Overview and current management of computerized adaptive testing in licensing/certification examinations
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychology, College of Social Science, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. wmotive@hallym.ac.kr
- KMID: 2406680
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3352/jeehp.2017.14.17
Abstract
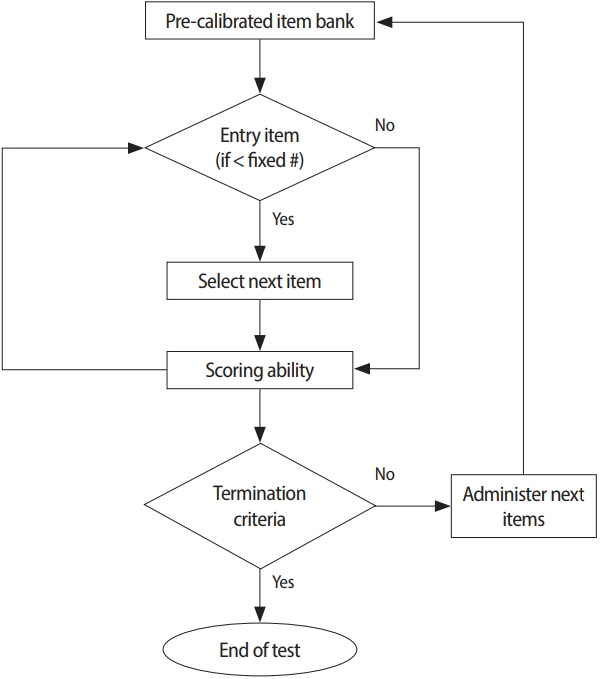
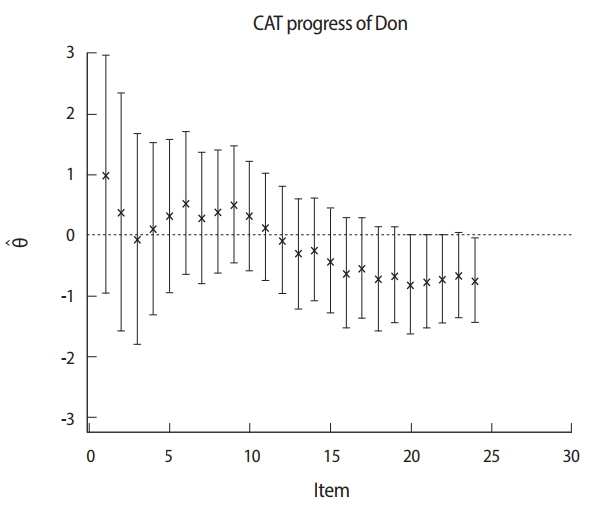
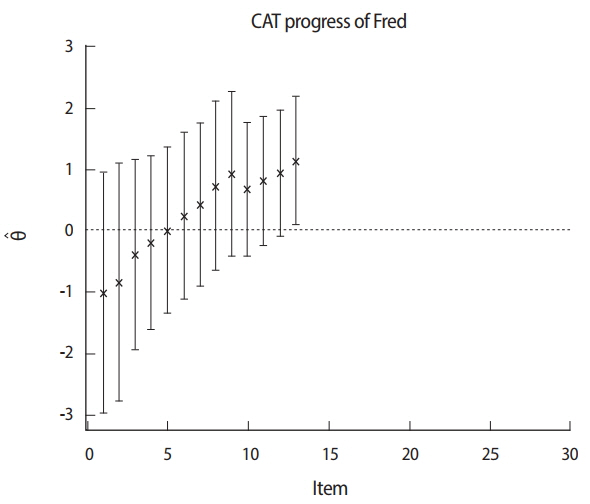
- Computerized adaptive testing (CAT) has been implemented in high-stakes examinations such as the National Council Licensure Examination-Registered Nurses in the United States since 1994. Subsequently, the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians in the United States adopted CAT for certifying emergency medical technicians in 2007. This was done with the goal of introducing the implementation of CAT for medical health licensing examinations. Most implementations of CAT are based on item response theory, which hypothesizes that both the examinee and items have their own characteristics that do not change. There are 5 steps for implementing CAT: first, determining whether the CAT approach is feasible for a given testing program; second, establishing an item bank; third, pretesting, calibrating, and linking item parameters via statistical analysis; fourth, determining the specification for the final CAT related to the 5 components of the CAT algorithm; and finally, deploying the final CAT after specifying all the necessary components. The 5 components of the CAT algorithm are as follows: item bank, starting item, item selection rule, scoring procedure, and termination criterion. CAT management includes content balancing, item analysis, item scoring, standard setting, practice analysis, and item bank updates. Remaining issues include the cost of constructing CAT platforms and deploying the computer technology required to build an item bank. In conclusion, in order to ensure more accurate estimations of examinees' ability, CAT may be a good option for national licensing examinations. Measurement theory can support its implementation for high-stakes examinations.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Presidential address: Preparing for permanent test centers and computerized adaptive testing
Chang Hwi Kim, Sun Huh
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2018;15:1. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2018.15.1.Linear programming method to construct equated item sets for the implementation of periodical computer-based testing for the Korean Medical Licensing Examination
Dong Gi Seo, Myeong Gi Kim, Na Hui Kim, Hye Sook Shin, Hyun Jung Kim, Sun Huh
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2018;15:26. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2018.15.26.Updates from 2018: Being indexed in Embase, becoming an affiliated journal of the World Federation for Medical Education, implementing an optional open data policy, adopting principles of transparency and best practice in scholarly publishing, and appreciation to reviewers
Sun Huh, A Ra Cho
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2018;15:36. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2018.15.36.Introduction to the LIVECAT web-based computerized adaptive testing platform
Dong Gi Seo, Jeongwook Choi, Sun Huh
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2020;17:27. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2020.17.27.The irtQ R package: a user-friendly tool for item response theory-based test data analysis and calibration
Hwanggyu Lim, Kyungseok Kang, Sun Huh
J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2024;21:23. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2024.21.23.
Reference
-
References
1. Spearman C. Demonstration of formulae for true measurement of correlation. Am J Psychol. 1907; 18:161. https://doi.org/10.2307/1412408.
Article2. Embretson SE, Reise SP. Item response theory for psychologists. Mahwah(NJ): Erlbaum;2000.3. Thompson NA, Weiss DJ. A framework for the development of computerized adaptive tests. Pract Assess Res Eval. 2011; 16:1–9.4. Weiss DJ. Computerized adaptive testing for effective and efficient measurement is counseling and education. Meas Eval Couns Dev. 2004; 37:70–84.5. Luecht RM, Sireci SG. A review of models for computer-based testing. New York (NY): The College Board;2011.6. Eignor DR, Way WD, Stocking ML, Steffen M. Case studies in computer adaptive test design through simulation (RR-93-56). Princeton(NJ): Educational Testing Service;1993.7. Zara AR. An overview of the NCLEX/CAT beta test. In : Proceedings of the meeting of the American Educational Research Association; 1994 Mar; New Orleans, USA. American Educational Research Association. 1994.8. Sands WA, Waters BK, McBride JR. Computerized adaptive testing: from inquiry to operation. Washington (DC): American Psychological Association;1997.9. Huh S. Preparing the implementation of computerized adaptive testing for high-stakes examinations. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2008; 5:1. https://doi.org/10.3352/jeehp.2008.5.1.
Article10. Binet A, Simon TH. The development of intelligence in young children. Vineland (NJ): the Training School;1916.11. Lawley DN. X.—The Factorial Analysis of Multiple Item Tests. Proc R Soc Edinburgh Sect A Math. 1944; 62:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0080454100006440.
Article12. Lord FM. A theory of test scores. New York (NY): Psychometric Society;1952.13. Samejima F. Estimation of latent ability using a response pattern of graded scores. Psychometrika. 1969; 35:139. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02290599.
Article14. Lord FM. Application of item response theory to practical testing problems. Hillsdale (NJ): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates;1980.15. Birnbaum A. Some latent trait models and their use in inferring an examinee’s ability. In : Lord FM, Novick MR, editors. Statistical theories of mental test scores. Reading (MA): Addison-Wesley;1968.16. Hambleton RK, Swaminathan H. Item response theory: principles and applications. Hingham (MA): Kluwer Boston Inc.;1985.17. Seo DG, Weiss DJ. Best design multidimensional computerized testing with the bifactor model. Educ Psychol Meas. 2015; 75:954–978. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164415575147.
Article18. Van der Linden WJ. How to make adaptive testing more efficient? In : Proceedings of the first annual conference of the International Association for Computerized Adaptive Testing; 2010 Jun 7-9; Arnhem, The Netherlands. [place unknown]. International Association for Computerized Adaptive Testing. 2010.19. Seo DG. Application of the bifactor model to computerized adaptive testing [unpublished dissertation]. Minneapolis (MN): University of Minnesota;2011.20. Weiss DJ. Adaptive testing by computer. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1985; 53:774–789.
Article21. Baker FB. Item response theory parameter estimation techniques. New York (NY): Marcel Dekker;1992.22. Weiss DJ, McBride JR. Bias and information of Bayesian adaptive testing. Appl Psychol Meas. 1984; 8:273–285. https://doi.org/10.1177/014662168400800303.
Article23. Castro F, Suarez J, Chirinos R. Competence’s initial estimation in computer adaptive testing. In : Proceedings of the first annual conference of the International Association for Computerized Adaptive Testing; 2010 Jun 7-9; Arnhem, The Netherlands. [place unknown]. International Association for Computerized Adaptive Testing. 2010.24. Owen RJ. A Bayesian sequential procedure for quantal response in the context of adaptive mental testing. J Am Stat Assoc. 1975; 70:351–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1975.10479871.
Article25. Thompson NA. Item selection in computerized classification testing. Educ Psychol Meas. 2009; 69:778–793. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164408324460.
Article26. Green BF, Bock RD, Humphreys LG, Linn RL, Reckase MD. Technical guidelines for assessing computerized adaptive tests. J Educ Meas. 1984; 21:347–360. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-3984.1984.tb01039.x.
Article27. Kingsbury CG, Zara AR. A comparison of procedures for contentsensitive item selection in computerized adaptive tests. Appl Meas Educ. 1991; 4:241–261. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15324818ame0403_4.
Article28. Weiss DJ, Kingsbury GG. Application of computerized adaptive testing to educational problems. J Educ Meas. 1984; 21:361–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-3984.1984.tb01040.x.
Article29. McDonald RP. The dimensionality of tests and items. Br J Math Stat Psychol. 1981; 34:100–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8317.1981.tb00621.x.
Article30. Brown JM, Weiss DJ. An adaptive testing strategy for achievement test batteries. Minneapolis (MN): University of Minnesota, Department of Psychology, Psychometric Methods Program, Computerized Adaptive Testing Laboratory;1977.31. Becker KA, Bergstrom BA. Test administration models. Pract Assess Res Eval. 2013; 18:1–7.32. Segall DO. Multidimensional adaptive testing. Psychometrika. 1996; 61:331–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02294343.
Article33. Luecht RM. Multidimensional computerized adaptive testing in a certification or licensure context. Appl Psychol Meas. 1996; 20:389–404. https://doi.org/10.1177/014662169602000406.
Article34. National Council of State Boards of Nursing. NCLEX-RN examination: detailed test plan for the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses: item writer/nurse educator version [Internet]. Chicago (IL): National Council of State Boards of Nursing;2016. [cited 2017 May 18]. Available from: https://www.ncsbn.org/2016_RN_DetTestPlan_Educator.pdf.35. McGahee TW, Ball J. How to read and really use an item analysis. Nurs Educ. 2009; 34:166–171. https://doi.org/10.1097/nne.0b013e3181aaba94.
Article36. Wells CS, Subkoviak MJ, Serlin RC. The effect of item parameter drift on examinee ability estimates. Appl Psychol Meas. 2002; 26:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146621602026001005.
Article37. Cizek GJ, Bunch M. Standard setting: a guide to establishing and evaluating performance standards on test. Thousand Oaks (CA): Sage Publications;2007.38. Angoff WH. Scales, norms, and equivalent scores. In : Thorndike RL, editor. Educational measurement. Washington (DC): American Council on Education;1971. p. 508–600.39. American Psychological Association; American Psychological Association; National Council on Measurement in Education. Standards for educational and psychological testing. Washington (DC): American Educational Research Association;1999.40. Raymond MR. Job analysis and the specification of content for licensure and certification examinations. Appl Meas Educ. 2001; 14:369–415. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15324818ame1404_4.
Article41. Sutherland K, Schwartz J, Dickinson P. Best practices for writing test items. J Nurs Regul. 2012; 3:35–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2155-8256(15)30217-9.
Article42. Loyd BH, Hoover HD. Vertical equating using the Rasch model. J Educ Meas. 1980; 17:179–193. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-3984.1980.tb00825.x.
Article43. Marco GL. Item characteristic curve solutions to three intractable testing problems. J Educ Meas. 1977; 14:139–160.44. Haebara T. Equating ability scales by a weighted least squares method. Jpn Psychol Res. 1980; 22:144–149.45. Stocking ML, Lord FM. Developing a common metric in item response theory. Appl Psychol Meas. 1983; 7:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1177/014662168300700208.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Conducting simulation studies for computerized adaptive testing using SimulCAT: an instructional piece
- Can computerized tests be introduced to the Korean Medical Licensing Examination?
- Correlations between the scores of computerized adaptive testing, paper and pencil tests, and the Korean Medical Licensing Examination
- Presidential address: Preparing for permanent test centers and computerized adaptive testing
- Post-hoc simulation study of computerized adaptive testing for the Korean Medical Licensing Examination