J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2018 Feb;59(2):117-122. 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.2.117.
Comparison of Osmolarity of Various Artificial Tears Products Commercially Available in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. crisim@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2403803
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2018.59.2.117
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the osmolarity of various artificial tear products commercially available in the Republic of Korea.
METHODS
The osmolarity of the artificial tears was analyzed using TearLab® and Multi-Osmetteâ„¢. We divided the artificial tear products into five groups, including hypo-osmolar 0.18% sodium hyaluronate (HA), iso-osmolar 0.1%, 0.15%, 0.3% HA, and 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC), and measured three products per group.
RESULTS
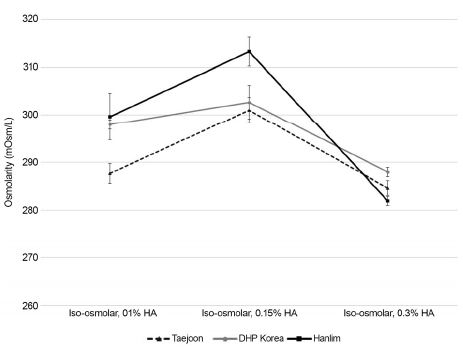
Among the 12 products of iso-osmolar artificial tears, there were seven products (58.3%) < 300 mOsm/L, and among the three products of hypo-osmolar artificial tears, there were two products (66.6%) < 150 mOsm/L. A significant difference (p < 0.05) was observed between the iso-osmolar 0.3% HA group and the hypo-osmolar 0.18% HA group. In the iso-osmolar 0.1% HA and 0.15% HA, the difference between the products in each group was approximately 12 mOsm/L, and the CMC group had the smallest deviation among products, which was close to 300 mOsm/L. There was a significant difference of 305.57 ± 6.38 mOsm/L in the iso-osmolar 0.15% HA group, 293.44 ± 8.71 mOsm/L in the 0.1% HA group, and 285.67 ± 3.67 mOsm/L in the 0.3% HA group (p < 0.001). There was no significant difference in osmolarity between the iso-osmolar products containing HA and CMC (p = 0.117).
CONCLUSIONS
There was a difference in osmolarity between the published and actual measured values of commercial artificial tears, and there was a difference in osmolality depending on the content of HA and the manufacturer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. The definition. report of the Definition and Classification Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (2007). Ocul Surf. 2007; 5:75–92.2. Luo L, Li DQ, Corrales RM, Pflugfelder SC. Hyperosmolar saline is a proinflammatory stress on the mouse ocular surface. Eye Contact Lens. 2005; 31:186–193.
Article3. Li DQ, Chen Z, Song XJ, et al. Stimulation of matrix metalloproteinases by hyperosmolarity via a JNK pathway in human corneal epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45:4302–4311.
Article4. Luo L, Li DQ, Pflugfelder SC. Hyperosmolarity-induced apoptosis in human corneal epithelial cells is mediated by cytochrome c and MAPK pathways. Cornea. 2007; 26:452–460.
Article5. Tomlinson A, Khanal S, Ramaesh K, et al. Tear film osmolarity: determination of a referent for dry eye diagnosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47:4309–4315.
Article6. Lemp MA, Bron AJ, Baudouin C, et al. Tear osmolarity in the diagnosis and management of dry eye disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 151:792–798.
Article7. Versura P, Profazio V, Campos EC. Performance of tear osmolarity compared to previous diagnostic teasts for dry eye diseases. Curr Eye Res. 2010; 35:553–564.8. Versura P, Campos EC. TearLab(R) Osmolarity System for diagnosing dry eye. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2013; 13:119–129.9. Sullivan BD, Whitmer D, Nichols KK, et al. An objective approach to dry eye disease severity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:6125.
Article10. Suzuki M, Massingale ML, Ye F, et al. Tear osmolarity as a biomarker for dry eye disease severity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:4557–4561.
Article11. Aragona P, Di Stefano G, Ferreri F, et al. Sodium hyaluronate eye drops of different osmolarity for the treatment of dry eye in Sjögren's syndrome patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:879–884.12. Bitton E, Perugino C, Charette S. Comparison of ocular lubricant osmolalities. Optom Vis Sci. 2017; 94:694–699.
Article13. Kim JH, Kim JH, Nam WH, et al. Oral alcohol administration disturbs tear film and ocular surface. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:965–971.
Article14. Behrens A, Doyle JJ, Stern L, et al. Dysfunctional tear syndrome: a Delphi approach to treatment recommendations. Cornea. 2006; 25:900–907.15. Management and. report of the Management and Therapy Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (2007). Ocul Surf. 2007; 5:163–178.16. Milner MS, Beckman KA, Luchs JI, et al. Dysfunctional tear syndrome: dry eye disease and associated tear film disorders - new strategies for diagnosis and treatment. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2017; 27:Suppl 1. 3–47.17. Papa V, Aragona P, Russo S, et al. Comparison of hypotonic and isotonic solutions containing sodium hyaluronate on the symptomatic treatment of dry eye patients. Ophthalmologica. 2001; 215:124–127.
Article18. Li Y, Cui L, Lee HS, et al. Comparison of 0.3% hypotonic and isotonic sodium hyaluronate eye drops in the treatment of experimental dry eye. Curr Eye Res. 2017; 42:1108–1114.
Article19. Benelli U, Nardi M, Posarelli C, Albert TG. Tear osmolarity measurement using the TearLab Osmolarity System in the assessment of dry eye treatment effectiveness. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2010; 33:61–67.
Article20. Cömez AT, Tufan HA, Kocabıyık O, Gencer B. Effects of lubricating agents with different osmolalities on tear osmolarity and other tear function tests in patients with dry eye. Curr Eye Res. 2013; 38:1095–1103.21. Dutescu RM, Panfil C, Schrage N. Osmolarity of prevalent eye drops, side effects, and therapeutic approaches. Cornea. 2015; 34:560–566.
Article22. Tomlinson A, McCann LC, Pearce EI. Comparison of human tear film osmolarity measured by electrical impedance and freezing point depression techniques. Cornea. 2010; 29:1036–1041.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Topical Cyclosporine 0.05% on Tear Osmolarity for Dry Eye Syndrome
- The Comparison of Viscosity-dependent Distribution of Tear Film after Dropping of Three Artificial Tears
- Evaluation and Categorization of Commercially Prepared Enteral Nutrition Formulas
- Comparative Evaluation of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Immunoassay and Tear Osmolarity Measurement for Diagnosing Severity of Dry Eye Disease
- Inflammatory Cytokine and Osmolarity Changes in the Tears of Dry Eye Patients Treated with Topical 1% Methylprednisolone