Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2018 Jan;20(1):26-30. 10.14253/acn.2018.20.1.26.
Applicability of the digital instrument to improve the reproducibility of motor unit number index
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. icandr@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2403218
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2018.20.1.26
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
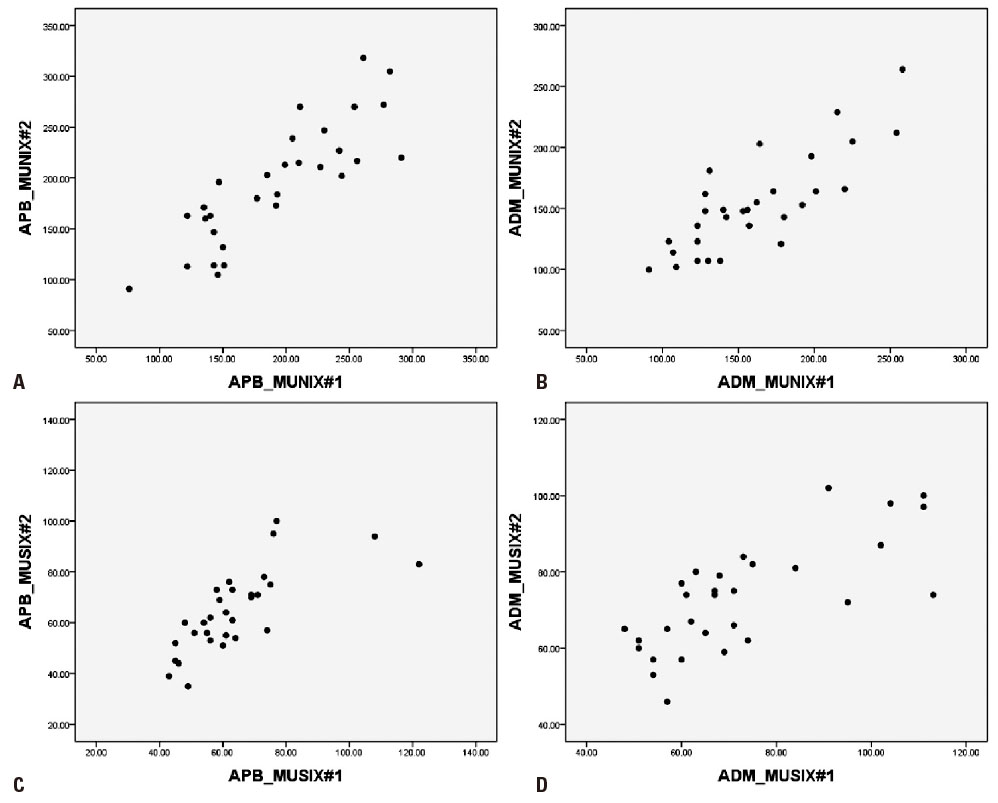
The motor unit number index (MUNIX) and motor unit size index (MUSIX) refer to the electrophysiological measurement of the motor units using the surface electromyographic interference pattern (SIP) recorded during graded muscle contraction. In order to improve the reliability and reproducibility of MUNIX by the systematization of the graded muscle contractions, we applied a digital hand instrument to the procedure of recording SIP signals.
METHODS
We tested the applicability of the digital instrument in the MUNIX technique by assessing the mean values and the reproducibility of the MUNIX involving the abductor pollicis brevis (APB) and the abductor digiti minimi (ADM) muscles in 30 healthy adults.
RESULTS
The digital dynamometer was successfully applied to the MUNIX measurements of the APB and ADM muscles, and showed high reproducibility across trials.
CONCLUSIONS
Application of the digital instrument would be useful in improving the reliability and reproducibility of MUNIX.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nandedkar SD, Nandedkar DS, Barkhaus PE, Stalberg EV. Motor unit number index (MUNIX). IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2004; 51:2209–2211.
Article2. Ahn SW, Kim SH, Kim JE, Kim SM, Kim SH, Park KS, et al. Reproducibility of the motor unit number index (MUNIX) in normal controls and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 42:808–813.
Article3. Nandedkar SD, Barkhaus PE, Stålberg EV. Motor unit number index (MUNIX): principle, method, and findings in healthy subjects and in patients with motor neuron disease. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 42:798–807.
Article4. Neuwirth C, Nandedkar S, Stålberg E, Barkhaus PE, Carvalho Md, Furtula J, et al. Motor Unit Number Index (MUNIX): reference values of five different muscles in healthy subjects from a multi-centre study. Clin Neurophysiol. 2011; 122:1895–1898.
Article5. Nandedkar SD, Barkhaus PE, Stålberg EV. Reproducibility of MUNIX in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve. 2011; 44:919–922.
Article6. Ahn SW, Kim KW, Kim JE, Shin JY, Kim DG, Lee KW, et al. Motor unit number index (MUNIX) in the orbicularis oculi muscle of healthy subjects. Muscle Nerve. 2015; 51:197–200.
Article7. Bromberg MB. Motor unit estimation: reproducibility of the spike-triggered averaging technique in normal and ALS subjects. Muscle Nerve. 1993; 16:466–471.
Article8. Felice KJ. Thenar motor unit number estimates using the multiple point stimulation technique: reproducibility studies in ALS patients and normal subjects. Muscle Nerve. 1995; 18:1412–1416.
Article9. Lomen-Hoerth C, Olney RK. Comparison of multiple point and statistical motor unit number estimation. Muscle Nerve. 2000; 23:1525–1533.
Article10. Simmons Z, Epstein DK, Borg B, Mauger DT, Kothari MJ, Shefner JM. Reproducibility of motor unit number estimation in individual subjects. Muscle Nerve. 2001; 24:467–473.
Article11. Olney RK, Yuen EC, Engstrom JW. Statistical motor unit number estimation: reproducibility and sources of error in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve. 2000; 23:193–197.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Motor Unit Number Estimation of the Thenar Muscles
- Motor Unit Number Estimation of Normal Thenar Muscle
- Motor Unit Numbers Estimation in Abductor Pollicis Brevis Muscle of Normal Adult
- Motor Unit Number Estimation in Thenar Muscles of the Hemiplegic Patients
- Effects of Temperature on Motor Unit Action Potentials