Diabetes in Asians
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hongsiri@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2407075
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.263
Abstract
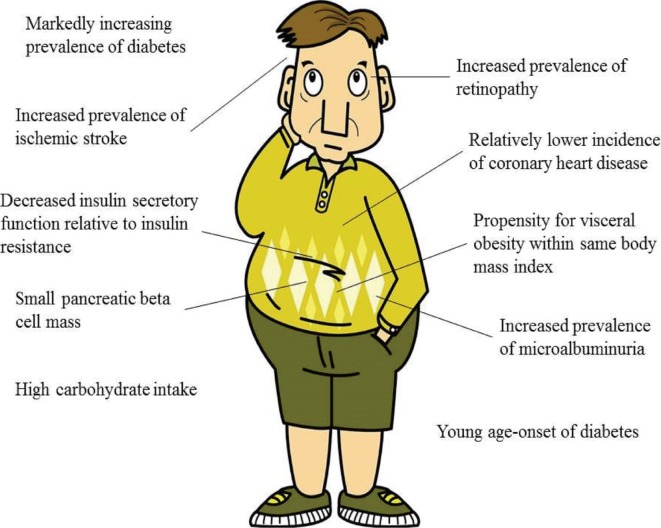
- The prevalence of diabetes is increasing globally, particularly in Asia. According to the 2013 Diabetes Atlas, an estimated 366 million people are affected by diabetes worldwide; 36% of those affected live in the Western Pacific region, with a significant proportion in East Asia. The reasons for this marked increase in the prevalence of diabetes can be extrapolated from several distinct features of the Asian region. First, the two most populated countries, China and India, are located in Asia. Second, Asians have experienced extremely rapid economic growth, including rapid changes in dietary patterns, during the past decades. As a result, Asians tend to have more visceral fat within the same body mass index range compared with Westerners. In addition, increased insulin resistance relative to reduced insulin secretory function is another important feature of Asian individuals with diabetes. Young age of disease onset is also a distinctive characteristic of these patients. Moreover, changing dietary patterns, such as increased consumption of white rice and processed red meat, contributes to the deteriorated lifestyle of this region. Recent studies suggest a distinctive responsiveness to novel anti-diabetic agents in Asia; however, further research and efforts to reverse the increasing prevalence of diabetes are needed worldwide.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 15 articles
-
Update on Monogenic Diabetes in Korea
Ye Seul Yang, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park
Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):627-639. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0214.Trends of Diabetes and Prediabetes Prevalence among Korean Adolescents From 2007 to 2018
Ji Hyun Kim, Jung Sub Lim
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(17):e112. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e112.Dose-Dependent Effect of Smoking on Risk of Diabetes Remains after Smoking Cessation: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Se Eun Park, Mi Hae Seo, Jung-Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Yang-Hyun Kim, Kyung-Do Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):539-546. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0061.Physician-Directed Diabetes Education without a Medication Change and Associated Patient Outcomes
Hun-Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim, Hae-Kyung Yang, Eun Young Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In Young Choi, Hyeon Woo Yim, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(3):187-194. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.187.Relation between Baseline Height and New Diabetes Development: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Eun-Jung Rhee, Jung-Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se-Eun Park, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):794-803. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0184.Endocrinology and Metabolism Is Indexed in the Emerging Sources Citation Index
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(3):350-352. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2017.32.3.350.How to Prepare
Endocrinology and Metabolism for Reapplication to MEDLINE
Sun Huh
Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(1):58-61. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.58.Increasing Age Associated with Higher Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition Rate Is a Predictive Factor for Efficacy of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors
Sangmo Hong, Chang Hee Jung, Song Han, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):63-70. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0253.Not Control but Conquest: Strategies for the Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jinyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):165-180. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0377.Best Achievements in Clinical Medicine in Diabetes and Dyslipidemia in 2020
Eun-Jung Rhee, Mee-Kyung Kim, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):41-50. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.106.Risk of Diabetes in Subjects with Positive Fecal Immunochemical Test: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Kwang Woo Kim, Hyun Jung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Jung Min Moon, Seung Wook Hong, Eun Ae Kang, Jooyoung Lee, Hosim Soh, Seong-Joon Koh, Jong Pil Im, Joo Sung Kim
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1069-1077. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1119.Risk and Risk Factors for Postpartum Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Women with Gestational Diabetes: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
Mi Jin Choi, Jimi Choi, Chae Weon Chung
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):112-123. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1276.Extra-Glycemic Effects of Anti-Diabetic Medications: Two Birds with One Stone?
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):415-429. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.304.Association of Body Composition Changes with the Development of Diabetes Mellitus: A Nation-Wide Population Study
Hyung Jun Kim, Hyung-Woo Lee, Min-Kyoung Kang, Gwang Hyun Leem, Min-Ho Kim, Tae-Jin Song
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(6):1093-1104. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0243.Evolving Characteristics of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in East Asia
Joonyub Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Endocrinol Metab. 2025;40(1):57-63. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.2193.
Reference
-
1. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas, 6th ed [Internet]. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation;c2014. cited 2015 Aug 18. Available from: http://www.idf.org/sites/default/files/EN_6E_Atlas_Full_0.pdf.2. Ma RC, Chan JC. Type 2 diabetes in East Asians: similarities and differences with populations in Europe and the United States. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013; 1281:64–91. PMID: 23551121.
Article3. Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, et al. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006; 368:1681–1688. PMID: 17098087.
Article4. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:303–308. PMID: 21977448.
Article5. Weber MB, Oza-Frank R, Staimez LR, Ali MK, Narayan KM. Type 2 diabetes in Asians: prevalence, risk factors, and effectiveness of behavioral intervention at individual and population levels. Annu Rev Nutr. 2012; 32:417–439. PMID: 22524185.
Article6. Gujral UP, Pradeepa R, Weber MB, Narayan KM, Mohan V. Type 2 diabetes in South Asians: similarities and differences with white Caucasian and other populations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013; 1281:51–63. PMID: 23317344.
Article7. Ramachandran A, Ma RC, Snehalatha C. Diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2010; 375:408–418. PMID: 19875164.
Article8. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Trends in the diabetes epidemic in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2015; 30:142–146. PMID: 26194073.
Article9. Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:1090–1101. PMID: 20335585.
Article10. Li H, Oldenburg B, Chamberlain C, O'Neil A, Xue B, Jolley D, et al. Diabetes prevalence and determinants in adults in China mainland from 2000 to 2010: a systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012; 98:226–235. PMID: 22658670.
Article11. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2013 [Internet]. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association;c2011. cited 2015 Aug 18. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr/temp/diabetes_factsheet_2013111.pdf.12. Jeon JY, Kim DJ, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Lim S, Choi SH, et al. Current status of glycemic control of patients with diabetes in Korea: the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:197–203. PMID: 25003073.
Article13. Ko KS, Oh TG, Kim CH, Park KS, Lee MK, Kim SY, et al. A clinical study on the complications of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1991; 15:257–262.14. Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korea health statistics 2012: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Seoul: Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare;2014.15. Cockram CS. The epidemiology of diabetes mellitus in the Asia-Pacific region. Hong Kong Med J. 2000; 6:43–52. PMID: 10793402.16. Popkin BM. The nutrition transition and its health implications in lower-income countries. Public Health Nutr. 1998; 1:5–21. PMID: 10555527.
Article17. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National Center for Health Statistics. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2013 [Internet]. Hyattsville: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2014. updated 2014 Feb 3. cited 2015 Apr 27. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov.18. Chan JC, So W, Ma RC, Tong PC, Wong R, Yang X. The complexity of vascular and non-vascular complications of diabetes: the Hong Kong Diabetes Registry. Curr Cardiovasc Risk Rep. 2011; 5:230–239. PMID: 21654912.
Article19. Chiu M, Austin PC, Manuel DG, Shah BR, Tu JV. Deriving ethnic-specific BMI cutoff points for assessing diabetes risk. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:1741–1748. PMID: 21680722.
Article20. Yeung RO, Zhang Y, Luk A, Yang W, Sobrepena L, Yoon KH, et al. Metabolic profiles and treatment gaps in young-onset type 2 diabetes in Asia (the JADE programme): a cross-sectional study of a prospective cohort. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014; 2:935–943. PMID: 25081582.
Article21. Sellayah D, Cagampang FR, Cox RD. On the evolutionary origins of obesity: a new hypothesis. Endocrinology. 2014; 155:1573–1588. PMID: 24605831.
Article22. Bar-Or O, Foreyt J, Bouchard C, Brownell KD, Dietz WH, Ravussin E, et al. Physical activity, genetic, and nutritional considerations in childhood weight management. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998; 30:2–10. PMID: 9475638.
Article23. Kim C. Gestational diabetes mellitus in korean women: similarities and differences from other racial/ethnic groups. Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:1–12. PMID: 24627822.
Article24. Deurenberg P, Yap M, van Staveren WA. Body mass index and percent body fat: a meta analysis among different ethnic groups. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998; 22:1164–1171. PMID: 9877251.
Article25. Deurenberg P, Deurenberg-Yap M, Guricci S. Asians are different from Caucasians and from each other in their body mass index/body fat per cent relationship. Obes Rev. 2002; 3:141–146. PMID: 12164465.
Article26. Wang J, Thornton JC, Burastero S, Shen J, Tanenbaum S, Heymsfield SB, et al. Comparisons for body mass index and body fat percent among Puerto Ricans, blacks, whites and Asians living in the New York City area. Obes Res. 1996; 4:377–384. PMID: 8822762.
Article27. Araneta MR, Wingard DL, Barrett-Connor E. Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome in Filipina-American women: a high-risk nonobese population. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:494–499. PMID: 11874936.29. Deurenberg-Yap M, Li T, Tan WL, van Staveren WA, Deurenberg P. Validation of a semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire for estimation of intakes of energy, fats and cholesterol among Singaporeans. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2000; 9:282–288. PMID: 24394504.
Article30. World Health Organization, International Obesity Task Force. The Asian-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. Geneva: WHO Western Pacific Region;2000.31. Kim MK, Lee WY, Kang JH, Kang JH, Kim BT, Kim SM, et al. 2014 Clinical practice guidelines for overweight and obesity in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2014; 29:405–409. PMID: 25559568.
Article32. Unger RH, Clark GO, Scherer PE, Orci L. Lipid homeostasis, lipotoxicity and the metabolic syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010; 1801:209–214. PMID: 19948243.
Article33. Fukushima M, Suzuki H, Seino Y. Insulin secretion capacity in the development from normal glucose tolerance to type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004; 66(Suppl 1):S37–S43. PMID: 15563978.
Article34. Rattarasarn C, Soonthornpan S, Leelawattana R, Setasuban W. Decreased insulin secretion but not insulin sensitivity in normal glucose tolerant Thai subjects. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:742–743. PMID: 16505544.
Article35. Yoon KH, Ko SH, Cho JH, Lee JM, Ahn YB, Song KH, et al. Selective beta-cell loss and alpha-cell expansion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:2300–2308. PMID: 12727989.36. Taniguchi A, Fukushima M, Sakai M, Nagata I, Doi K, Nagasaka S, et al. Insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, and glucose effectiveness in nonobese individuals with varying degrees of glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23:127–128. PMID: 10857985.
Article37. Cho YS, Chen CH, Hu C, Long J, Ong RT, Sim X, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies eight new loci for type 2 diabetes in east Asians. Nat Genet. 2012; 44:67–72. PMID: 22158537.38. Yasuda K, Miyake K, Horikawa Y, Hara K, Osawa H, Furuta H, et al. Variants in KCNQ1 are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Genet. 2008; 40:1092–1097. PMID: 18711367.
Article39. Popkin BM, Horton S, Kim S, Mahal A, Shuigao J. Trends in diet, nutritional status, and diet-related noncommunicable diseases in China and India: the economic costs of the nutrition transition. Nutr Rev. 2001; 59:379–390. PMID: 11766908.
Article40. Villegas R, Liu S, Gao YT, Yang G, Li H, Zheng W, et al. Prospective study of dietary carbohydrates, glycemic index, glycemic load, and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in middle-aged Chinese women. Arch Intern Med. 2007; 167:2310–2316. PMID: 18039989.
Article41. Nanri A, Mizoue T, Noda M, Takahashi Y, Kato M, Inoue M, et al. Rice intake and type 2 diabetes in Japanese men and women: the Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010; 92:1468–1477. PMID: 20980490.
Article42. Henry CJ, Lightowler HJ, Newens K, Sudha V, Radhika G, Sathya RM, et al. Glycaemic index of common foods tested in the UK and India. Br J Nutr. 2008; 99:840–845. PMID: 17903341.
Article43. Lee ET, Lu M, Bennett PH, Keen H. Vascular disease in younger-onset diabetes: comparison of European, Asian and American Indian cohorts of the WHO Multinational Study of Vascular Disease in Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001; 44(Suppl 2):S78–S81. PMID: 11587054.
Article44. Parving HH, Lewis JB, Ravid M, Remuzzi G, Hunsicker LG. DEMAND investigators. Prevalence and risk factors for microalbuminuria in a referred cohort of type II diabetic patients: a global perspective. Kidney Int. 2006; 69:2057–2063. PMID: 16612330.
Article45. Clarke PM, Glasziou P, Patel A, Chalmers J, Woodward M, Harrap SB, et al. Event rates, hospital utilization, and costs associated with major complications of diabetes: a multicountry comparative analysis. PLoS Med. 2010; 7:e1000236. PMID: 20186272.
Article46. Liu J, Hong Y, D'Agostino RB Sr, Wu Z, Wang W, Sun J, et al. Predictive value for the Chinese population of the Framingham CHD risk assessment tool compared with the Chinese Multi-Provincial Cohort Study. JAMA. 2004; 291:2591–2599. PMID: 15173150.
Article47. Woodward M, Zhang X, Barzi F, Pan W, Ueshima H, Rodgers A, et al. The effects of diabetes on the risks of major cardiovascular diseases and death in the Asia-Pacific region. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:360–366. PMID: 12547863.48. Kim JH, Kim DJ, Jang HC, Choi SH. Epidemiology of micro-and macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:571–577. PMID: 22247898.49. Weng J, Soegondo S, Schnell O, Sheu WH, Grzeszczak W, Watada H, et al. Efficacy of acarbose in different geographical regions of the world: analysis of a real-life database. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015; 31:155–167. PMID: 25044702.
Article50. Pan CY, Landen H. Post-marketing surveillance of acarbose treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and subjects with impaired glucose tolerance in China. Clin Drug Investig. 2007; 27:397–405.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Young-Onset Diabetes in East Asians: from Epidemiology to Precision Medicine
- MODY Syndrome
- Changes of Guidelines in the Management of Obese Patients With Diabetes in the Metabolic Surgery Perspective
- Eyelid Incision for Dacryocystorhinostomy in Asians
- Evolution of Diabetes Care in Hong Kong: From the Hong Kong Diabetes Register to JADE-PEARL Program to RAMP and PEP Program