J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2018 Mar;61(2):282-286. 10.3340/jkns.2017.0404.003.
True Aneurysms of the Extracranial Carotid Artery : An Evaluation of Two “Giant Aneurysms†and the Current Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Karadeniz Technical University, School of Medicine, Trabzon, Turkey. gokalpaltun@gmail.com
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Kanuni Training and Research Hospital, Trabzon, Turkey.
- KMID: 2408031
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2017.0404.003
Abstract
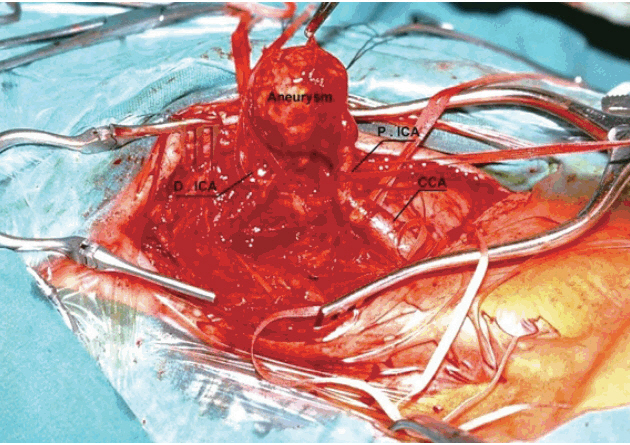
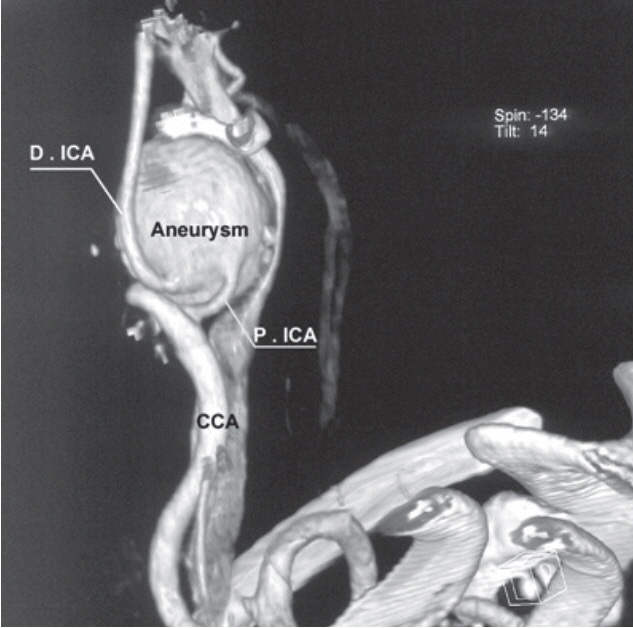
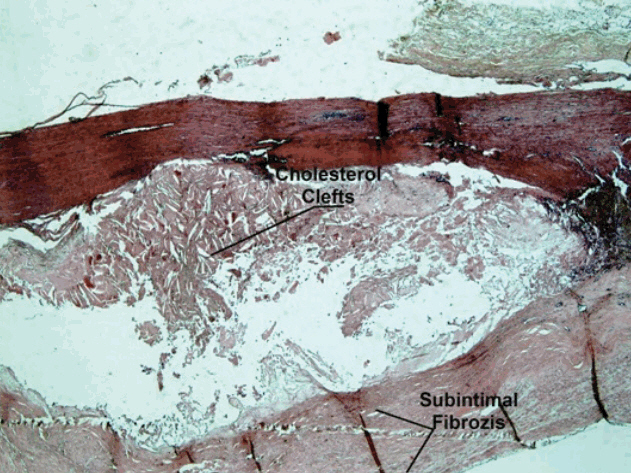
- True extracranial carotid artery aneurysms (ECCAs) are uncommon. Atherosclerosis is the most common etiological factor. Neck pain, a pulsatile mass and murmur at auscultation are the most common symptoms. ECCAs may exhibit severe clinical manifestations due to complications. Cases of rupture can be fatal. There is a risk of distal embolization and stroke in thrombosed cases. We discuss two cases of enlarged ECCA treated surgically in the light of the most recent literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Attigah N, Külkens S, Zausig N, Hansmann J, Ringleb P, Hakimi M, et al. Surgical therapy of extracranial carotid artery aneurysms: long-term results over a 24-year period. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 37:127–133. 2009.
Article2. Cinar B, Fazlioğullari O, Goksel O. True aneurysm of extracranial internal carotid artery in a 10-year-old. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 32:386–388. 2006.
Article3. DeFatta RJ, Verret DJ, Bauer P. Extracranial internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 69:1135–1139. 2005.
Article4. Donas KP, Schulte S, Pitoulias GA, Siebertz S, Horsch S. Surgical outcome of degenerative versus postreconstructive extracranial carotid artery aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 49:93–98. 2009.
Article5. Faggioli GL, Freyrie A, Stella A, Pedrini L, Gargiulo M, Tarantini S, et al. Extracranial internal carotid artery aneurysms: results of a surgical series with long-term follow-up. J Vasc Surg. 23:587–594. 1996.
Article6. Fankhauser GT, Stone WM, Fowl RJ, O’Donnell ME, Bower TC, Meyer FB, et al. Surgical and medical management of extracranial carotid artery aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 61:389–393. 2015.
Article7. Garg K, Rockman CB, Lee V, Maldonado TS, Jacobowitz GR, Adelman MA, et al. Presentation and management of carotid artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 55:1618–1622. 2012.
Article8. Li Z, Chang G, Yao C, Guo L, Liu Y, Wang M, et al. Endovascular stenting of extracranial carotid artery aneurysm: a systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 42:419–426. 2011.
Article9. Longo GM, Kibbe MR. Aneurysms of the carotid artery. Semin Vasc Surg. 18:178–183. 2005.
Article10. Ni L, Pu Z, Zeng R, Zhang R, Zheng YH, Ye W, et al. Endovascular stenting for extracranial carotid artery aneurysms: experiences and mid-term results. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e5442. 2016.11. Rivera-Chavarría IJ, Alvarado-Marín JC. Endovascular repair for an extracranial internal carotid aneurysm with cervical access: a case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 19:14–16. 2016.
Article12. Szopinski P, Ciostek P, Kielar M, Myrcha P, Pleban E, Noszczyk W. A series of 15 patients with extracranial carotid artery aneurysms: surgical and endovascular treatment. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 29:256–261. 2005.
Article13. Welleweerd JC, den Ruijter HM, Nelissen BG, Bots ML, Kappelle LJ, Rinkel GJ, et al. Management of extracranial carotid artery aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 50:141–147. 2015.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Asymptomatic Extracranial Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysm: A Case Report
- Two Cases of Extracranial Carotid Artery Aneurysm Accompanied by Cerebral Infarction
- Extracranial Carotid Disease: An Interpretation of Extracranial Carotid Artery Disease Guideline 2011
- Five Aneurysms Arising from the Ipsilateral Internal Carotid Artery : Case Report
- Extracranial Carotid Artery Aneurysm: Various Therapeutic Options and Outcome