Lab Med Online.
2018 Jan;8(1):15-18. 10.3343/lmo.2018.8.1.15.
Comparison of Interferon-gamma Secretion by Stimulated NK Cells and T cells from Healthy Subjects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. progreen@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Rheumatology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2398414
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2018.8.1.15
Abstract
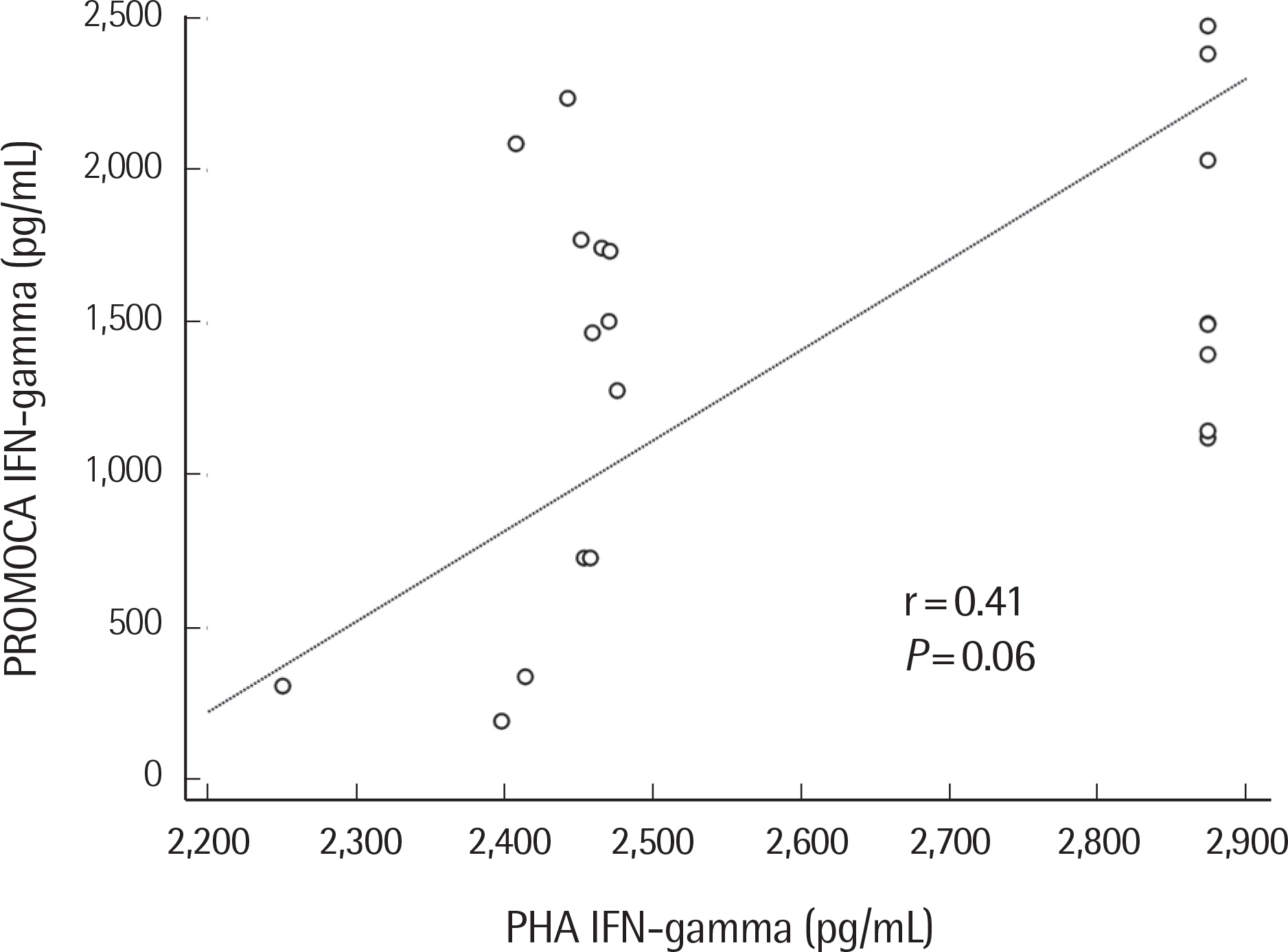
- Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) is an important cytokine produced by natural killer (NK) cells and T cells in response to various stimuli. The levels of IFN-γ secreted after stimulation of NK cells using a recombinant cytokine is represented as one of functions of NK cells. Recently, a method for evaluating NK cell activity in whole blood samples was developed. The levels of IFN-γ secreted after NK cell stimulation with PROMOCA™ (ATGen, Korea) and T cell stimulation with phytohemagglutinin (PHA) were compared using two different commercial kits: NK Vue Gold (ATGen, Korea) and QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube (Cellestis, Australia). Participants included 43 healthy individuals. Whole blood samples were incubated with either PROMOCA, a recombinant cytokine that specifically activates NK cells, or with PHA. IFN-γ levels in the supernatants were measured by ELISA. The level of IFN-γ by PROMOCA stimulation (PROMOCA IFN-γ) was more varied than that by stimulation with PHA (PHA IFN-γ) (median 1,544.4 pg/mL [ range 193.7-2,530.9] vs. median 2,470.1 pg/mL [ 2,250.1-2,874.4] P=0.0001). The median of PHA IFN-γ/PROMOCA IFN-γ ratio was 1.9 (1.1-12.4). There was a significant difference in levels of IFN-γ secreted after stimulation with PROMOCA or PHA in the healthy population.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Vivier E., Raulet DH., Moretta A., Caligiuri MA., Zitvogel L., Lanier LL, et al. Innate or adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells. Science. 2011. 331:44–9.
Article2.Brunner KT., Mauel J., Cerottini JC., Chapuis B. Quantitative assay of the lytic action of immune lymphoid cells on 51-Cr-labelled allogeneic target cells in vitro; inhibition by isoantibody and by drugs. Immunology. 1968. 4:181–96.3.Jang YY., Cho D., Kim SK., Shin DJ., Park MH., Lee JJ, et al. An improved fow cytometry-based natural killer cytotoxicity assay involving cal-cein AM staining of effector cells. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2012. 42:42–9.4.Yamashita M., Kitano S., Aikawa H., Kuchiba A., Hayashi M., Yamamoto N, et al. A novel method for evaluating antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity by fowcytometry using cryopreserved human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Sci Rep. 2016. 6:19772.
Article5.Alter G., Malenfant JM., Altfeld M. CD107a as a functional marker for the identifcation of natural killer cell activity. J Immunol Methods. 2004. 294:15–22.6.Lee SB., Cha J., Kim IK., Yoon JC., Lee HJ., Park SW, et al. A high-throughput assay of NK cell activity in whole blood and its clinical application. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. 445:584–90.
Article7.Nowell PC. Phytohemagglutinin: an initiator of mitosis in cultures of normal human leukocytes. Cancer Res. 1960. 20:462–6.8.Wheelock EF. Interferon-like virus inhibitor induced in human leukocytes by phytohemagglutinin. Science. 1965. 149:310–1.9.Chilson OP., Boylston AW., Crumpton MJ. Phaseolus vulgaris phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) binds to the human T lymphocyte antigen receptor. EMBO J. 1984. 3:3239–45.
Article10.Billiau A., Matthys P. Interferon-gamma: a historical perspective. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009. 20:97–113.11.Woo KS., Choi JL., Kim BR., Kim JE., Kim BG., Lee H, et al. Signifcance of interferon-gamma response to mitogen in serial QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube assay of routine laboratory practice. Clin Chim Acta. 2014. 430:79–83.12.Lange B., Vavra M., Kern WV., Wagner D. Indeterminate results of a tuberculosis-specifc interferon gamma release assay in immunocompromised patients. Eur Respir J. 2010. 35:1179–82.13.Fabre V., Shoham S., Page KR., Shah M. High proportion of indeterminate QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube results in an inpatient population is related to host factors and preanalytical steps. Open Forum In-fect Dis. 2014. 1:ofu088.
Article14.Aichelburg MC., Tittes J., Breitenecker F., Reiberger T., Kohrgruber N., Rieger A. Prognostic value of indeterminate IFN-γ release assay results in HIV-1 infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2012. 50:2767–9.
Article15.Banaei N., Gaur RL., Pai M. Interferon gamma release assays for latent tuberculosis: What are the sources of variability? J Clin Microbiol. 2016. 54:845–50.
Article16.De Maria A., Bozzano F., Cantoni C., Moretta L. Revisiting human natural killer cell subset function revealed cytolytic CD56(dim)CD16+ NK cells as rapid producers of abundant IFN-gamma on activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011. 108:728–32.17.Imai K., Matsuyama S., Miyake S., Suga K., Nakachi K. Natural cytotoxic activity of peripheral-blood lymphocytes and cancer incidence: an 11-year follow-up study of a general population. Lancet. 2000. 356:1795–9. 18. Lim YA, Kim SS, Cho SW, Cheong JY. Evaluation of the effectiveness of NK Vue Gold kit in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Lab Med Qual Assur 2016;38: 151-8.
Article18.Lim YA., Kim SS., Cho SW., Cheong JY. Evaluation of the effectiveness of NK Vue Gold kit in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2016. 38:151–8.
Article19.Hou H., Mao L., Wang J., Liu W., Lu Y., Yu J, et al. Establishing the reference intervals of NK cell functions in healthy adults. Hum Immunol. 2016. 77:637–42.
Article20.Koo KC., Shim DH., Yang CM., Lee SB., Kim SM., Shin TY, et al. Reduction of the CD16(-)CD56bright NK cell subset precedes NK cell dysfunction in prostate cancer. PLoS One. 2013. 8:e78049.
Article21.Dahlberg CI., Sarhan D., Chrobok M., Duru AD., Alici E. Natural killer cell-based therapies targeting cancer: possible strategies to gain and sustain anti-tumor activity. Front Immunol. 2015. 6:605.
Article22.Guillerey C., Huntington ND., Smyth MJ. Targeting natural killer cells in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Immunol. 2016. 17:1025–36.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nickel induces secretion of IFN-gamma by splenic natural killer cells
- Functional Changes of Interleukin-4 and Interferon-gamma of Peripheral Blood and Nasal Mucosa after Immunotherapy in Patients with Perennial Allergic Rhinitis
- The effects of interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma on the expression of FcepsilonR II on B cells
- Production of Interleukin-5, Interleukin-13 and Interferon-gamma in Peripheral Blood CD8+T Cells from Children with Wheezing
- Production of interleukin 4 and interferon gamma in CD8+ T cells from patients with intrinsic and extrinsic asthma