Ann Lab Med.
2018 Mar;38(2):172-175. 10.3343/alm.2018.38.2.172.
Bone Marrow Involvement of Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Large B-Cell Lymphoma in a Patient with Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. borae.park@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Oncology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2403365
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2018.38.2.172
Abstract
- No abstract available.
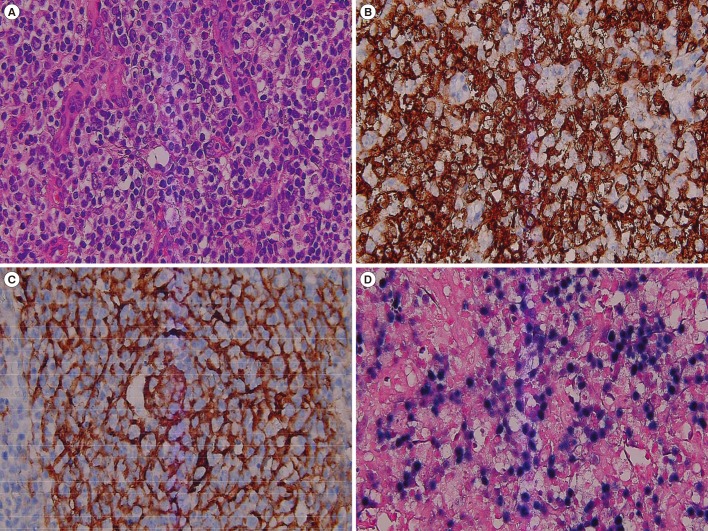
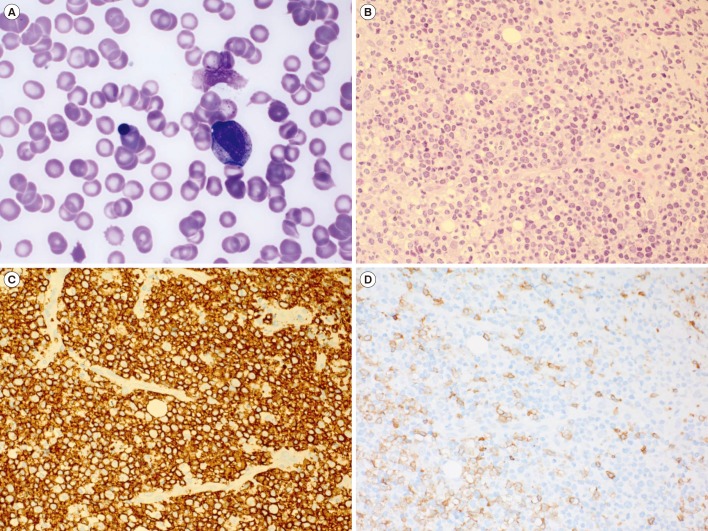
Figure
Reference
-
1. Swerdlow S, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2008. p. 309–311.2. Hawley RC, Cankovic M, Zarbo RJ. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma with supervening Epstein-barr virus-associated large B-cell lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006; 130:1707–1711. PMID: 17076535.3. Xu J, Tang Y, Zhao S, Zhang W, Xiu Y, Liu T, et al. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma with coexisting plasma cell myeloma: a case report and review of the literature. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2015; 235:283–288. PMID: 25816919.4. Foucar K, Reichard K, Czuchlewski D, editors. Bone marrow pathology. 3rd ed. Chicago: American Society for Clinical Pathology;2010. p. 557–577.5. Grogg KL, Morice WG, Macon WR. Spectrum of bone marrow findings in patients with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2007; 137:416–422. PMID: 17488486.6. Zettl A, Lee SS, Rudiger T, Starostik P, Marino M, Kirchner T, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders in angloimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002; 117:368–379. PMID: 11888076.7. Choi YH, Kim HS, Nam SB, Kang HJ, Na II, Yang SH, et al. A case of Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse, large B-cell lymphoma after angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Korean J Hematol. 2008; 43:174–178.8. Zhou Y, Rosenblum MK, Dogan A, Jungbluth AA, Chiu A. Cerebellar EBV-associated diffuse large B cell lymphoma following angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma. J Hematop. 2015; 8:235–241. PMID: 27559423.9. Kasahara H, Kakimoto T, Saito H, Akuta K, Yamamoto K, Ujiie H, et al. Successful treatment with rituximab for angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Leuk Res Rep. 2013; 2:36–38. PMID: 24371775.10. Delfau-Larue MH, de Leval L, Joly B, Plonquet A, Challine D, Parrens M, et al. Targeting intratumoral B cells with rituximab in addition to CHOP in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. A clinicobiological study of the GELA. Haematologica. 2012; 97:1594–1602. PMID: 22371178.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-positive Diffuse, Large B-cell Lymphoma after Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Occurring in Thyroid Gland
- Persistent Anemia in a Patient with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma: Pure Red Cell Aplasia Associated with Latent Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Bone Marrow
- Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma in a Patient with Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma
- A Case of Cutaneous Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in an Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma