J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2018 Jan;56(1):50-55. 10.4047/jkap.2018.56.1.50.
Complete denture of a skeletal class III patient with occlusal scheme in consideration: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Republic of Korea. paek217@gmail.com
- KMID: 2402987
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2018.56.1.50
Abstract
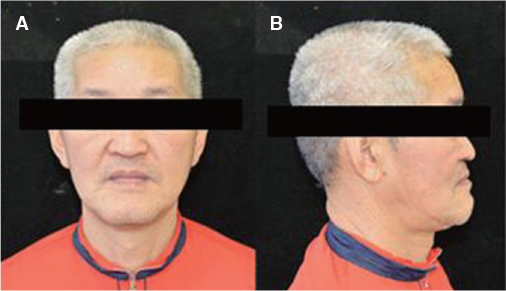
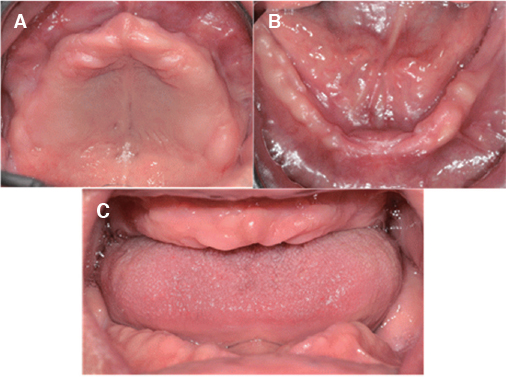
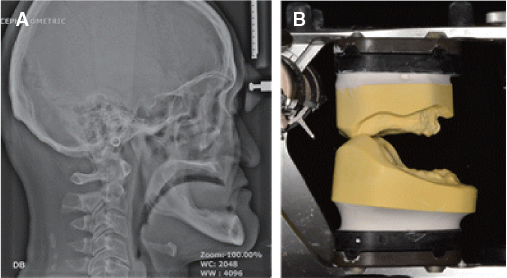
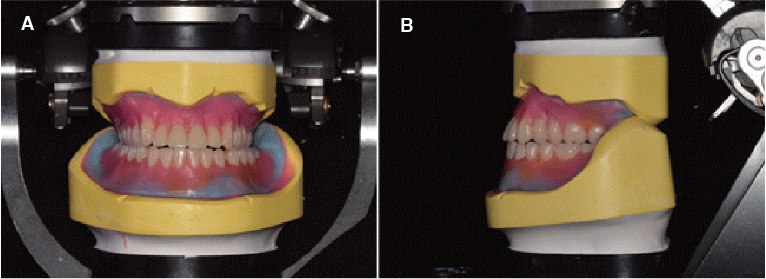
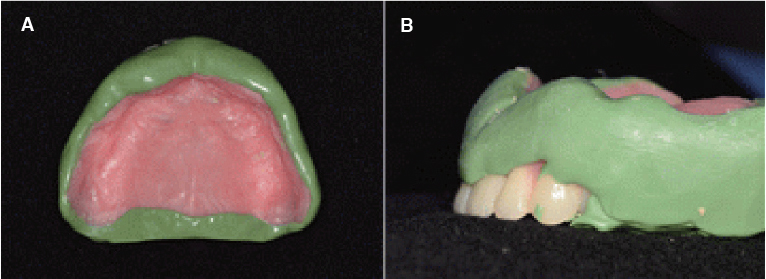
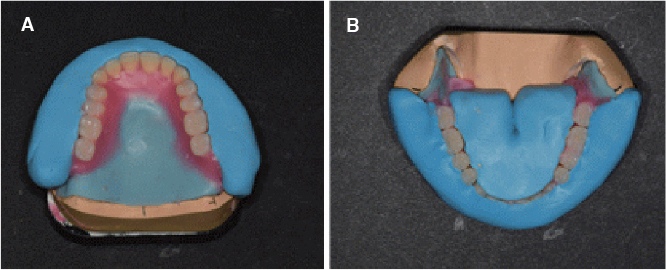
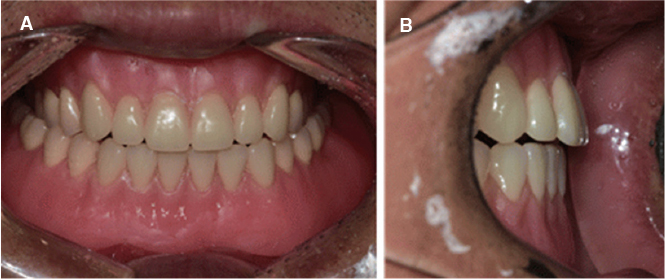
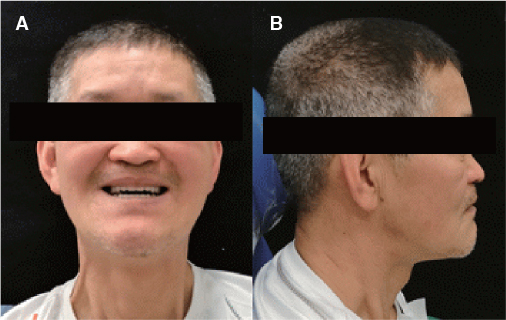
- Occlusal disharmony is frequently observed among edentulous patients. When artificial teeth come into contact, the unfavorable displacing force may lead to the discomfort, mucosal trauma, or even neuromuscular alterations and emotional disturbances. An optimal occlusal scheme is a critical factor for successful complete dentures. For this case, an edentulous patient with significant interarch size discrepancy due to mandibular prognathism contributing to inadequate function of dentures was treated with complete dentures. The posterior cross-bite tooth setup for compensating the abnormal jaw relations provided a stable and retentive complete denture prosthesis, which was considered adequate by both patient and dentist.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ministry of Health & Welfare. 2010 Korean national oral health survey. Seoul: Ministry of Health & Welfare;2010. p. 518–525.2. Jacobson TE, Krol AJ. A contemporary review of the factors involved in complete denture retention, stability, and support. Part I: Retention. J Prosthet Dent. 1983; 49:5–15.
Article3. Atashrazm P, Dashti MH. The prevalence of occlusal disharmony and its associated causes in complete dentures. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2009; 10:E041–E048.
Article4. McGarry TJ, Nimmo A, Skiba JF, Ahlstrom RH, Smith CR, Koumjian JH. The American College of Prosthodontics. Classification system for complete edentulism. J Prosthodont. 1999; 8:27–39.
Article5. LaVere AM, Freda AL. Artificial tooth arrangement for prognathic patients. J Prosthet Dent. 1972; 28:650–654.
Article6. Gysi A. Special teeth for cross-bite cases. Dent Dig. 1927; 33:167–171.7. Pietrokovski J, Massler M. Alveolar ridge resorption following tooth extraction. J Prosthet Dent. 1967; 17:21–27.
Article8. Kawano F, Nagao K, Inoue S, Matsumoto N. Influence of the buccolingual position of artificial posterior teeth on the pressure distribution on the supporting tissue under a complete denture. J Oral Rehabil. 1996; 23:456–463.
Article9. Hickey JC, Zarb GA. Boucher's prosthodontic treatment for edentulous patients. 8th ed: CV Mosby;1980. p. 339.10. Boucher CO. Complete denture prosthodontics-the state of art. J Prosthet Dent. 1975; 34:372–383.11. Misch CE. Dental implant prosthetics. 2nd ed. Elsevier Mosby;2015. p. 954–956.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Complete denture fabrication of a skeletal class III edentulous patient considering anterior neutral zone: a case report
- Evaluation of suitability and stability in a skeletal Class III complete denture patient with flabby tissue: A case report
- Conversion of implant overdenture to an implant assisted removable partial denture in maxilla: case report
- A study on the vertical dysplasia in the skeletal class iii malocclusion
- Full arch rehabilitation using a digital diagnostic model in a patient with skeletal class III malocclusion