J Dent Anesth Pain Med.
2017 Dec;17(4):281-287. 10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.4.281.
A comparison of the effects of epinephrine and xylometazoline in decreasing nasal bleeding during nasotracheal intubation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Republic of Korea. drjack@nate.com
- KMID: 2399798
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.4.281
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Various techniques have been introduced to decrease complications during nasotracheal intubation. A common practice is to use nasal packing with a cotton stick and 0.01% epinephrine jelly. However, this procedure can be painful to patients and can damage the nasal mucosa. Xylometazoline spray can induce effective vasoconstriction of the nasal mucosa without direct nasal trauma. In this study, we aimed to compare the efficacy of these two methods.
METHODS
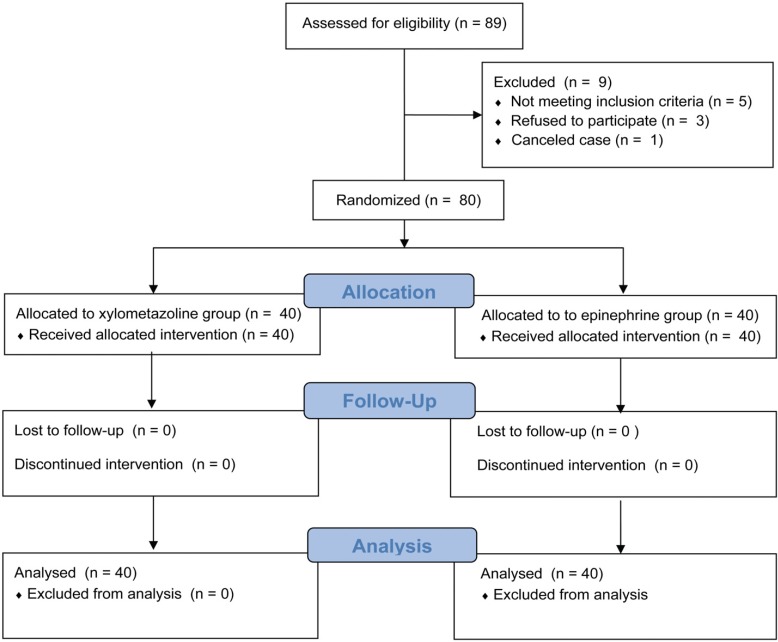
Patients were randomly allocated into two groups (n = 40 each): xylometazoline spray group or epinephrine packing group. After the induction of general anesthesia, patients allocated to the xylometazoline spray group were treated with xylometazoline spray to induce nasal cavity mucosa vasoconstriction, and the epinephrine packing group was treated with nasal packing with two cotton sticks and 0.01% epinephrine jelly. The number of attempts to insert the endotracheal tube into the nasopharynx, the degree of difficulty during insertion, and bleeding during bronchoscopy were recorded. An anesthesiologist, blinded to the intubation method, estimated the severity of epistaxis 5 min after intubation and postoperative complications.
RESULTS
No significant intergroup difference was observed in navigability (P = 0.465). The xylometazoline spray group showed significantly less epistaxis during intubation (P = 0.02). However, no differences were observed in epistaxis 5 min after intubation or postoperative epistaxis (P = 0.201). No inter-group differences were observed in complications related to nasal intubation and nasal pain.
CONCLUSION
Xylometazoline spray is a good alternative to nasal packing for nasal preparation before nasotracheal intubation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Reverse tube direction and epistaxis in left nasotracheal intubation: a randomized controlled trial
Jun-Young Park, Jihion Yu, Chan-Sik Kim, Taeho Mun, Woo Shik Jeong, Jong Woo Choi, Kichang Lee, Young-Kug Kim
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2024;77(6):596-604. doi: 10.4097/kja.24337.
Reference
-
1. Sanuki T, Hirokane M, Kotani J. Epistaxis during nasotracheal intubation: a comparison of nostril sides. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:618–621. PMID: 19931965.
Article2. Krebs MJ, Sakai T. Retropharyngeal dissection during nasotracheal intubation: a rare complication and its management. J Clin Anesth. 2008; 20:218–221. PMID: 18502368.
Article3. Kuo MJ, Reid AP, Smith JE. Unilateral nasal obstruction: an unusual presentation of a complication of nasotracheal intubation. J Laryngol Otol. 1994; 108:991–992. PMID: 7829957.
Article4. Paul M, Dueck M, Kampe S, Petzke F, Ladra A. Intracranial placement of a nasotracheal tube after transnasal trans-sphenoidal surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2003; 91:601–604. PMID: 14504169.
Article5. Scamman FL, Babin RW. An unusual complication of nasotracheal intubation. Anesthesiology. 1983; 59:352–353. PMID: 6614546.
Article6. Arendt KW, Khan K, Curry TB, Tsen LC. Topical vasoconstrictor use for nasal intubation during pregnancy complicated by cardiomyopathy and preeclampsia. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2011; 20:246–249. PMID: 21315577.
Article7. Kihara S, Komatsuzaki T, Brimacombe JR, Yaguchi Y, Taguchi N, Watanabe S. A silicone-based wire-reinforced tracheal tube with a hemispherical bevel reduces nasal morbidity for nasotracheal intubation. Anesth Analg. 2003; 97:1488–1491. PMID: 14570671.
Article8. Kim YC, Lee SH, Noh GJ, Cho SY, Yeom JH, Shin WJ. Thermosoftening treatment of the nasotracheal tube before intubation can reduce epistaxis and nasal damage. Anesth Analg. 2000; 91:698–701. PMID: 10960403.
Article9. Lee JH, Kim CH, Bahk JH, Park KS. The influence of endotracheal tube tip design on nasal trauma during nasotracheal intubation: magill-tip versus murphy-tip. Anesth Analg. 2005; 101:1226–1229. PMID: 16192550.
Article10. Li YC, Zhang L, Li GH, Li DK, Li C. Establishment of artificial airway with a thermal-softened nasotracheal tube guided by fiberoptic bronchoscope. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2007; 19:549–551. PMID: 17767826.11. Morimoto Y, Sugimura M, Hirose Y, Taki K, Niwa H. Nasotracheal intubation under curve-tipped suction catheter guidance reduces epistaxis. Can J Anaesth. 2006; 53:295–298. PMID: 16527796.
Article12. Seo KS, Kim JH, Yang SM, Kim HJ, Bahk JH, Yum KW. A new technique to reduce epistaxis and enhance navigability during nasotracheal intubation. Anesth Analg. 2007; 105:1420–1424. PMID: 17959976.
Article13. El-Seify ZA, Khattab AM, Shaaban AA, Metwalli OS, Hassan HE, Ajjoub LF. Xylometazoline pretreatment reduces nasotracheal intubation-related epistaxis in paediatric dental surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2010; 105:501–505. PMID: 20682569.
Article14. Haenisch B, Walstab J, Herberhold S, Bootz F, Tschaikin M, Ramseger R. Alpha-adrenoceptor agonistic activity of oxymetazoline and xylometazoline. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2010; 24:729–739. PMID: 20030735.
Article15. Strandell B, Norgren-Holst E, Tran N, Jakobsen HB, Chen S. OTC use of a topical nasal spray solution containing xylometazoline plus ipratropium in patients with common cold. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009; 47:744–751. PMID: 19954713.
Article16. O'Hanlon J, Harper KW. Epistaxis and nasotracheal intubation--prevention with vasoconstrictor spray. Ir J Med Sci. 1994; 163:58–60. PMID: 7515382.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A prospective randomized trial of xylometazoline drops and epinephrine merocele nasal pack for reducing epistaxis during nasotracheal intubation
- The effect of xylometazoline spray for expansion of nasal cavity
- Effective removal of epistaxis during nasotracheal intubation utilizing a fiberoptic scope in a difficult airway: A case report
- Effects of Balloon on the Development of Epistaxis and Impingement during Nasotracheal Intubation
- Computed tomography evaluation and pretreatment for a safe nasotracheal intubation, avoiding nasal cavity injuries