Korean J Health Promot.
2017 Dec;17(4):259-268. 10.15384/kjhp.2017.17.4.259.
Accuracy of Capillary Blood Glucose Test When Fasting in Diabetes Patients or General Population: Performance Evaluation of G300 Based on ISO 15197:2013 Standards
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Family Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Asan, Korea. dryoo@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Family Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Family Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 4Department of Family Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Gumi Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Gumi, Korea.
- KMID: 2399336
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.15384/kjhp.2017.17.4.259
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Self-monitoring of blood glucose plays an important role in management of diabetes mellitus. Blood glucose measurement is based on using plasma glucose separated from whole blood, but many people with diabetes and health care providers use a portable glucose meter for convenience. The aim of this study was to evaluate the accuracy and agreement of G300 portable glucose monitoring system against standard venous glucose testing methods, based on ISO 15197:2013 standards.
METHODS
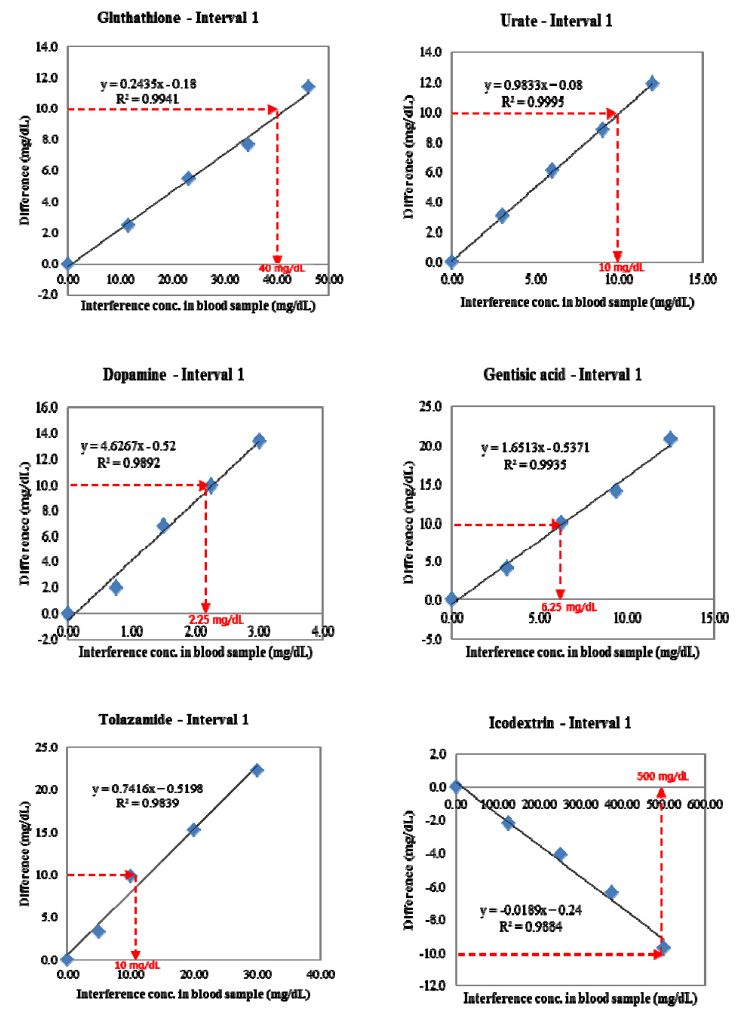
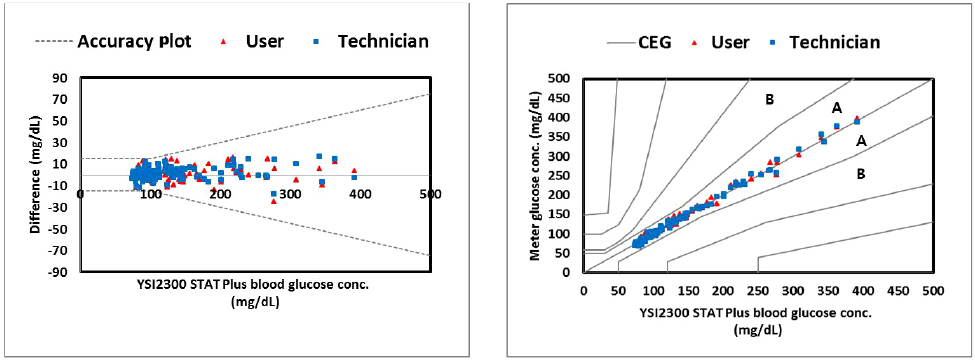
This study was the evaluation of G300 system accuracy following ISO 15197:2013 standards. We estimated precision, system accuracy, hematocrit interference, interfering substances, and user performance.
RESULTS
In repeatability precision evaluation of those glucometers, standard deviation was 2.9-3.7 mg/dL at glucose levels under 100 mg/dL and coefficient of variation was 1.7-3.2% at glucose levels over 100 mg/dL, respectively. In accuracy evaluation, 99.5% of difference values between results of G300 portable glucose monitoring system and clinical laboratory were within 95%. Consensus Error grid analysis showed that all values (100%) are within zone A. Hematocrit range between 20% and 60% did not cause interference. These results were acceptable for the ISO15197:2013 criteria in all glucose concentrations.
CONCLUSIONS
This study showed that G300 can provide reliable blood glucose results for patients and health care providers to manage diabetes mellitus, satisfying the ISO 15197:2013 criteria.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ohkubo Y, Kishikawa H, Araki E, Miyata T, Isami S, Motoyoshi S, et al. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a randomized prospective 6-year study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1995; 28(2):103–117.
Article2. Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA. 1999; 281(21):2005–2012.3. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, Cleary P, Crofford O, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329(14):977–986.
Article4. Karter AJ. Role of self-monitoring of blood glucose in glycemic control. Endocr Pract. 2006; 12:Suppl 1. 110–117.
Article5. Welschen LM, Bloemendal E, Nijpels G, Dekker JM, Heine RJ, Stalman WA, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin: a systematic review. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28(6):1510–1517.6. Sacks DB, Arnold M, Bakris GL, Bruns DE, Horvath AR, Kirkman MS, et al. Guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34(6):e61–e99.
Article7. An D, Chung HJ, Lee HW, Lee W, Chun S, Min WK. Analytical performance evaluation of glucose monitoring system following ISO15197. Korean J Lab Med. 2009; 29(5):423–429.
Article8. Noh J. The diabetes epidemic in Korea. Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 31(3):349–353.
Article9. Clark LC Jr, Lyons C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962; 102:29–45.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analytic Performance Evaluation of Blood Monitoring System G400 according to ISO 15197:2013
- Performance Evaluation of B. Braun Omnitest 5 Blood Glucose Monitoring System for Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose
- Performance Evaluation of BAROZEN H, a Networking Blood Glucose Monitoring System for Medical Institutions
- Performance Evaluation of Glucometer Barozen H Based on ISO 15197 Standards
- Accuracy Evaluation of GlucoLAB Auto-coding and Finetest Lite Glucose Monitoring Systems Following ISO 15197:2013