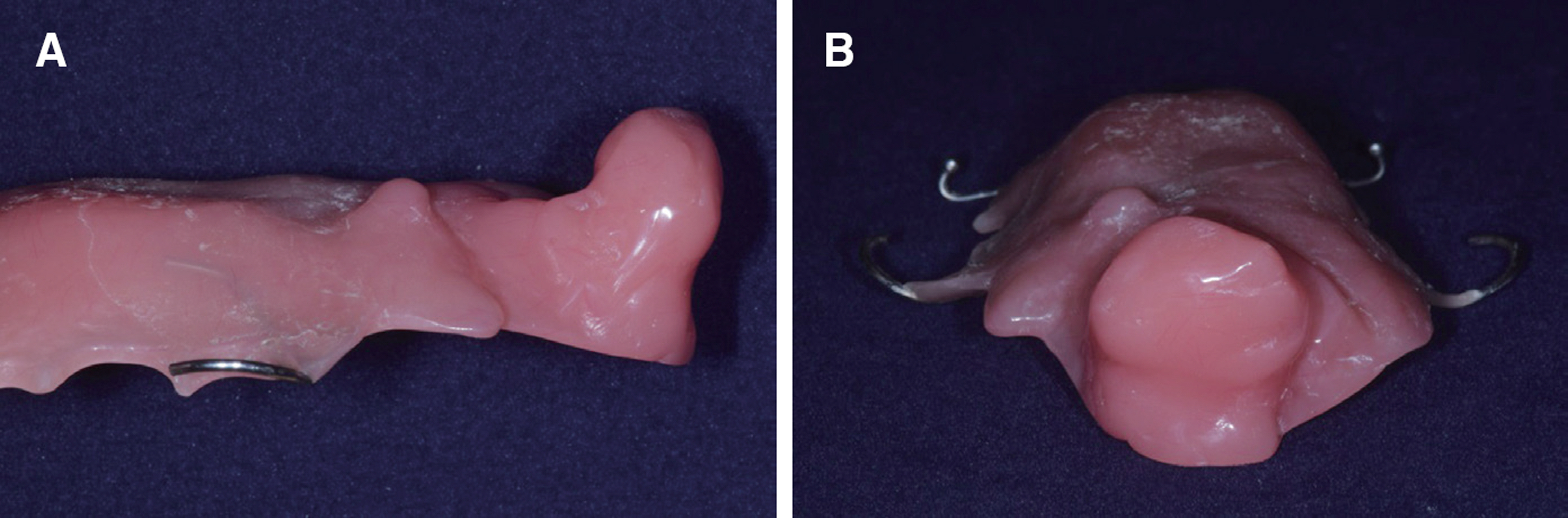
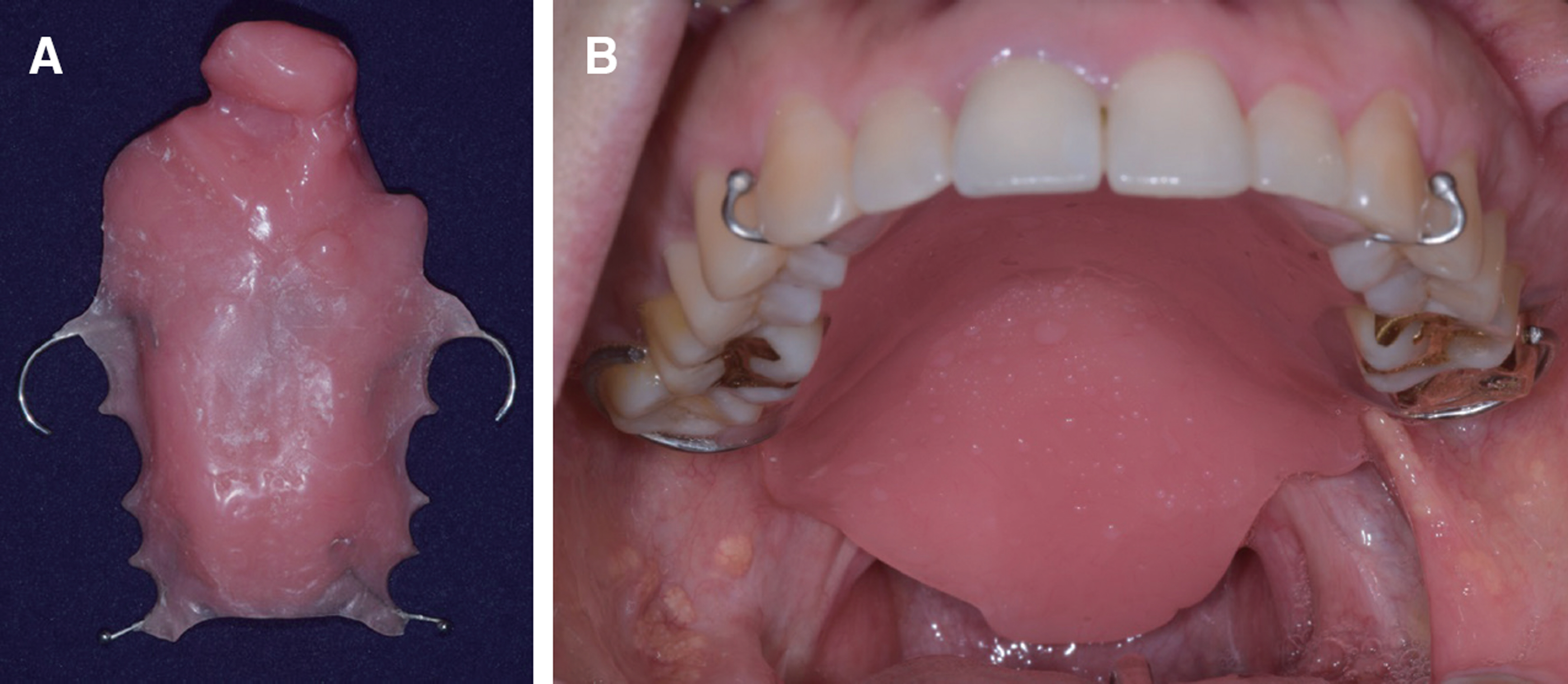
- This report is a case of 38-year old female patient who had a chief complaint about having pronounciation disorder after going under mass excision due to mucoepidermoid carcinoma. She was referred to department of prosthodontics, Yonsei university. Palatal lift prosthesis was fabricated which was then relined with tissue conditioner. Evaluations on phonetics and swallowing were done and improvements were shown. Tissue conditioner was replaced with heat polymerizing resin and the patient was satisfied with the results of treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Schneider E., Shprintzen RJ. A survey of speech pathologists: current trends in the diagnosis and management of velopharyngeal insufficiency. Cleft Palate J. 1980. 17:249–53.2.Johns DF., Rohrich RJ., Awada M. Velopharyngeal incompetence: a guide for clinical evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. 112:1890–7.3.Beumer J., Marunick MT., Esposito SJ. Maxillofacial rehabilitation: prosthodontic and surgical management of cancer-related, acquired, and congenital defects of the head and neck. 3rd ed.Illinois: Quintessence Pub.;2011. p. 213–54.4.Gibbons P., Blommer H. A supportive-type prosthetic speech aid. J Prosthet Dent. 1958. 8:362–9.
Article5.Raj N., Raj V., Aeran H. Interim palatal lift prosthesis as a constituent of multidisciplinary approach in the treatment of velopharyngeal incompetence. J Adv Prosthodont. 2012. 4:243–7.
Article6.Marshall RC., Jones RN. Effects of a palatal lift prosthesis upon the speech intelligibility of a dysarthric patient. J Prosthet Dent. 1971. 25:327–33.
Article7.Kipfmueller LJ., Lang BB. Treating velopharyngeal inadequacies with a palatal lift prosthesis. J Prosthet Dent. 1972. 27:63–72.
Article8.La Velle WE., Hardy JC. Palatal lift prostheses for treatment of palatopharyngeal incompetence. J Prosthet Dent. 1979. 42:308–15.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fabrication of palatal lift prosthesis using thermoplastic resin for a patient with velopharyngeal insufficiency
- Reconstruction of palatal defect using palatal flap
- Maxillary complete denture fabrication cases with posterior palatal seal considering palatal form and tissue displacement
- Complete denture rehabilitation of partially glossectomized patient using palatal augmentation prosthesis: A case report
- Interim palatal lift prosthesis as a constituent of multidisciplinary approach in the treatment of velopharyngeal incompetence