Ann Surg Treat Res.
2018 Feb;94(2):88-93. 10.4174/astr.2018.94.2.88.
Evaluation of intradermal absorbable and mattress sutures to close pilonidal sinus wounds with Limberg flap: a prospective randomized comparative study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Dr. Lutfi Kirdar Kartal Research and Education Hospital, Department of General Surgery, Istanbul, Turkey. hasan.sikar@me.com
- KMID: 2402851
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2018.94.2.88
Abstract
- PURPOSE
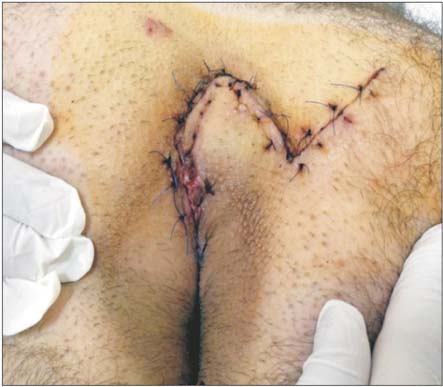
We aimed to compare skin closure techniques, standard (intermittent mattress) and continuous subcuticular sutures, following Limberg flap procedure.
METHODS
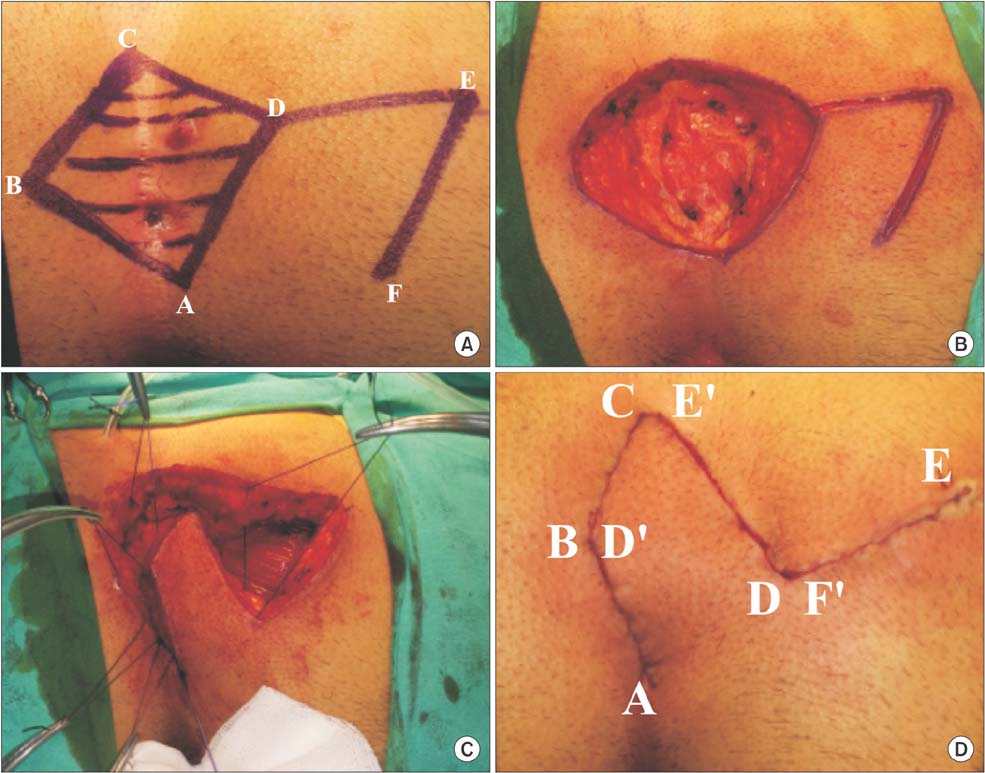
From July 2013 to July 2015, 92 patients with sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease were prospectively randomized into 2 groups consisting of 46 patients for both. Patients underwent sinus excision and closure with Limberg flap; continuous subcuticular suture was used in subcuticular group (SG) and intermittent mattress sutures were used in mattress group (MG) for skin closure. Characteristics of patients, features of pilonidal disease, macerations, infections, wound dehiscence, flap necrosis, operation time, time of drain removal, wound complications, early recurrences, and time till return to work were compared between the 2 groups.
RESULTS
There was no statistical difference between groups per sex, age, body mass index, smoking, number of sinuses, depth of intergluteal sulcus, distance of incision to anus, volume of extracted tissue, number of hair follicles per cm2, recurrence, operation, and mean follow-up time. Two patients showed signs of wound complications (4.4%) in SG, whereas 8 cases (17.4%) showed signs in MG (P < 0.05). One patient in SG had surgical site infection and required antibiotics (2.2%), where as there were 6 cases treated in MG (13.0%) (P < 0.05). Removal of drain tube, and time till return to work rates are lower for SG than MG (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, surgical procedures which include Limberg flap method and subcuticular closure may reduce infection and maceration rates. Future studies are needed to achieve greater detailed evaluation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Inverse ‘D’ incision technique in treatment of pilonidal sinus disease; excision with minimal tissue loss, closure without tension and lateral location of the suture line
Sami Dogan, Fuat Cetin, Emin Gurleyik
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019;97(5):261-265. doi: 10.4174/astr.2019.97.5.261.
Reference
-
1. Can MF, Sevinc MM, Yilmaz M. Comparison of Karydakis flap reconstruction versus primary midline closure in sacroco ccygeal pilonidal disease: results of 200 military service members. Surg Today. 2009; 39:580–586.2. Kaser SA, Zengaffinen R, Uhlmann M, Glaser C, Maurer CA. Primary wound closure with a Limberg flap vs. secondary wound healing after excision of a pilo nidal sinus: a multicentre randomised controlled study. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2015; 30:97–103.3. Chintapatla S, Safarani N, Kumar S, Haboubi N. Sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus: historical review, pathological insight and surgical options. Tech Coloproctol. 2003; 7:3–8.4. Fazeli MS, Adel MG, Lebaschi AH. Com parison of outcomes in Z-plasty and delayed healing by secondary intention of the wound after excision of the sacral pilo nidal sinus: results of a randomized, clinical trial. Dis Colon Rectum. 2006; 49:1831–1836.5. Cihan A, Ucan BH, Comert M, Cesur A, Cakmak GK, Tascilar O. Superiority of asym metric modified Limberg flap for sur gical treatment of pilonidal disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 2006; 49:244–249.6. Akinci OF, Bozer M, Uzunkoy A, Duzgun SA, Coskun A. Incidence and aetiological fac tors in pilonidal sinus among Turkish soldiers. Eur J Surg. 1999; 165:339–342.7. Milone M, Musella M, Maietta P, Bianco P, Taffuri C, Salvatore G, et al. Intradermal ab sor bable sutures to close pilonidal sinus wounds: a safe closure method? Surg Today. 2014; 44:1638–1642.8. Khan PS, Hayat H, Hayat G. Limberg flap versus primary closure in the treatment of primary sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease; a randomized clinical trial. Indian J Surg. 2013; 75:192–194.
Article9. Dass TA, Zaz M, Rather A, Bari S. Elliptical exci sion with midline primary closure ver sus rhomboid excision with limberg flap reconstruction in sacrococcygeal piloni dal disease: a prospective, randomized study. Indian J Surg. 2012; 74:305–308.10. Zorlu M, Sahiner IT, Zobacı E, Kocak C, Yastı AC, Dolapcı M. Early results with the Mutaf technique: a novel off-midline approach in pilonidal sinus surgery. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2016; 90:265–271.
Article11. Altintoprak F, Dikicier E, Arslan Y, Ozkececi T, Akbulut G, Dilek ON. Compa ri sion of the Limberg flap with the V-Y flap technique in the treatment of pilo nidal disease. J Korean Surg Soc. 2013; 85:63–67.12. Tokac M, Dumlu EG, Aydin MS, Yalcın A, Kilic M. Comparison of modified Limberg flap and Karydakis flap operations in pilonidal sinus surgery: prospective randomized study. Int Surg. 2015; 100:870–877.
Article13. Altintoprak F, Gundogdu K, Ergonenc T, Dikicier E, Cakmak G, Celebi F. Retrospective review of pilonidal sinus patients with early discharge after Limberg flap procedure. Int Surg. 2014; 99:28–34.
Article14. Topgul K, Ozdemir E, Kilic K, Gokbayir H, Ferahkose Z. Long-term results of limberg flap procedure for treatment of pilonidal sinus: a report of 200 cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 2003; 46:1545–1548.15. Cihan A, Mentes BB, Tatlicioglu E, Ozmen S, Leventoglu S, Ucan BH. Modified Limberg flap reconstruction compares favourably with primary repair for pilonidal sinus surgery. ANZ J Surg. 2004; 74:238–242.
Article16. Jamal A, Shamim M, Hashmi F, Qureshi MI. Open excision with secondary healing versus rhomboid excision with Limberg transposition flap in the management of sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease. J Pak Med Assoc. 2009; 59:157–160.17. Horwood J, Hanratty D, Chandran P, Billings P. Primary closure or rhomboid excision and Limberg flap for the management of primary sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Colorectal Dis. 2012; 14:143–151.
Article18. Kaya B, Eris C, Atalay S, Bat O, Bulut NE, Mantoglu B, et al. Modified Limberg transposition flap in the treatment of pilonidal sinus disease. Tech Coloproctol. 2012; 16:55–59.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Limberg flap reconstruction for sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus disease with and without acute abscess: Our experience and a review of the literature
- Effect of Modified Rhomboid Excision and Limberg Flap for the Treatment of Recurrent Pilonodal Sinus
- Comparative analysis of the same technique-the same surgeon approach in the surgical treatment of pilonidal sinus disease: a retrospective cohort study
- Comparison of Limberg flap and excision and primary closure of pilonidal sinus disease, in terms of quality of life and complications
- Early results with the Mutaf technique: a novel off-midline approach in pilonidal sinus surgery