J Nutr Health.
2017 Dec;50(6):552-564. 10.4163/jnh.2017.50.6.552.
Energy expenditure of physical activity in Korean adults and assessment of accelerometer accuracy by gender
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung 25457, Korea. ekkim@gwnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Physical Education, Korea University, Seoul 02841, Korea.
- KMID: 2401012
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/jnh.2017.50.6.552
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to measure energy expenditure (EE) the metabolic equivalents (METs) of 13 common physical activities by using a portable telemetry gas exchange system (K4b2) and to assess the accuracy of the accelerometer (Actigraph GT3X+) by gender in Korean adults.
METHODS
A total of 109 adults (54 males, 55 females) with normal BMI (body mass index) participated in this study. EE and METs of 13 selected activities were simultaneously measured by the K4b2 portable indirect calorimeter and predicted by the GT3X+ Actigraph accelerometer. The accuracy of the accelerometer was assessed by comparing the predicted with the measured EE and METs.
RESULTS
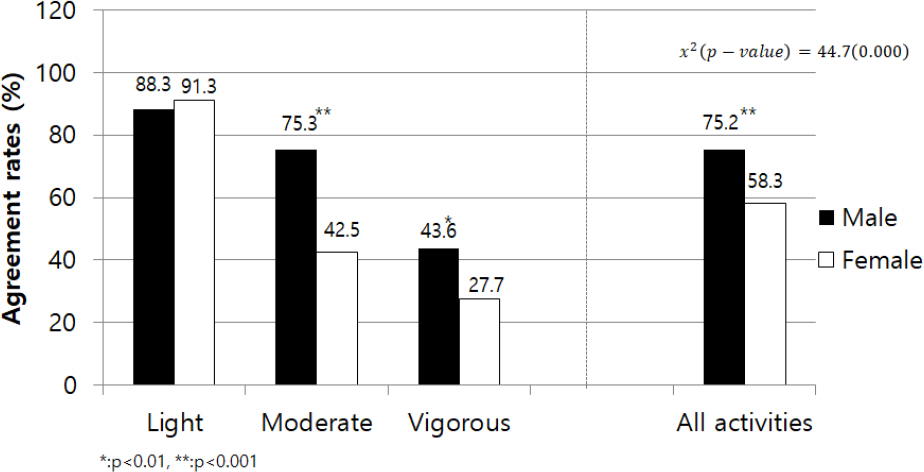
EE (kcal/kg/hr) and METs of treadmill walking (3.2 km/h, 4.8 km/h and 5.6 km/h) and running (6.4 km/h) were significantly higher in female than in male participants (p < 0.05). On the other hand, the accelerometer significantly underestimated the EE and METs for all activities except descending stairs, moderate walking, and fast walking in males as well as descending stairs in females. Low intensity activities had the highest rate of accurate classifications (88.3% in males and 91.3% females), whereas vigorous intensity activities had the lowest rate of accurate classifications (43.6% in males and 27.7% in females). Across all activities, the rate of accurate classification was significantly higher in males than in females (75.2% and 58.3% respectively, p < 0.01). Error between the accelerometer and K4b2 was smaller in males than in females, and EE and METs were more accurately estimated during treadmill activities than other activities in both males and females.
CONCLUSION
The accelerometer underestimated EE and METs across various activities in Korean adults. In addition, there appears to be a gender difference in the rate of accurate accelerometer classification of activities according to intensity. Our results indicate the need to develop new accelerometer equations for this population, and gender differences should be considered.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ministry of Health and Welfare (KR); The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans 2015. Sejong: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2016.2. Mifflin MD, St Jeor ST, Hill LA, Scott BJ, Daugherty SA, Koh YO. A new predictive equation for resting energy expenditure in healthy individuals. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990; 51(2):241–247.
Article3. Henry CJ. Basal metabolic rate studies in humans: measurement and development of new equations. Public Health Nutr. 2005; 8(7A):1133–1152.
Article4. Institute of Medicine Panel on Macronutrients (US). Dietary reference intakes for energy, carbohydrate, fiber, fat, fatty acids, cholesterol, protein, and amino acids. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press;2002.5. Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Leon AS, Jacobs DR Jr, Montoye HJ, Sallis JF, Paffenbarger RS Jr. Compendium of physical activities: classification of energy costs of human physical activities. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1993; 25(1):71–80.
Article6. Lee MY. Preparation in kinesmetrics to develop physical activity guidelines for Korean. Korean Soc Meas Eval Phys Edu Sports Sci. 2011; 13(3):17–31.7. Kim YJ, An HS, Kim EK. Energy expenditure of eight walking activities in normal weight and obese high school students: using an indirect calorimeter and accelerometers worn on ankle and waist. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2017; 23(1):78–93.8. Kim YJ, Wang CS, Kim EK. Measurement of energy expenditure through treadmill-based walking and self-selected hallway walking of college students: using indirect calorimeter and accelerometer. Korean J Community Nutr. 2016; 21(6):520–532.9. Lee MY, Lee H, Choi JY. Error rates of prediction equations and cut-points of Actigraph GT3X+. Korean Soc Meas Eval Phys Edu Sports Sci. 2016; 18(1):17–29.10. Ahn HJ, Lee MC, Lee DT. Validity and energy expenditure of physical activity estimated by accelerometer. J Coaching Dev. 2006; 8(4):69–77.11. Troiano RP, Berrigan D, Dodd KW, Mâsse LC, Tilert T, McDowell M. Physical activity in the United States measured by accelerometer. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008; 40(1):181–188.
Article12. Sirard JR, Trost SG, Pfeiffer KA, Dowda M, Pate RR. Calibration and evaluation of an objective measure of physical activity in preschool children. J Phys Act Health. 2005; 2(3):345–357.
Article13. Freedson PS, Melanson E, Sirard J. Calibration of the Computer Science and Applications, Inc. accelerometer. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998; 30(5):777–781.
Article14. Lee MY. Criterion and convergent validity evidences of an accelerometer and a pedometer. Korean Soc Meas Eval Phys Edu Sports Sci. 2012; 14(2):1–13.15. Crouter SE, Churilla JR, Bassett DR Jr. Estimating energy expenditure using accelerometers. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006; 98(6):601–612.
Article16. Sasaki JE, John D, Freedson PS. Validation and comparison of ActiGraph activity monitors. J Sci Med Sport. 2011; 14(5):411–416.
Article17. Kim DY, Jeon SH, Kang SY, Kim NH. Customized estimating algorithm of physical activities energy expenditure using a triaxial accelerometer. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2011; 11(12):103–111.
Article18. Trost SG, Loprinzi PD, Moore R, Pfeiffer KA. Comparison of accelerometer cut points for predicting activity intensity in youth. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011; 43(7):1360–1368.
Article19. Lyden K, Kozey SL, Staudenmeyer JW, Freedson PS. A comprehensive evaluation of commonly used accelerometer energy expenditure and MET prediction equations. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011; 111(2):187–201.
Article20. Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Herrmann SD, Meckes N, Bassett DR Jr, Tudor-Locke C, Greer JL, Vezina J, Whitt-Glover MC, Leon AS. 2011 compendium of physical activities: a second update of codes and MET values. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011; 43(8):1575–1581.21. Kim MH, Kim JH, Kim EK. Accuracy of predictive equations for resting energy expenditure (REE) in nonobese and obese Korean children and adolescents. Nutr Res Pract. 2012; 6(1):51–60.
Article22. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea Health Statistics 2015: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VI-3). Sejong: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2016.23. McLaughlin JE, King GA, Howley ET, Bassett DR Jr, Ainsworth BE. Validation of the COSMED K4 b2 portable metabolic system. Int J Sports Med. 2001; 22(4):280–284.
Article24. Spurr GB, Prentice AM, Murgatroyd PR, Goldberg GR, Reina JC, Christman NT. Energy expenditure from minute-by-minute heart-rate recording: comparison with indirect calorimetry. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988; 48(3):552–559.
Article25. Park JY, Park ST, Jun TW, Eom WS, Lee DG, Park IR, Kang HJ. Prediction of energy expenditure during exercise through heart rate in young adult. Exerc Sci. 2004; 13(3):311–322.26. Pate RR, Kriska A. Physiological basis of the sex difference in cardiorespiratory endurance. Sports Med. 1984; 1(2):87–98.
Article27. Hall KS, Howe CA, Rana SR, Martin CL, Morey MC. METs and accelerometry of walking in older adults: standard versus measured energy cost. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013; 45(3):574–582.28. Kim JH, Son HR, Choi JS, Kim EK. Energy expenditure measurement of various physical activity and correlation analysis of body weight and energy expenditure in elementary school children. J Nutr Health. 2015; 48(2):180–191.
Article29. An JH. The model for the walking and running program for the health of the aged. Korean J Phys Educ. 1996; 35(3):299–308.30. Howe CA, Staudenmayer JW, Freedson PS. Accelerometer prediction of energy expenditure: vector magnitude versus vertical axis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009; 41(12):2199–2206.31. Bassett DR Jr, Ainsworth BE, Swartz AM, Strath SJ, O'Brien WL, King GA. Validity of four motion sensors in measuring moderate intensity physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000; 32(9 Suppl):S471–S480.
Article32. Rowlands AV, Thomas PW, Eston RG, Topping R. Validation of the RT3 triaxial accelerometer for the assessment of physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004; 36(3):518–524.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Test of Validity Using an Accelerometer for the Assessment of Physical Activity-related Eenergy Expenditure
- Comparison of Physical Activity Recall with Triaxial Accelerometer
- The Study of Daily Physical Activity in Old Women using Pedometer with Accelerometer
- Energy cost of walking in older adults: accuracy of the ActiGraph accelerometer predictive equations
- Measurement Methods for Physical Activity and Energy Expenditure: a Review