Asia Pac Allergy.
2011 Apr;1(1):30-35. 10.5415/apallergy.2011.1.1.30.
Prolonged bedtime bottle feeding and respiratory symptoms in infants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan 609-735, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea. childslee@skku.edu
- KMID: 2397143
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5415/apallergy.2011.1.1.30
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Infants with chronic respiratory symptoms should be evaluated thoroughly because there are various causes which are different from those of children and adolescents.
OBJECTIVE
This study was designed to investigate the relationship between chronic respiratory symptoms and bedtime bottle feeding in infants after the age of 6 months.
METHODS
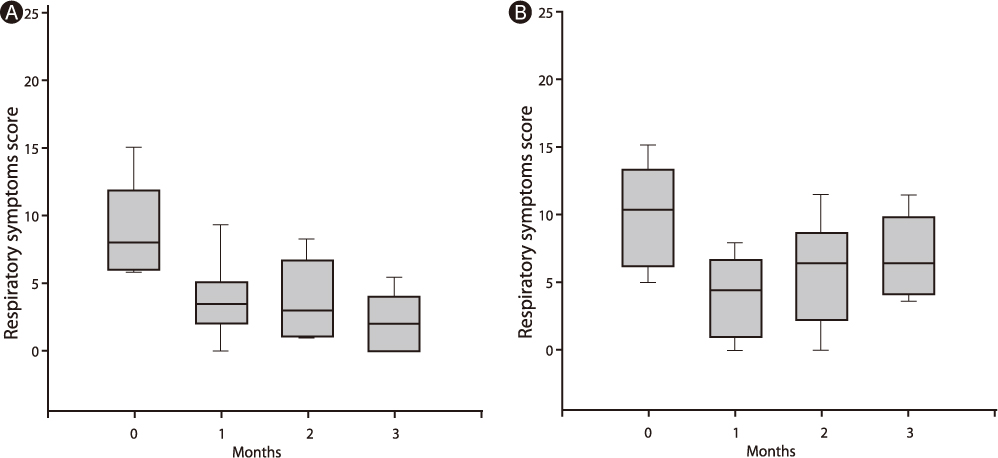
We conducted a prospective study that included 44 infants who presented with respiratory symptoms for more than 8 weeks and also had been bottle-fed during bedtime even after 6 months of age. The infants were divided into 2 groups; infants who discontinued bedtime bottle feeding and those who did not. Respiratory symptom scores were graded with a four-point scale at 0, 1, 2 and 3 months, and were compared between the 2 groups.
RESULTS
Twenty eight infants (63.6%) stopped being bottle-fed during bedtime and 16 infants (36.4%) were still bottle-fed. The respiratory symptom scores were significantly decreased in infants who stopped bedtime bottle feeding (p = 0.0003).
CONCLUSION
It is suggested that prolonged bedtime bottle feeding might be one of the causes of chronic respiratory symptoms in infants.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Irwin RS, Madison JM. The diagnosis and treatment of cough. N Engl J Med. 2000. 343:1715–1721.2. Cypress BK. Patterns of ambulatory care in pediatrics: The national ambulatory medical care survey. Vital Health Stat 13. 1983. 75:1–60.
Article3. Chung KF, Pavord ID. Prevalence, pathogenesis, and causes of chronic cough. Lancet. 2008. 371:1364–1374.
Article4. Morice AH, Fontana GA, Sovijarvi AR, Pistolesi M, Chung KF, Widdicombe J, O'Connell F, Geppetti P, Gronke L, De Jongste J, Belvisi M, Dicpinigaitis P, Fischer A, McGarvey L, Fokkens WJ, Kastelik J. ERS Task Force. The diagnosis and management of chronic cough. Eur Respir J. 2004. 24:481–492.5. Kelly BN, Huckabee ML, Jones RD, Frampton CM. The first year of human life: coordinating respiration and nutritive swallowing. Dysphagia. 2007. 22:37–43.6. Poets CF. Gastroesophageal reflux: a critical review of its role in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2004. 113:e128–e132.
Article7. Heacock HJ, Jeffery HE, Baker JL, Page M. Influence of breast versus formula milk on physiological gastroesophageal reflux in healthy, newborn infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1992. 14:41–46.
Article8. Mizuno K, Ueda A, Takeuchi T. Effects of different fluids on the relationship between swallowing and breathing during nutritive sucking in neonates. Biol Neonate. 2002. 81:45–50.9. Foresman BH. Sleep-related gastroesophageal reflux. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2000. 100:S7–S10.10. Sondheimer JM. Clearance of spontaneous gastroesophageal reflux in awake and sleeping infants. Gastroenterology. 1989. 97:821–826.
Article11. Størdal K, Johannesdottir GB, Bentsen BS, Knudsen PK, Carlsen KC, Closs O, Handeland M, Holm HK, Sandvik L. Acid suppression does not change respiratory symptoms in children with asthma and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Arch Dis Child. 2005. 90:956–960.
Article12. Kleinman RE. American Academy of Pediatrics recommendations for complementary feeding. Pediatrics. 2000. 106:1274.13. Shaikh U, Chantry C. Reflections on the American Academy of Pediatrics' 2005 policy statement on "Breastfeeding and the use of human milk". J Hum Lact. 2006. 22:108–110.14. Gaffney KE, Farrar-Simpson MA, Claure D, Davilla G. Prolonged baby bottle feeding: a health risk factor. Pediatr Nurs. 2004. 30:242–245.
Article15. Ganesh M, Tandon S, Sajida B. Prolonged feeding practice and its effects on developing dentition. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2005. 23:141–145.
Article16. Wetzel WE, Hanisch S, Sziegoleit A. The germ colonization of the oral cavity in small children with the nursing bottle syndrome. Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed. 1993. 103:1107–1112.17. Frazier JP, Countie D, Elerian L. Parental barriers to weaning infants from the bottle. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1998. 152:889–892.18. Celedón JC, Litonjua AA, Ryan L, Weiss ST, Gold DR. Bottle feeding in the bed or crib before sleep time and wheezing in early childhood. Pediatrics. 2002. 110:e77.
Article19. Gleeson K, Eggli DF, Maxwell SL. Quantitative aspiration during sleep in normal subjects. Chest. 1997. 111:1266–1272.
Article20. Gurski RR, da Rosa AR, do Valle E, de Borba MA, Valiati AA. Extraesophageal manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Bras Pneumol. 2006. 32:150–160.21. Orenstein SR. An overview of reflux-associated disorders in infants: apnea, laryngospasm, and aspiration. Am J Med. 2001. 111:Suppl 8A. 60S–63S.22. Schan CA, Harding SM, Haile JM, Bradley LA, Richter JE. Gastroesophageal reflux-induced bronchoconstriction. An intraesophageal acid infusion study using state-of-the-art technology. Chest. 1994. 106:731–737.
Article23. Colombo JL, Hallberg TK. Airway reactivity following repeated milk aspiration in rabbits. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000. 29:113–119.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of an Oral Stimulation Program on the Transition from Tube to Bottle Feeding in Premature Infants
- Differences in Breast feeding and Bottle feeding Primiparas' Perceptions of their Babies during the Early time of Post-partum Period
- Effects of Nonnutritive Sucking on Lingual Lipase Activity and Body Weight of Low Birth Weight Infants with Bottle Feeding
- Feeding Desaturation and Effects of Orocutaneous Stimulation in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants
- Plastic bottle feeding produces changes in biochemical parameters in human infants – A pilot study