J Vet Sci.
2017 Dec;18(4):551-554. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.551.
Eosinophilic encephalomyelitis in horses caused by protostrongylid parasites
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul 03722, Korea.
- 2Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Gimcheon 39660, Korea.
- 3Laboratory of Histopathology, Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, Semyung University, Jecheon 27136, Korea. ghwoo@naver.com
- KMID: 2398516
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2017.18.4.551
Abstract
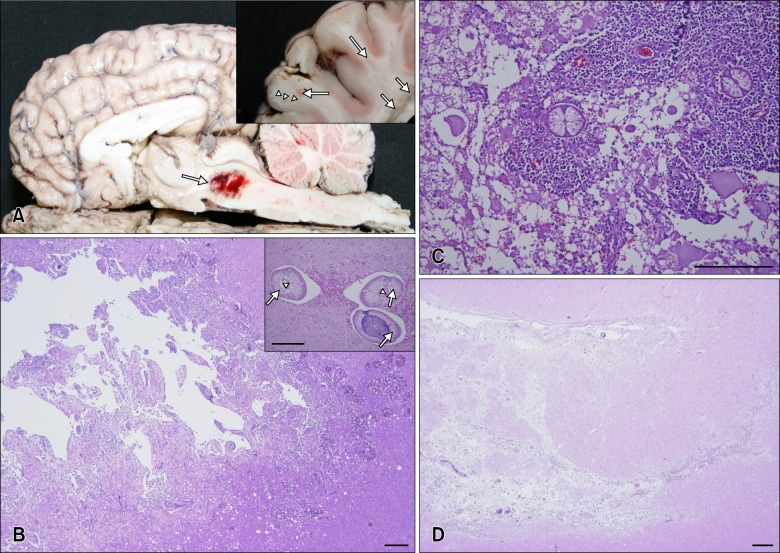
- Four thoroughbred horses showing lameness, ataxia, circling, depression, recumbency, and seizures, were examined. The horses had gross, pale- to dark-red manifestations and foci in the central nervous system (CNS). Multifocal to coalescing eosinophilic necrotizing encephalomyelitis was observed histologically in the CNS along with intact or degenerated nematodes. Nematodes had polymyarian-coelomyarian musculature, a smooth thin cuticle, and intestines lined by multinucleated cells with microvilli. These traits suggested the nematodes belonged to the family Protostrongylidae, which includes Parelaphostrongylus tenuis. It was concluded that the horses were infected by nematodes, presumably Parelaphostrongylus tenuis, resulting in eosinophilic necrotizing encephalomyelitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Anderson RC. The superfamily metastrongyloidea. In : Anderson RC, editor. Nematode Parasites of Vertebrates. Their Development and Transmission. 2nd ed. Oxon: CABI Publishing;p. 129–172.2. Chitwood M, Lichtenfels JR. Identification of parasitic metazoa in tissue sections. Exp Parasitol. 1972; 32:407–519. PMID: 4675138.
Article3. Handeland K. Experimental studies of Elaphostrongylus rangiferi in reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus): life cycle, pathogenesis, and pathology. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1994; 41:351–365. PMID: 7839758.4. Handeland K, Gibbons LM, Skorping A. Experimental Elaphostrongylus cervi infection in sheep and goats. J Comp Pathol. 2000; 123:248–257. PMID: 11041994.5. Lester G. Parasitic encephalomyelitis in horses. Compend Contin Educ Pract Vet. 1992; 14:1624–1630.6. Mitchell KJ, Peters-Kennedy J, Stokol T, Gerhold RW, Beckstead RB, Divers TJ. Diagnosis of Parelaphostrongylus spp. infection as a cause of meningomyelitis in calves. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2011; 23:1097–1103. PMID: 22362788.7. Tanabe M, Kelly R, de Lahunta A, Duffy MS, Wade SE, Divers TJ. Verminous encephalitis in a horse produced by nematodes in the family protostrongylidae. Vet Pathol. 2007; 44:119–122. PMID: 17197637.
Article8. Van Biervliet J, De Lahunta A, Ennulat D, Oglesbee M, Summers B. Acquired cervical scoliosis in six horses associated with dorsal grey column chronic myelitis. Equine Vet J. 2004; 36:86–92. PMID: 14756379.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Eosinophilic Cholecystitis associated with Eosinophilic Cholangitis and Pancreatitis
- Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
- Praziquantel Treatment of Eosinophilic Gastritis Suspected to Be Due to Cerebral Sparganosis
- A case of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
- A case of eosinophilic cholecystitis associated with gallstones