J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2017 Sep;24(3):198-202. 10.4184/jkss.2017.24.3.198.
Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Mimicking Myelitis in an Adolescent Patient: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Korea. jrcha@uuh.ulsan.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, School of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 2402834
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2017.24.3.198
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Case report
OBJECTIVES
This study introduces an interesting case of adolescent cervical myelopathy with atypical cervical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings. A differential diagnosis was made, followed by successful surgical treatment. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: A careful differential diagnosis of high signal intensity on T2-weighted cervical MRI is necessary if there is no evidence of cervical stenosis. Recent reports have suggested that the differential diagnosis should be based on a comprehensive analysis of data, including brain MRI, a cerebrospinal fluid examination, and empirical steroid treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
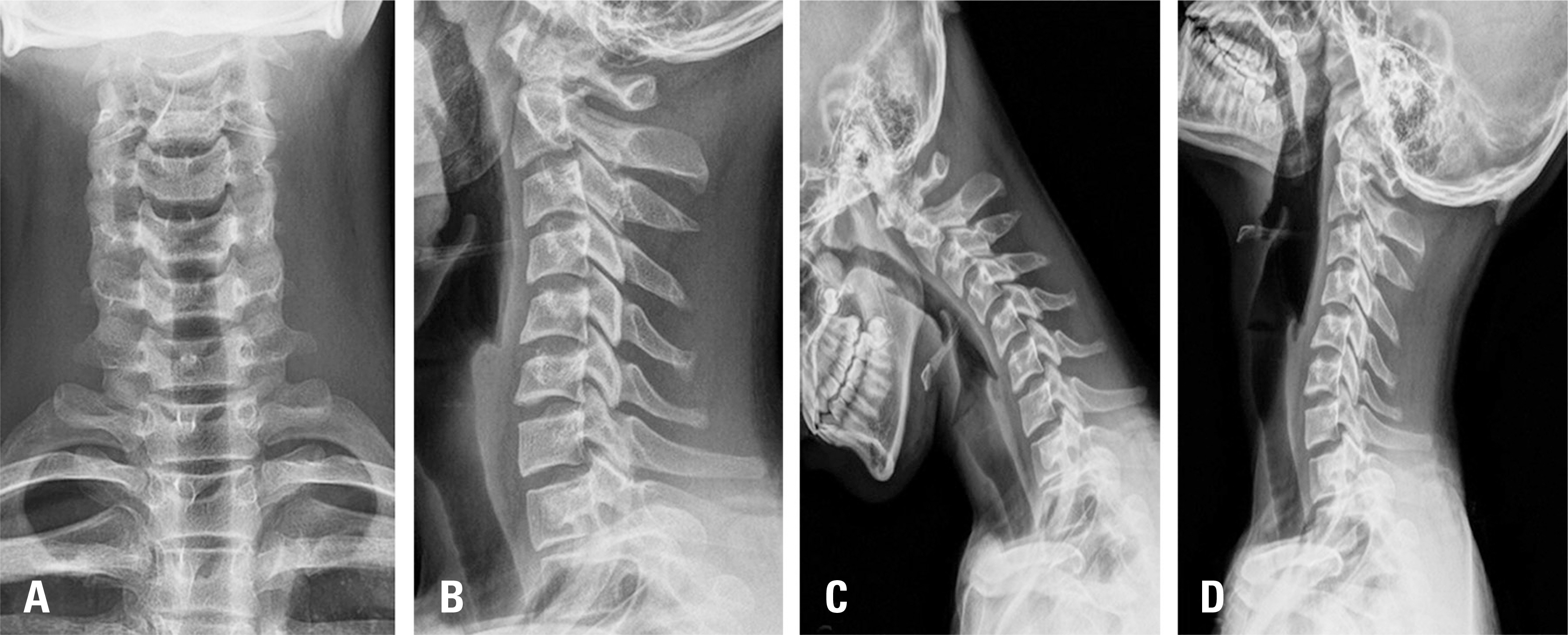
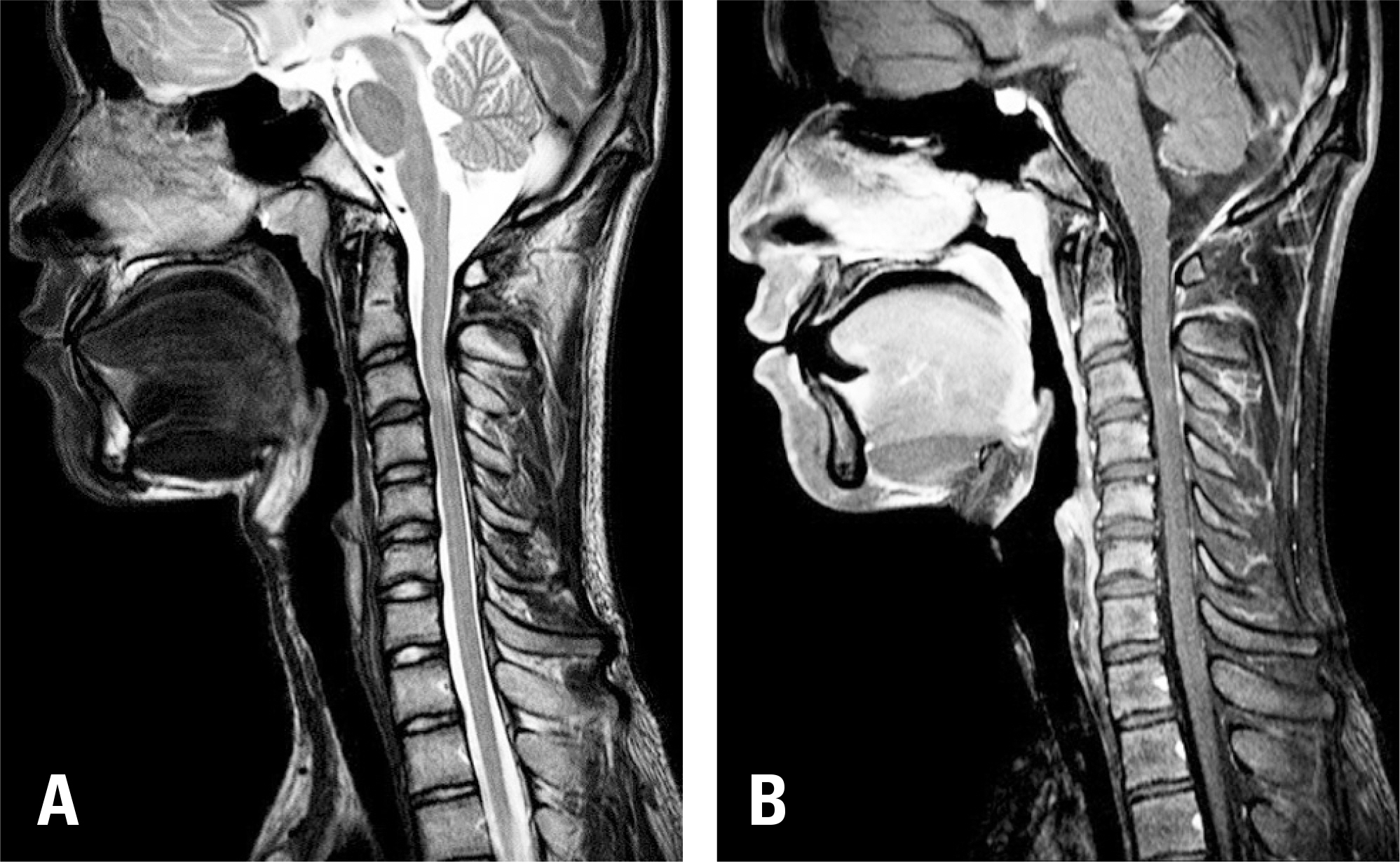
A 17-year-old male patient complained of upper extremity weakness, gait disturbance, and decreased sensation in the upper extremity. Cervical spine MRI findings suggested C3/4 disc herniation, moderate cervical stenosis, and high signal intensity in the spinal cord. A differential diagnosis was made between cervical myelopathy and myelitis.
RESULTS
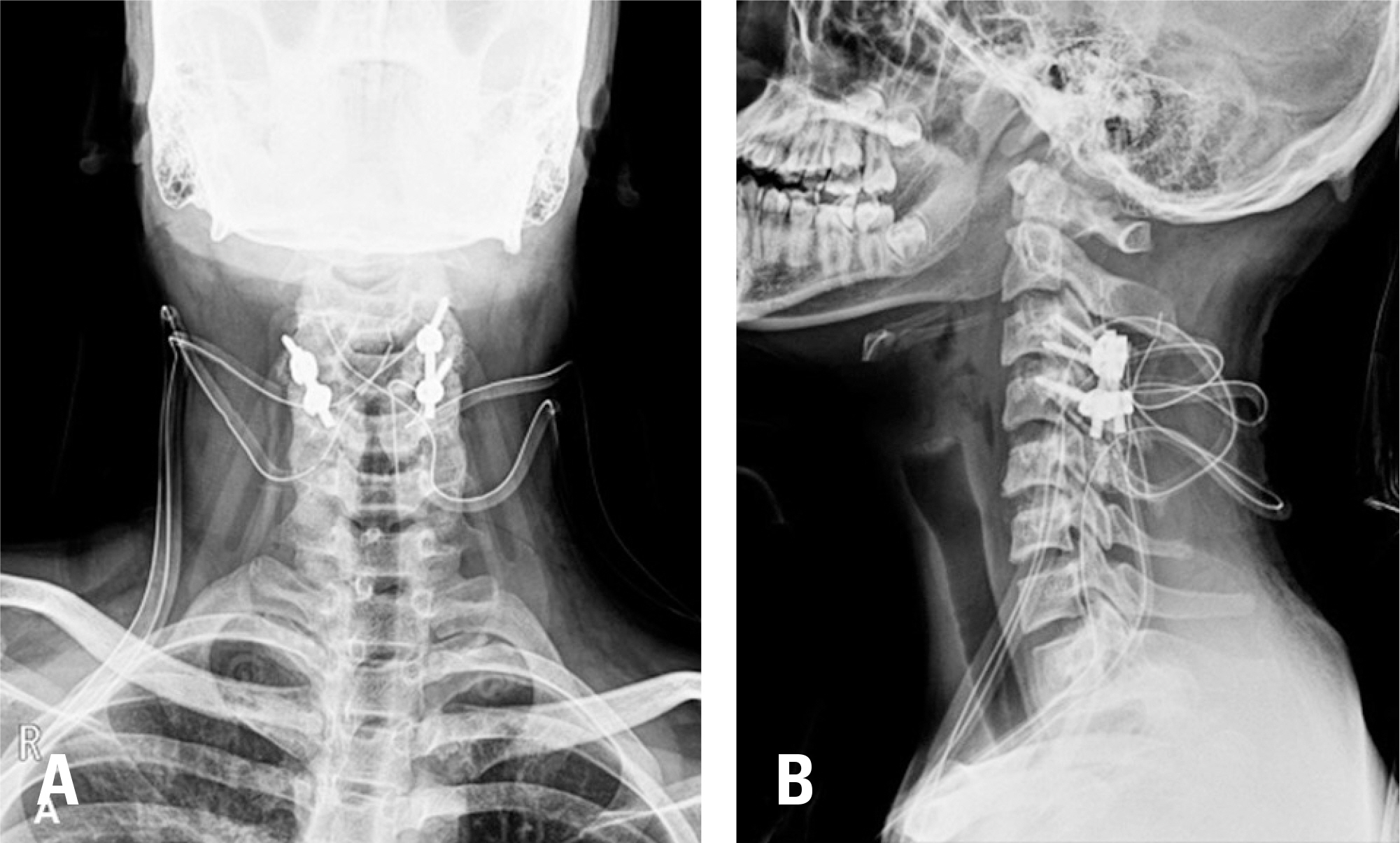
Decompression and posterolateral fusion of C3/4 were performed in a 17-year-old patient with cervical myelopathy without significant cervical stenosis. Postoperatively, upper extremity sensation and weakness and gait disturbance showed improvement, and the Japanese Orthopedic Association score improved to 17 points at 6 months after surgery.
CONCLUSIONS
In patients with cervical myelopathy showing high signal intensity on T2-weighted imaging without evident spinal stenosis, a differential diagnosis should be made between cervical myelopathy and myelitis; surgical decompression can be an effective treatment choice upon the diagnosis of cervical myelopathy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Garfin SR. Cervical degenerative disorders: etiology, presentation, and imaging studies. Instr Course Lect. 2000; 49:335–8.2. Bernhardt M, Hynes RA, Blume HW, et al. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993; 75:119–28.
Article3. Conway BL, Clarke MJ, Kaufmann TJ, et al. Utility of extension views in spondylotic myelopathy mimicking trans-verseMyelitis. Mult scler Relat Disord. 2017; 11:62–4.4. Flanagan EP, Krecke KN, Marsh RW, et al. Specific Pattern of Gadolinium Enhancement in Spondylotic Myelopathy. Ann Neurol. 2014; 76:54–65.
Article5. Paternostro-Sluga T, Grim-Stieger M, Posch M, et al. Reliability and validity of the Medical Research Council (MRC) scale and a modified scale for testing muscle strength in patients with radial palsy. J Rehabil Med. 2008; 40:665–71.
Article6. Anderst W, Donaldson W, Lee J, et al. Cervical Spine Disc Deformation During In Vivo Three-Dimensional Head Movements. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016; 44:1598–612.
Article7. Rua A, Blanco Y, Sepulveda M, et al. Spondylotic myelopathy mimicking myelitis: diagnostic clues by magnetic resonance imaging. Rev Neurol. 2015; 61:499–502.8. Weinshenker BG, Wingerchuk DM, Vukusic S, et al. Neuromyelitis optica IgG predicts relapse after longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Ann Neurol. 2006; 59:566–9.
Article9. Jeffrey DeSanto, Jeffrey S. Ross, Spine infection/inflammation. Radiol Clin North Am. 2011; 49:105–27.10. Jacob A, Weinshenker BG. An Approach to the Diagnosis of Acute Transverse Myelitis. Semin Neurol. 2008; 28:105–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Eosinophilic Myelitis in the Cervical Cord Mimicking Intramedullary Cord Tumor
- A Case of Gait Disturbance due to Chronic Bilateral Subdural Hematoma Mimicking Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
- Surgical Treatment of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
- Bacterial Meningitis Complicated by Myelitis Following Anterior Cervical Spinal Surgery
- Surgical Treatment in Cervical Myelopathy Combined with Flail Arm Syndrome