World J Mens Health.
2015 Dec;33(3):202-208. 10.5534/wjmh.2015.33.3.202.
Long-Term Safety and Longevity of a Mixture of Polymethyl Methacrylate and Cross-Linked Dextran (Lipen-10(R)) after Penile Augmentation: Extension Study from Six to 18 Months of Follow-Up
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea. yang1408@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2405149
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2015.33.3.202
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The goal of this study was to investigate the long-term efficacy and safety of a mixture of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and cross-linked dextran Lipen-10(R) used for penile augmentation under the physical impact generated during sexual intercourse.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
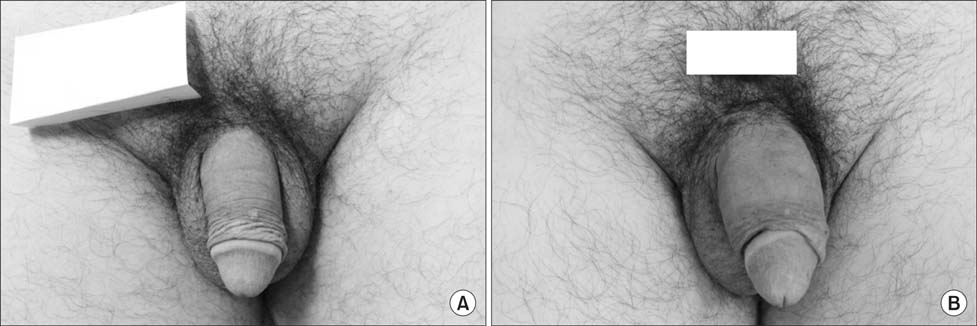
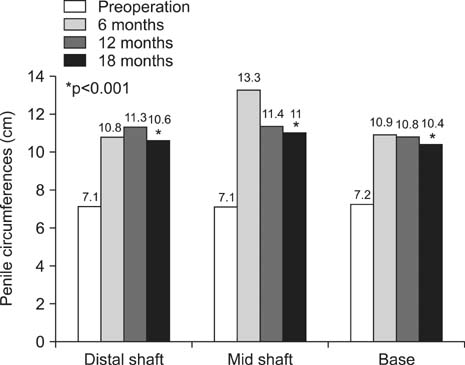
From March 2010 to October 2011, a total of 20 patients with a mean age of 44 years (interquartile range, 20~70 years) who requested penile augmentation participated in this study. Lipen-10(R) filler is a mixture of 75% cross-linked dextran, 15% PMMA, and 10% hypromellose solution. With the patient in the supine position, Lipen-10(R) was injected into the subcutaneous tissue between the dartos fascia and Buck's fascia of the penis using a fanning technique. Penile length and circumference were measured before the procedure and six, 12, and 18 months after the procedure. Values were compared using the Student's t-test and the paired t-test.
RESULTS
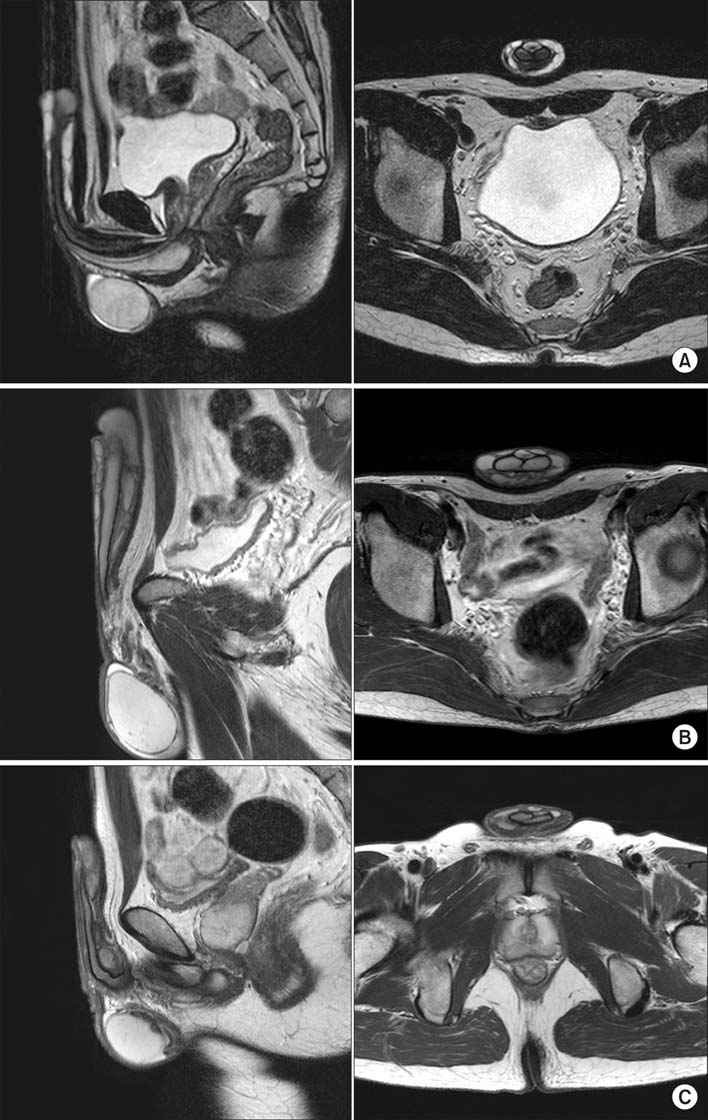
A total of 15 patients completed this study. The increases in circumference and length observed six months after the procedure were found to have been maintained without change at 12 and 18 months of follow-up. At 12 and 18 months of follow-up, no abnormal findings were observed. Pelvic magnetic resonance imaging conducted at 18 months of follow-up showed no trace of the injected filler having migrated to other sites, and the volume was well maintained.
CONCLUSIONS
Lipen-10(R), a mixture of PMMA and cross-linked dextran, showed good durability and tolerability over 18 months of follow-up during which the participants were sexually active.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
New bulking agent for the treatment of vesicoureteral reflux: Polymethylmethacrylate/dextranomer
Sang Woon Kim, Yong Seung Lee, Young Jae Im, Sang Won Han
Investig Clin Urol. 2018;59(3):206-212. doi: 10.4111/icu.2018.59.3.206.
Reference
-
1. Nicolle FV. Use of Zyderm in the aging face. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 1982; 6:193–195.
Article2. Goldberg DJ. Breakthroughs in US dermal fillers for facial soft-tissue augmentation. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2009; 11:240–247.
Article3. Baumann L. Collagen-containing fillers: alone and in combination. Clin Plast Surg. 2006; 33:587–596.
Article4. Rostan E. Collagen fillers. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2007; 15:55–61.
Article5. Monheit GD, Coleman KM. Hyaluronic acid fillers. Dermatol Ther. 2006; 19:141–150.
Article6. Jang MW, Jin BK, Lee SH, Park JH, Ryu JM, Yun SP, et al. Effect of PMMA and cross-linked dextran mixture on biosafety and volume in rat. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2010; 7:57–63.7. Yang DY, Lee WK, Kim SC. Tolerability and efficacy of newly developed penile injection of cross-linked dextran and polymethylmethacrylate mixture on penile enhancement: 6 months follow-up. Int J Impot Res. 2013; 25:99–103.
Article8. Vardi Y, Har-Shai Y, Gil T, Gruenwald I. A critical analysis of penile enhancement procedures for patients with normal penile size: surgical techniques, success, and complications. Eur Urol. 2008; 54:1042–1050.
Article9. Talalaj J, Talalaj S. The strangest human sex, ceremonies and customs. 1st ed. Melbourne: Hill of Content;1994.10. Francoeur R, Perper T, Scherzer N. A descriptive dictionary and atlas of sexology. 1st ed. New York, NY: Greenwood Press;1991.11. Vardi Y, Lowenstein L. Penile enlargement surgery: fact or illusion? Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2005; 2:114–115.12. Son H. Normal penile size and self esteem about penile size of the third decade men in Korea. Korean J Urol. 1999; 40:1037–1042.13. Schwartz BJ. The measurement of castration anxiety and anxiety over loss of love. J Personal. 1955; 24:204–219.
Article14. Reinsch JM, Beasley R. The kinsey institute new report on sex: what you must know to be sexually literate. 1st ed. New York, NY: St Martin's press;1990. p. 43–65.15. Nguyen A, Pasyk KA, Bouvier TN, Hassett CA, Argenta LC. Comparative study of survival of autologous adipose tissue taken and transplanted by different techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990; 85:378–386.
Article16. Vardi Y, Gruenwald I. The status of penile enhancement procedures. Curr Opin Urol. 2009; 19:601–605.
Article17. Wassermann RJ, Greenwald DP. Debilitating silicone granuloma of the penis and scrotum. Ann Plast Surg. 1995; 35:505–509.
Article18. Comper WD, Laurent TC. Physiological function of connective tissue polysaccharides. Physiol Rev. 1978; 58:255–315.
Article19. Artefill prescribing information [Internet]. Sandiego, CA: Artes Medical, Inc;c2007. cited 2013 Jan 7. Available from: http://www.artefil.com.20. Xiaoling F, Yi C, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Li W, Yang M, et al. Analysis of the complications induced by polyacrylamide hydrogel injection. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 114:261–262.
Article21. Lemperle G, Morhenn V, Charrier U. Human histology and persistence of various injectable filler substances for soft tissue augmentation. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2003; 27:354–366.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pedicle Screw Loosening Treated by Modified Transpedicular Screw Augmentation with Polymethylmethacrylate
- Usefulness of Frontal Sinus Reconstruction Using Polymethyl-methacrylate
- PMMA microspheres (ARTECOLL(R)) injection for nasal ridge augmentation in the orthognathic surgery
- New bulking agent for the treatment of vesicoureteral reflux: Polymethylmethacrylate/dextranomer
- A biomechanical study on diaphyseal defect filled with polymethylmethacrylate