Ann Surg Treat Res.
2018 Apr;94(4):174-182. 10.4174/astr.2018.94.4.174.
Evaluation of prophylactic and therapeutic effects of ruscogenin on acute radiation proctitis: an experimental rat model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of General Surgery, Istanbul Bagcilar Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey. 81drerkanyavuz@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Kocaeli Derince Training and Research Hospital, Kocaeli, Turkey.
- KMID: 2407746
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2018.94.4.174
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Radiation proctitis (RP) is inflammation and damage to the rectum, manifested secondary to ionizing radiation utilized for treatment. In this study, we evaluated the anti-inflammatory therapeutical and protective effects of ruscogenin in a model of acute RP.
METHODS
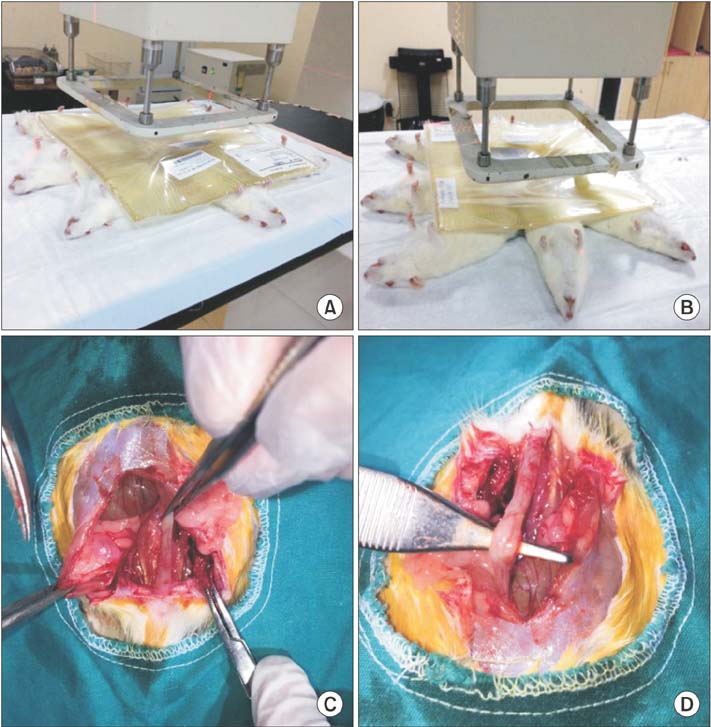
Thirty-two Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into 4 groups (n = 8) as sham, control, treatment, and prophylaxis groups. Prophylaxis group and treatment group were dosed ruscogenin by oral gavage for 14 days pre- and postradiation. At the end of the 28th day, all subjects were sacrificed.
RESULTS
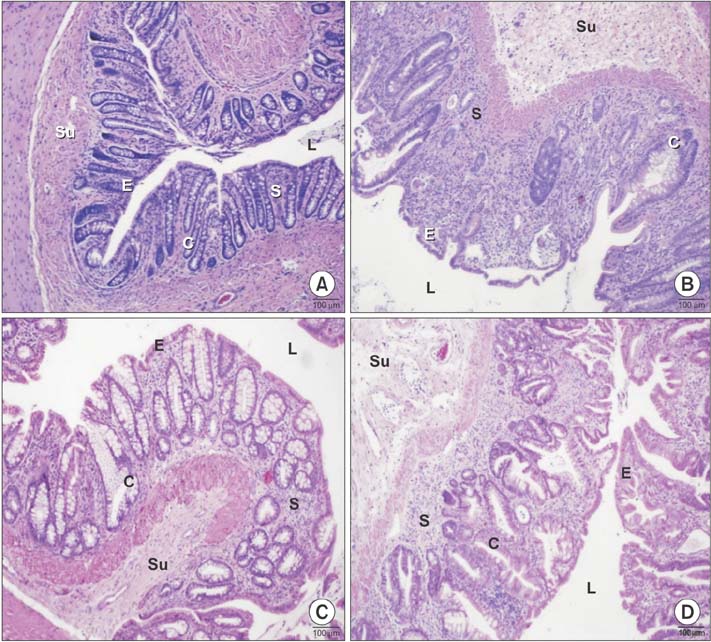
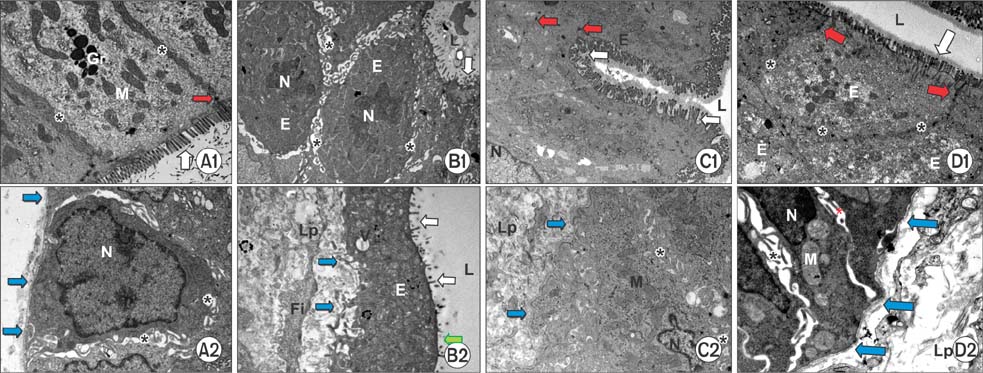
Histopathological analysis showed a significant increase in cryptitis abscess, cryptitis and reactive atypia, and depth of lymphocytic infiltration of the control group, compared to the other groups (P < 0.05), while treatment and prophylaxis groups showed significant decreases (P < 0.05). Immunohistochemical analysis indicated that immunoreactivity were significantly higher in control group (P < 0.05, P < 0.001, and P < 0.01, respectively), but vice versa for treatment and prophylaxis groups. There was not any significant difference for fibroblast growth factor 2 immunoreactivity. The epithelium of control rectums indicated an increase in TNF-α immunoreactivity while other groups had significant decrease (P < 0.01). Electron microscopical findings were parallel to light microscopy.
CONCLUSION
In this study, ruscogenin was observed to be effective on prophylaxis or treatment of acute RP. Although there are various reports on the treatment of the rectum damaged by acute RP in the literature, this could be the first study since there is no research indicating the ultrastructural effect of ruscogenin.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hauer-Jensen M, Wang J, Boerma M, Fu Q, Denham JW. Radiation damage to the gastrointestinal tract: mechanisms, diagnosis, and management. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2007; 1:23–29.
Article2. Swaroop VS, Gostout CJ. Endoscopic treatment of chronic radiation proctopathy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1998; 27:36–40.
Article3. Novak JM, Collins JT, Donowitz M, Farman J, Sheahan DG, Spiro HM. Effects of radiation on the human gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1979; 1:9–39.
Article4. Hayne D, Vaizey CJ, Boulos PB. Anorectal injury following pelvic radiotherapy. Br J Surg. 2001; 88:1037–1048.
Article5. Okunieff P, Cornelison T, Mester M, Liu W, Ding I, Chen Y, et al. Mechanism and modification of gastrointestinal soft tissue response to radiation: role of growth factors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 62:273–278.
Article6. Shadad AK, Sullivan FJ, Martin JD, Egan LJ. Gastrointestinal radiation injury: symptoms, risk factors and mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:185–198.
Article7. Anseline PF, Lavery IC, Fazio VW, Jagelman DG, Weakley FL. Radiation injury of the rectum: evaluation of surgical treatment. Ann Surg. 1981; 194:716–724.8. Frishman WH, Sinatra ST, Moizuddin M. The use of herbs for treating cardiovascular disease. In : Frishman WH, Sonnenblick EH, Sica DA, editors. Cardiovascular pharmacotherapeutics. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw Hill;2004. p. 23–35.9. Huang YL, Kou JP, Ma L, Song JX, Yu BY. Possible mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of ruscogenin: role of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008; 108:198–205.10. Facino RM, Carini M, Stefani R, Aldini G, Saibene L. Anti-elastase and anti-hyaluronidase activities of saponins and sapogenins from Hedera helix, Aesculus hippocastanum, and Ruscus aculeatus: factors contributing to their efficacy in the treatment of venous insufficiency. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 1995; 328:720–724.11. Capra C. Pharmacology and toxicology of some components of Ruscus aculeatus. Fitoterapia. 1972; 43:99–113.12. Sezer A, Usta U, Kocak Z, Yagci MA. The effect of a flavonoid fractions diosmin + hesperidin on radiation-induced acute proctitis in a rat model. J Cancer Res Ther. 2011; 7:152–156.
Article13. Erturkuner SP, Yaprak Sarac E, Gocmez SS, Ekmekci H, Ozturk ZB, Seckin İ, et al. Anti-inflammatory and ultrastructural effects of Turkish propolis in a rat model of endotoxin-induced uveitis. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2016; 54:49–57.14. Do NL, Nagle D, Poylin VY. Radiation proctitis: current strategies in management. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2011; 2011:917941.
Article15. Gultekin FA, Bakkal BH, Sumer D, Kokturk F, Bektas S. Effects of ozonated olive oil on acute radiation proctitis in rats. Balkan Med J. 2013; 30:369–374.
Article16. Doi H, Kamikonya N, Takada Y, Fujiwara M, Tsuboi K, Inoue H, et al. Efficacy of polaprezinc for acute radiation proctitis in a rat model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 80:877–884.
Article17. Kronfol Z, Remick DG. Cytokines and the brain: implications for clinical psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry. 2000; 157:683–694.
Article18. Drenth JP, Van Uum SH, Van Deuren M, Pesman GJ, Van der Ven-Jongekrijg J, Van der Meer JW. Endurance run increases circulating IL-6 and IL-1ra but downregulates ex vivo TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta production. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1995; 79:1497–1503.
Article19. Duff GW. Cytokines and anti-cytokines. Br J Rheumatol. 1993; 32:Suppl 1. 15–20.20. Karaca G, Aydin O, Pehlivanli F, Altunkaya C, Uzun H, Guler O. Effectiveness of thymoquinone, zeolite, and platelet-rich plasma in model of corrosive oesophagitis induced in rats. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2017; 92:396–401.
Article21. Cetin M, Capan Y. Basic fibroblast growth factor and a novel approach to its formulations. HacettepeUniversitesi Eczacılık Fakultesi Dergisi. 2004; 24:2.22. Demirel SH, Cetinkaya S. Hipoksiyl eİnduklenen Faktor-1. Sakaryamj. 2014; 4:171–177.23. Yazır Y, Gonca S, Filiz S, Dalcık H. An Important protein family for endothelial cells; vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) members of the family, structure and synthesis. Cumhur Univ Tıp FakultesiDergisi. 2004; 26:181–184.24. Ito Y, Kinoshita M, Yamamoto T, Sato T, Obara T, Saitoh D, et al. A combination of pre- and post-exposure ascorbic acid rescues mice from radiation-induced lethal gastrointestinal damage. Int J Mol Sci. 2013; 14:19618–19635.25. Lu HJ, Tzeng TF, Liou SS, Da Lin S, Wu MC, Liu IM. Ruscogenin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by its anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014; 14:110.
Article26. Haboubi NY, Schofield PF, Rowland PL. The light and electron microscopic features of early and late phase radiation-induced proctitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988; 83:1140–1144.27. Hovdenak N, Fajardo LF, Hauer-Jensen M. Acute radiation proctitis: a sequential clinicopathologic study during pelvic radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000; 48:1111–1117.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A rat model for radiation-induced proctitis
- Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Treatment on Radiation-Induced Proctitis in Rats
- Radiation-Induced Proctitis in Rat and Role of Nitric Oxide
- Examination of protective and therapeutic effects of ruscogenin on cerulein-induced experimental acute pancreatitis in rats
- Development of Experimental 9L Gliosarcoma Rat Brain Tumor Model