Cancer Res Treat.
2015 Oct;47(4):549-554. 10.4143/crt.2014.362.
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation Status in the Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Lessons Learned
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand.
- 3Eli Lilly and Company, Taipei, Taiwan.
- 4Eli Lilly and Company, Shanghai, China.
- 5Eli Lilly Interamerica Inc., Buenos Aires, Argentina. orlando_mauro@lilly.com
- KMID: 2403370
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.362
Abstract
- Advances in oncology research have led to identification of tumor-specific biomarkers, some of which are important predictive indicators and ideal targets for novel therapeutics. One such biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Patients with NSCLC who harbor an activating EGFR mutation show a more favorable response to treatment with an EGFR inhibitor, such as gefitinib, erlotinib, or afatinib, than to chemotherapy. The prevalence of EGFR mutations in East Asian patients is higher than that in other populations, and in some clinical settings, patients have been treated with EGFR inhibitors based on clinicopathologic characteristics with no information on EGFR status. However, based on results from a series of studies in which East Asian patients with advanced non-squamous NSCLC were treated with EGFR inhibitors alone or in combination with standard chemotherapy, this may not be the best practice because EGFR mutation status was found to be a key predictor of outcome. Data from these studies highlight the necessity of EGFR testing in determining the most suitable treatment for patients with advanced or metastatic NSCLC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Brega E, Brandao G. Non-small cell lung carcinoma biomarker testing: the pathologist's perspective. Front Oncol. 2014; 4:182.
Article2. Ulivi P, Zoli W, Capelli L, Chiadini E, Calistri D, Amadori D. Target therapy in NSCLC patients: relevant clinical agents and tumour molecular characterisation. Mol Clin Oncol. 2013; 1:575–81.
Article3. Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE, Adjei AA. Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008; 83:584–94.
Article4. Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Beasley MB, Chitale DA, Dacic S, Giaccone G, et al. Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors: guideline from the College of American Pathologists, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Association for Molecular Pathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013; 137:828–60.
Article5. Miller VA, Kris MG, Shah N, Patel J, Azzoli C, Gomez J, et al. Bronchioloalveolar pathologic subtype and smoking history predict sensitivity to gefitinib in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:1103–9.
Article6. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2129–39.
Article7. Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:2380–8.
Article8. Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010; 11:121–8.
Article9. Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as firstline treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13:239–46.10. Yang JC, Hirsh V, Schuler M, Yamamoto N, O'Byrne KJ, Mok TS, et al. Symptom control and quality of life in LUX-Lung 3: a phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin/pemetrexed in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:3342–50.
Article11. Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:735–42.
Article12. Garassino MC, Borgonovo K, Rossi A, Mancuso A, Martelli O, Tinazzi A, et al. Biological and clinical features in predicting efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anticancer Res. 2009; 29:2691–701.13. Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:947–57.
Article14. Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S, Srinivasan S, Tsai CM, Khoa MT, et al. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol. 2014; 9:154–62.
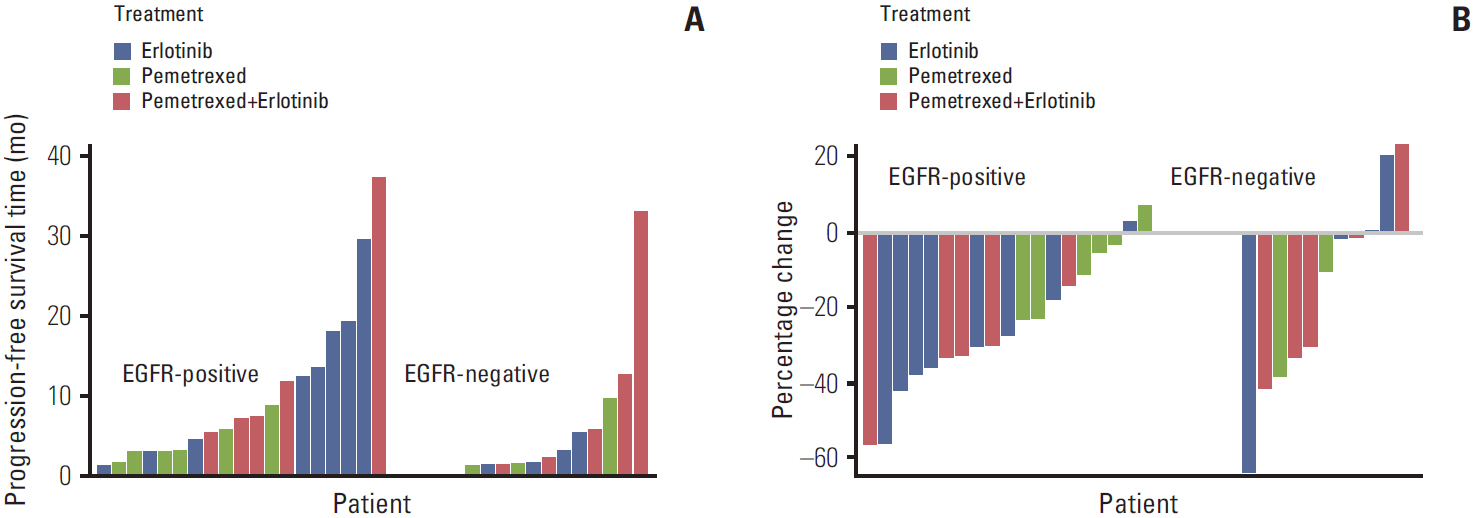
Article15. Lee DH, Lee JS, Kim SW, Rodrigues-Pereira J, Han B, Song XQ, et al. Three-arm randomised controlled phase 2 study comparing pemetrexed and erlotinib to either pemetrexed or erlotinib alone as second-line treatment for never-smokers with nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2013; 49:3111–21.
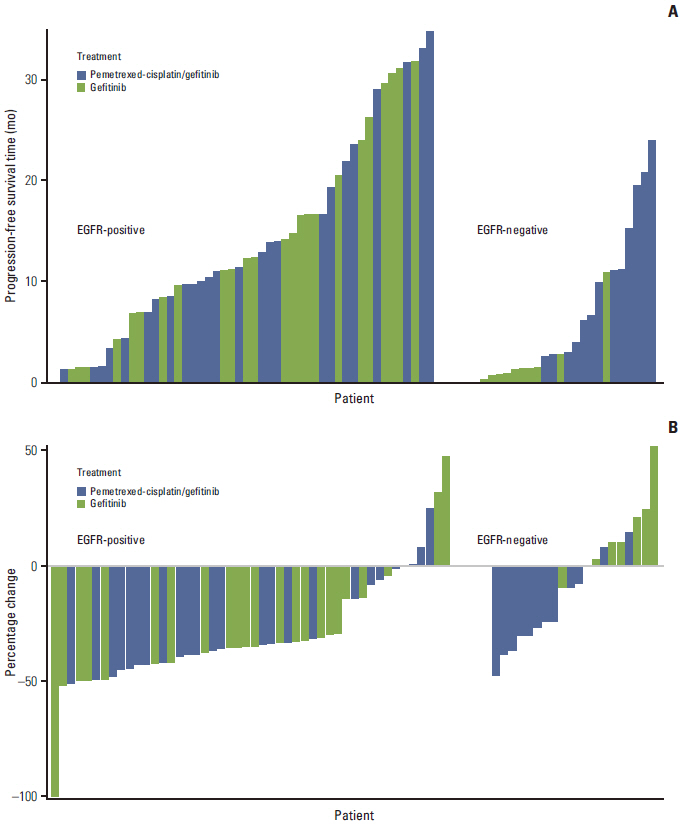
Article16. Yang JC, Kang JH, Mok T, Ahn MJ, Srimuninnimit V, Lin CC, et al. First-line pemetrexed plus cisplatin followed by gefitinib maintenance therapy versus gefitinib monotherapy in East Asian patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: a randomised, phase 3 trial. Eur J Cancer. 2014; 50:2219–30.
Article17. Lee DH, Lee JS, Wang J, Hsia TC, Wang X, Kim J, et al. Pemetrexed-erlotinib, pemetrexed alone, or erlotinib alone as second-line treatment for East Asian and non-East Asian never-smokers with locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer: exploratory subgroup analysis of a phase II trial. Cancer Res Treat. 2014; Nov. 24. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.051.
Article18. Ahn MJ, Yang JC, Liang J, Kang JH, Xiu Q, Chen YM, et al. Randomized phase II trial of first-line treatment with pemetrexed-cisplatin, followed sequentially by gefitinib or pemetrexed, in East Asian, never-smoker patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2012; 77:346–52.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ovarian Metastasis from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Responding to Erlotinib
- Carcinoembryonic antigen and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in non-small cell lung cancer definited by immunohistoc- hemical stain
- A Case of Favorable Responses after Gefitinib in a Patient with EGFR Mutated Adenosquamous Lung Carcinoma
- Does the efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor differ according to the type of EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer?
- Discordance of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation between Brain Metastasis and Primary Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer