Ann Rehabil Med.
2017 Dec;41(6):1065-1075. 10.5535/arm.2017.41.6.1065.
Quantitative Lymphoscintigraphy to Predict the Possibility of Lymphedema Development After Breast Cancer Surgery: Retrospective Clinical Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. bduck@gachon.ac.kr
- 2Department of Breast Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2400292
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.6.1065
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To predict the probability of lymphedema development in breast cancer patients in the early post-operation stage, we investigated the ability of quantitative lymphoscintigraphic assessment.
METHODS
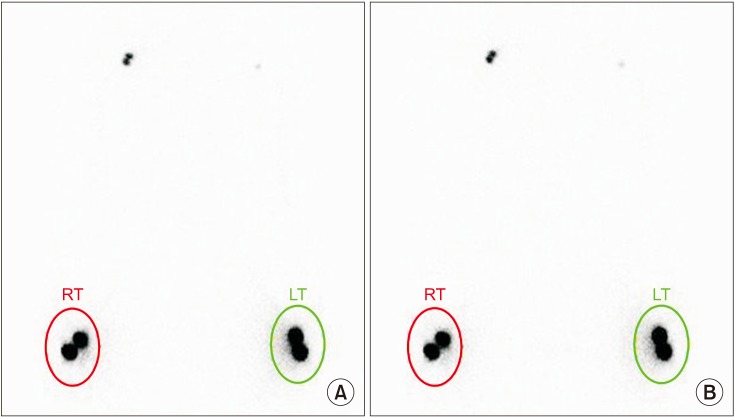
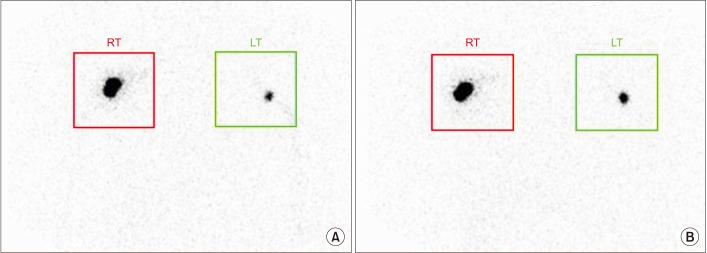
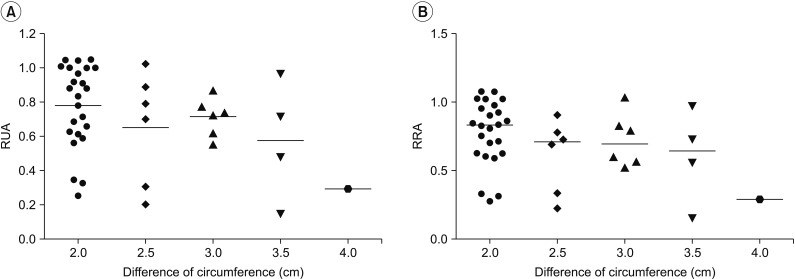
This retrospective study included 201 patients without lymphedema after unilateral breast cancer surgery. Lymphoscintigraphy was performed between 4 and 8 weeks after surgery to evaluate the lymphatic system in the early postoperative stage. Quantitative lymphoscintigraphy was performed using four methods: ratio of radiopharmaceutical clearance rate of the affected to normal hand; ratio of radioactivity of the affected to normal hand; ratio of radiopharmaceutical uptake rate of the affected to normal axilla (RUA); and ratio of radioactivity of the affected to normal axilla (RRA). During a 1-year follow-up, patients with a circumferential interlimb difference of 2 cm at any measurement location and a 200-mL interlimb volume difference were diagnosed with lymphedema. We investigated the difference in quantitative lymphoscintigraphic assessment between the non-lymphedema and lymphedema groups.
RESULTS
Quantitative lymphoscintigraphic assessment revealed that the RUA and RRA were significantly lower in the lymphedema group than in the non-lymphedema group. After adjusting the model for all significant variables (body mass index, N-stage, T-stage, type of surgery, and type of lymph node surgery), RRA was associated with lymphedema (odds ratio=0.14; 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.46; p=0.001).
CONCLUSION
In patients in the early postoperative stage after unilateral breast cancer surgery, quantitative lymphoscintigraphic assessment can be used to predict the probability of developing lymphedema.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effects of Different Bandaging Methods for Treating Patients With Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema
Se Hyun Oh, Sung Hwan Ryu, Ho Joong Jeong, Jung Hyun Lee, Young-Joo Sim
Ann Rehabil Med. 2019;43(6):677-685. doi: 10.5535/arm.2019.43.6.677.
Reference
-
1. Warren AG, Brorson H, Borud LJ, Slavin SA. Lymphedema: a comprehensive review. Ann Plast Surg. 2007; 59:464–472. PMID: 17901744.2. McLaughlin SA, Wright MJ, Morris KT, Giron GL, Sampson MR, Brockway JP, et al. Prevalence of lymphedema in women with breast cancer 5 years after sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary dissection: objective measurements. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:5213–5219. PMID: 18838709.
Article3. Dominick SA, Madlensky L, Natarajan L, Pierce JP. Risk factors associated with breast cancer-related lymphedema in the WHEL Study. J Cancer Surviv. 2013; 7:115–123. PMID: 23212606.
Article4. Rezende LF, Rocha AVR, Gomes CS. Risk factors for breast cancer related lymphedema. J Vasc Bras. 2010; 9:233–238.5. Sarri AJ, Moriguchi SM, Dias R, Peres SV, DA Silva ET, Koga KH, et al. Physiotherapeutic stimulation: Early prevention of lymphedema following axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer treatment. Exp Ther Med. 2010; 1:147–152. PMID: 23136607.
Article6. Dalia RM, Martins GR, Barbosa R, de Lima CF, Siqueira CF. Qualitative and quantitative lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lower limbs lymphedema. Braz Arch Biol Technol. 2005; 48:159–162.
Article7. Linnitt N. Lymphoedema: recognition, assessment and management. Br J Community Nurs. 2005; 10:S20–S26. PMID: 15824708.
Article8. Deltombe T, Jamart J, Recloux S, Legrand C, Vandenbroeck N, Theys S, et al. Reliability and limits of agreement of circumferential, water displacement, and optoelectronic volumetry in the measurement of upper limb lymphedema. Lymphology. 2007; 40:26–34. PMID: 17539462.9. Soo JK, Bicanic TA, Heenan S, Mortimer PS. Lymphatic abnormalities demonstrated by lymphoscintigraphy after lower limb cellulitis. Br J Dermatol. 2008; 158:1350–1353. PMID: 18241266.
Article10. Bernas MJ, Askew RL, Armer JM, Cormier JN. Lymphedema: how do we diagnose and reduce the risk of this dreaded complication of breast cancer treatment? Curr Breast Cancer Rep. 2010; 2:53–58.
Article11. Kwan ML, Darbinian J, Schmitz KH, Citron R, Partee P, Kutner SE, et al. Risk factors for lymphedema in a prospective breast cancer survivorship study: the pathways study. Arch Surg. 2010; 145:1055–1063. PMID: 21079093.12. Ahmed RL, Schmitz KH, Prizment AE, Folsom AR. Risk factors for lymphedema in breast cancer survivors, the Iowa Women's Health Study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 130:981–991. PMID: 21761159.
Article13. Norman SA, Localio AR, Kallan MJ, Weber AL, Torpey HA, Potashnik SL, et al. Risk factors for lymphedema after breast cancer treatment. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010; 19:2734–2746. PMID: 20978176.
Article14. Szuba A, Shin WS, Strauss HW, Rockson S. The third circulation: radionuclide lymphoscintigraphy in the evaluation of lymphedema. J Nucl Med. 2003; 44:43–57. PMID: 12515876.15. Yuan Z, Chen L, Luo Q, Zhu J, Lu H, Zhu R. The role of radionuclide lymphoscintigraphy in extremity lymphedema. Ann Nucl Med. 2006; 20:341–344. PMID: 16878705.
Article16. Sadeghi R, Kazemzadeh G, Keshtgar M. Diagnostic application of lymphoscintigraphy in the management of lymphoedema. Hell J Nucl Med. 2010; 13:6–10. PMID: 20411162.17. International Society of Lymphology. The diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema: 2013 Consensus Document of the International Society of Lymphology. Lymphology. 2013; 46:1–11. PMID: 23930436.18. Szuba A, Rockson SG. Lymphedema: classification, diagnosis and therapy. Vasc Med. 1998; 3:145–156. PMID: 9796078.
Article19. Ter SE, Alavi A, Kim CK, Merli G. Lymphoscintigraphy: a reliable test for the diagnosis of lymphedema. Clin Nucl Med. 1993; 18:646–654. PMID: 8403693.
Article20. Weissleder H, Weissleder R. Lymphedema: evaluation of qualitative and quantitative lymphoscintigraphy in 238 patients. Radiology. 1988; 167:729–735. PMID: 3363131.
Article21. Starritt EC, Joseph D, McKinnon JG, Lo SK, de Wilt JH, Thompson JF. Lymphedema after complete axillary node dissection for melanoma: assessment using a new, objective definition. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:866–874. PMID: 15492570.22. Hayes SC, Janda M, Cornish B, Battistutta D, Newman B. Lymphedema after breast cancer: incidence, risk factors, and effect on upper body function. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:3536–3542. PMID: 18640935.
Article23. DiSipio T, Rye S, Newman B, Hayes S. Incidence of unilateral arm lymphoedema after breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013; 14:500–515. PMID: 23540561.
Article24. Tsai RJ, Dennis LK, Lynch CF, Snetselaar LG, Zamba GK, Scott-Conner C. The risk of developing arm lymphedema among breast cancer survivors: a meta-analysis of treatment factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:1959–1972. PMID: 19365624.
Article25. Chandra RA, Miller CL, Skolny MN, Warren LE, Horick N, Jammallo LS, et al. Radiation therapy risk factors for development of lymphedema in patients treated with regional lymph node irradiation for breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015; 91:760–764. PMID: 25752389.
Article26. McLaughlin SA. Lymphedema: separating fact from fiction. Oncology (Williston Park). 2012; 26:242–249. PMID: 22545305.27. Herd-Smith A, Russo A, Muraca MG, Del Turco MR, Cardona G. Prognostic factors for lymphedema after primary treatment of breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2001; 92:1783–1787. PMID: 11745250.
Article28. Kiel KD, Rademacker AW. Early-stage breast cancer: arm edema after wide excision and breast irradiation. Radiology. 1996; 198:279–283. PMID: 8539394.
Article29. Paskett ED, Naughton MJ, McCoy TP, Case LD, Abbott JM. The epidemiology of arm and hand swelling in premenopausal breast cancer survivors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007; 16:775–782. PMID: 17416770.
Article30. Ozaslan C, Kuru B. Lymphedema after treatment of breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2004; 187:69–72. PMID: 14706589.
Article31. Hinrichs CS, Watroba NL, Rezaishiraz H, Giese W, Hurd T, Fassl KA, et al. Lymphedema secondary to postmastectomy radiation: incidence and risk factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004; 11:573–580. PMID: 15172932.
Article32. Shih YC, Xu Y, Cormier JN, Giordano S, Ridner SH, Buchholz TA, et al. Incidence, treatment costs, and complications of lymphedema after breast cancer among women of working age: a 2-year follow-up study. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:2007–2014. PMID: 19289624.
Article33. Yen TW, Fan X, Sparapani R, Laud PW, Walker AP, Nattinger AB. A contemporary, population-based study of lymphedema risk factors in older women with breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:979–988. PMID: 19194754.
Article34. Meeske KA, Sullivan-Halley J, Smith AW, McTiernan A, Baumgartner KB, Harlan LC, et al. Risk factors for arm lymphedema following breast cancer diagnosis in Black women and White women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 113:383–391. PMID: 18297429.
Article35. Wang L, Li HP, Liu AN, Wang DB, Yang YJ, Duan YQ, et al. A scoring system to predict arm lymphedema risk for individual Chinese breast cancer patients. Breast Care (Basel). 2016; 11:52–56. PMID: 27051397.
Article36. Carena M, Campini R, Zelaschi G, Rossi G, Aprile C, Paroni G. Quantitative lymphoscintigraphy. Eur J Nucl Med. 1988; 14:88–92. PMID: 3391216.
Article37. Toyserkani NM, Hvidsten S, Tabatabaeifar S, Simonsen JA, Hoilund-Carlsen PF, Sorensen JA. Tc-99m-human serum albumin transit time as a measure of arm breast cancer-related lymphedema. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017; 5:e1362. PMID: 28740776.
Article38. Simonsen J, Hvidsten S, Hoilund-Carlsen PF, Sorensen J, Toyserkani N. Quantification of breast cancer-related lymphedema of the upper limbs. J Nucl Med. 2017; 58(Suppl 1):468.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Traumatic Lymphedema without Tissue Injury Detected by Lymphoscintigraphy
- A Case of Conjunctival and Lid Lymphedema Confirmed with Lymphoscintigraphy
- Validity of Quantitative Lymphoscintigraphy as a Lymphedema Assessment Tool for Patients With Breast Cancer
- Rapid Lymphedema Progression in Breast Cancer Patient with Previous Forearm Fracture
- Early Stage Lymphedema in Breast Cancer Patient Detected by Indocyanine Green Lymphography but not by Lymphoscintigraphy: A Case Report