Clin Endosc.
2017 Nov;50(6):585-591. 10.5946/ce.2017.039.
Efficacy of Precut Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Treatment of Rectal Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jsbyeon@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Applied Statistics, Gachon University, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2398310
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.039
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
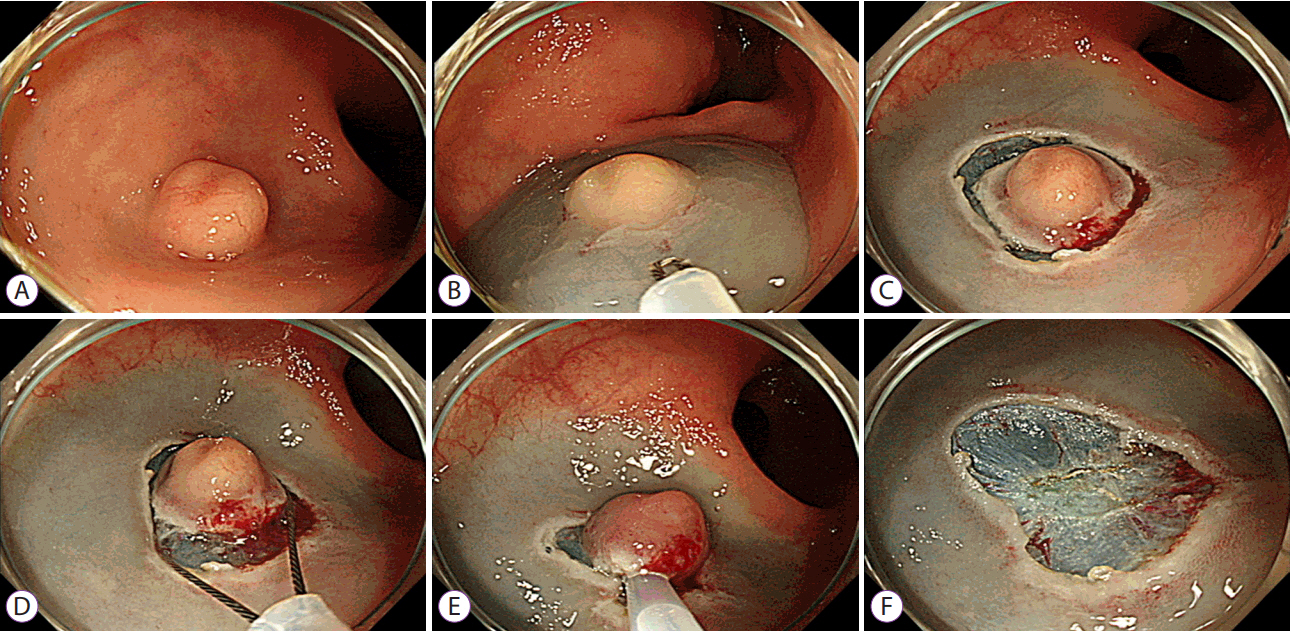
Endoscopic resection is the first-line treatment for rectal neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) measuring < 1 cm and those between 1 and 2 cm in size. However, conventional endoscopic resection cannot achieve complete resection in all cases. We aimed to analyze clinical outcomes of precut endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR-P) used for the management of rectal NET.
METHODS
EMR-P was used to treat rectal NET in 72 patients at a single tertiary center between 2011 and 2015. Both, circumferential precutting and EMR were performed with the same snare device in all patients. Demographics, procedural details, and histopathological features were reviewed for all cases.
RESULTS
Mean size of the tumor measured endoscopically was 6.8±2.8 mm. En bloc and complete resection was achieved in 71 (98.6%) and 67 patients (93.1%), respectively. The mean time required for resection was 9.0±5.6 min. Immediate and delayed bleeding developed in six (8.3%) and 4 patients (5.6%), respectively. Immediate bleeding observed during EMR-P was associated with the risk of delayed bleeding.
CONCLUSIONS
Both, the en bloc and complete resection rates of EMR-P in the treatment of rectal NETs using the same snare for precutting and EMR were noted to be high. The procedure was short and safe. EMR-P may be a good treatment choice for the management of rectal NETs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Proper Treatment Option for Small Rectal Neuroendocrine Tumors Using Precut Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
Seun Ja Park
Clin Endosc. 2017;50(6):516-517. doi: 10.5946/ce.2017.182.
Reference
-
1. Hauso O, Gustafsson BI, Kidd M, et al. Neuroendocrine tumor epidemiology: contrasting Norway and North America. Cancer. 2008; 113:2655–2664.2. Gastrointestinal Pathology Study Group of Korean Society of Pathologists, Cho MY, Kim JM, et al. Current trends of the incidence and pathological diagnosis of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs) in Korea 2000-2009: multicenter study. Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 44:157–165.
Article3. Kim BC, Park CH, Kim TI, et al. Variable clinical classifications and diagnostic coding systems of colorectal neuroendocrine tumor. Intest Res. 2013; 11:14–22.
Article4. Caplin M, Sundin A, Nillson O, et al. ENETS consensus guidelines for the management of patients with digestive neuroendocrine neoplasms: colorectal neuroendocrine neoplasms. Neuroendocrinology. 2012; 95:88–97.
Article5. Zhong DD, Shao LM, Cai JT. Endoscopic mucosal resection vs endoscopic submucosal dissection for rectal carcinoid tumours: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Colorectal Dis. 2013; 15:283–291.6. Park HW, Byeon JS, Park YS, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for treatment of rectal carcinoid tumors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:143–149.
Article7. Lee DS, Jeon SW, Park SY, et al. The feasibility of endoscopic submucosal dissection for rectal carcinoid tumors: comparison with endoscopic mucosal resection. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:647–651.
Article8. Choi HH, Kim JS, Cheung DY, Cho YS. Which endoscopic treatment is the best for small rectal carcinoid tumors? World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 5:487–494.
Article9. Mashimo Y, Matsuda T, Uraoka T, et al. Endoscopic submucosal resection with a ligation device is an effective and safe treatment for carcinoid tumors in the lower rectum. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:218–221.
Article10. Kim HH, Park SJ, Lee SH, et al. Efficacy of endoscopic submucosal resection with a ligation device for removing small rectal carcinoid tumor compared with endoscopic mucosal resection: analysis of 100 cases. Dig Endosc. 2012; 24:159–163.
Article11. Zhao ZF, Zhang N, Ma SR, et al. A comparative study on endoscopy treatment in rectal carcinoid tumors. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2012; 22:260–263.
Article12. Wang X, Xiang L, Li A, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of rectal carcinoid tumors 7-16 mm in diameter. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2015; 30:375–380.13. Huang J, Lu ZS, Yang YS, et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection with circumferential incision for treatment of rectal carcinoid tumours. World J Surg Oncol. 2014; 12:23.
Article14. Cheung DY, Choi SK, Kim HK, et al. Circumferential submucosal incision prior to endoscopic mucosal resection provides comparable clinical outcomes to submucosal dissection for well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of the rectum. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:1500–1505.
Article15. Okano A, Hajiro K, Takakuwa H, Nishio A, Matsushita M. Predictors of bleeding after endoscopic mucosal resection of gastric tumors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:687–690.
Article16. Burgess NG, Metz AJ, Williams SJ, et al. Risk factors for intraprocedural and clinically significant delayed bleeding after wide-field endoscopic mucosal resection of large colonic lesions. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 12:651–661.e1-e3.
Article17. Kim HS, Kim TI, Kim WH, et al. Risk factors for immediate postpolypectomy bleeding of the colon: a multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:1333–1341.
Article18. Jung Y, Chung IK, Cho YS, et al. Do we perform a perfect endoscopic hemostasis prophylactically with argon plasma coagulation in colonic endoscopic mucosal resection? Dig Dis Sci. 2015; 60:3100–3107.
Article19. Kim GU, Kim KJ, Hong SM, et al. Clinical outcomes of rectal neuroendocrine tumors ≤ 10 mm following endoscopic resection. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:1018–1023.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Proper Treatment Option for Small Rectal Neuroendocrine Tumors Using Precut Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- Endoscopic Treatment Outcome of Rectal Neuroendocrine Tumors Removed by Ligation-assisted Endoscopic Submucosal Resection
- Recurrence after endoscopic resection of small rectal neuroendocrine tumors: a retrospective cohort study
- Endoscopic treatment for rectal neuroendocrine tumor: which method is better?
- Diagnosis and Management of Rectal Neuroendocrine Tumors