Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2017 Dec;10(4):296-302. 10.21053/ceo.2016.00997.
The Effect of Insulin Like Growth Factor-1 on Recovery of Facial Nerve Crush Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Otolaryngology Department, Izmir Ataturk Training and Research Hospital, Izmir, Turkey. fedabolat@yahoo.com
- 2Otolaryngology Department, Dokuz Eylul University Medical Faculty, Izmir, Turkey.
- 3Otorhinolaryngology Department, Kutahya Simav State Hospital, Kutahya, Turkey.
- 4Basic Oncology Department, Dokuz Eylul University, Institue of Oncology, Izmir, Turkey.
- 5Neurology Department, Izmir Bozyaka Training and Research Hospital, Izmir, Turkey.
- 6Dokuz Eylul University, Animal Laboratory, Izmir, Turkey.
- 7Otorhinolaryngology Department, Izmir Bozyaka Training and Research Hospital, Izmir, Turkey.
- KMID: 2396782
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2016.00997
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study is to investigate the efficacy of locally applied insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) on the recovery of facial nerve functions after crush injury in a rabbit model.
METHODS
The rabbits were randomly assigned into three groups. Group 1 consisted of the rabbits with crush injury alone; group 2, the animals applied saline solution onto the crushed facial nerve and group 3, IGF-1 implemented to the nerve in the same manner. Facial nerve injury was first electrophysiologically studied on 10th and 42nd days of the procedure. The damage to the facial nerves was then investigated histopathologically, after sacrification of the animals.
RESULTS
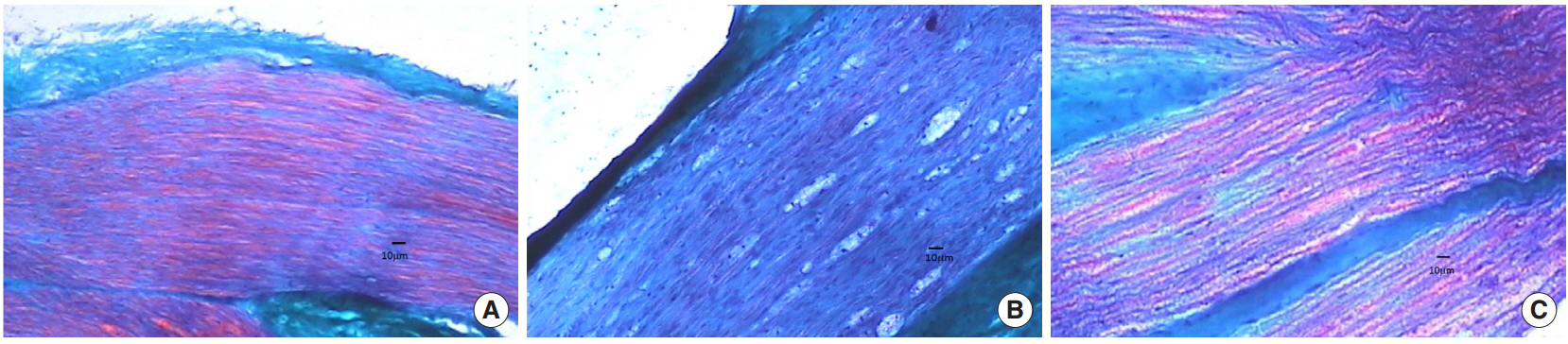
In the electrophysiological study, compound muscle action potential amplitudes of the crushed nerves in the second group were decreased. In pathological specimens of the first and second groups, the orders of axons were distorted; demyelination and proliferation of Schwann cells were observed. However, in IGF-1 treated group axonal order and myelin were preserved, and Schwann cell proliferation was close to normal (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSION
Local application of IGF-1 in a slow releasing gel was found efficacious in the recovery of the facial nerve crush injury in rabbits. IGF-1 was considered worthy of being tried in clinical studies in facial nerve injury cases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Skouras E, Angelov DN. Experimental studies on post-transectional facial nerve regrowth and functional recovery of paralyzed muscles of the face in rats and mice. Anatomy. 2010; Oct. 4:1–27.
Article2. Yakar S, Adamo ML. Insulin-like growth factor 1 physiology: lessons from mouse models. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2012; Jun. 41(2):231–47.3. Ishii DN, Glazner GW, Pu SF. Role of insulin-like growth factors in peripheral nerve regeneration. Pharmacol Ther. 1994; Apr-May. 62(1-2):125–44.
Article4. Rosenbloom AL, Rivkees SA. Off-label use of recombinant IGF-I to promote growth: is it appropriate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; Feb. 95(2):505–8.
Article5. Nachemson AK, Lundborg G, Hansson HA. Insulin-like growth factor I promotes nerve regeneration: an experimental study on rat sciatic nerve. Growth Factors. 1990; 3(4):309–14.
Article6. Ter Laak MP, Brakkee JH, Adan RA, Hamers FP, Gispen WH. The potent melanocortin receptor agonist melanotan-II promotes peripheral nerve regeneration and has neuroprotective properties in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003; Feb. 462(1-3):179–83.
Article7. Eriksson NP, Aldskogius H, Grant G, Lindsay RM, Rivero-Melian C. Effects of nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 on the laminar distribution of transganglionically fransported choleragenoid in the spinal cord dorsal horn following transection of the sciatic nerve in the adult rat. Neuroscience. 1997; Jun. 78(3):863–72.8. Costa HJ, Silva CF, Korn GP, Lazarini PR. Posttraumatic facial nerve regeneration in rabbits. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; Nov-Dec. 72(6):786–93.
Article9. Sachs NA, Chang EL, Vyas N, Sorensen BN, Weiland JD. Electrical stimulation of the paralyzed orbicularis oculi in rabbit. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2007; Mar. 15(1):67–75.
Article10. Volk GF, Klingner C, Finkensieper M, Witte OW, Guntinas-Lichius O. Prognostication of recovery time after acute peripheral facial palsy: a prospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2013; Jun. 3(6):pii: e003007.
Article11. Topdag M, Iseri M, Topdag DO, Kokturk S, Ozturk M, Iseri P. The effect of etanercept and methylprednisolone on functional recovery of the facial nerve after crush injury. Otol Neurotol. 2014; Aug. 35(7):1277–83.
Article12. Jang CH, Cho YB, Choi CH, Jang YS, Jung WK. Effect of topical dexamethasone in reducing dysfunction after facial nerve crush injury in the rat. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; Jun. 78(6):960–3.
Article13. Nakagawa T, Sakamoto T, Hiraumi H, Kikkawa YS, Yamamoto N, Hamaguchi K, et al. Topical insulin-like growth factor 1 treatment using gelatin hydrogels for glucocorticoid-resistant sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a prospective clinical trial. BMC Med. 2010; Nov. 8:76.
Article14. Matsumine H, Sasaki R, Tabata Y, Matsui M, Yamato M, Okano T, et al. Facial nerve regeneration using basic fibroblast growth factor-impregnated gelatin microspheres in a rat model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016; Oct. 10(10):E559–E567.
Article15. Cheng HL, Russell JW, Feldman EL. IGF-I promotes peripheral nervous system myelination. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999; Sep. 883:124–30.
Article16. Fex Svenningsen A, Kanje M. Insulin and the insulin-like growth factors I and II are mitogenic to cultured rat sciatic nerve segments and stimulate [3H]thymidine incorporation through their respective receptors. Glia. 1996; Sep. 18(1):68–72.17. Zhang H, Wei YT, Tsang KS, Sun CR, Li J, Huang H, et al. Implantation of neural stem cells embedded in hyaluronic acid and collagen composite conduit promotes regeneration in a rabbit facial nerve injury model. J Transl Med. 2008; Nov. 6:67.
Article18. Thanos PK, Tiangco DA, Terzis JK. Enhanced reinnervation of the paralyzed orbicularis oculi muscle after Insulin-like Growth Factor-I (IGF-I) delivery to a nerve graft. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2001; Jul. 17(5):357–62.
Article19. Emel E, Ergun SS, Kotan D, Gursoy EB, Parman Y, Zengin A, et al. Effects of insulin-like growth factor-I and platelet-rich plasma on sciatic nerve crush injury in a rat model. J Neurosurg. 2011; Feb. 114(2):522–8.
Article20. Werner H, LeRoith D. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors in the brain: physiological and pathological aspects. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014; Dec. 24(12):1947–53.
Article21. Tiangco DA, Papakonstantinou KC, Mullinax KA, Terzis JK. IGF-I and end-to-side nerve repair: a dose-response study. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2001; May. 17(4):247–56.
Article22. D’Ercole AJ, Ye P, O’Kusky JR. Mutant mouse models of insulin-like growth factor actions in the central nervous system. Neuropeptides. 2002; Apr-Jun. 36(2-3):209–20.
Article23. Yuan Q, Wu W, So KF, Cheung AL, Prevette DM, Oppenheim RW. Effects of neurotrophic factors on motoneuron survival following axonal injury in newborn rats. Neuroreport. 2000; Jul. 11(10):2237–41.
Article24. Ozdinler PH, Macklis JD. IGF-I specifically enhances axon outgrowth of corticospinal motor neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2006; Nov. 9(11):1371–81.
Article25. Kimpinski K, Mearow K. Neurite growth promotion by nerve growth factor and insulin-like growth factor-1 in cultured adult sensory neurons: role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and mitogen activated protein kinase. J Neurosci Res. 2001; Mar. 63(6):486–99.
Article26. Kiryakova S, Sohnchen J, Grosheva M, Schuetz U, Marinova TS, Dzhupanova R, et al. Recovery of whisking function promoted by manual stimulation of the vibrissal muscles after facial nerve injury requires insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). Exp Neurol. 2010; Apr. 222(2):226–34.
Article27. Gnavi S, di Blasio L, Tonda-Turo C, Mancardi A, Primo L, Ciardelli G, et al. Gelatin-based hydrogel for vascular endothelial growth factor release in peripheral nerve tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017; Feb. 11(2):459–70.
Article28. Lee KY, Nakagawa T, Okano T, Hori R, Ono K, Tabata Y, et al. Novel therapy for hearing loss: delivery of ınsulin-like growth factor 1 to the cochlea using gelatin hydrogel. Otol Neurotol. 2007; Oct. 28(7):976–81.29. Komobuchi H, Hato N, Teraoka M, Wakisaka H, Takahashi H, Gyo K, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor combined with biodegradable hydrogel promotes healing of facial nerve after compression injury: an experimental study. Acta Otolaryngol. 2010; Jan. 130(1):173–8.
Article30. Grosheva M, Wittekindt C, Guntinas-Lichius O. Prognostic value of electroneurography and electromyography in facial palsy. Laryngoscope. 2008; Mar. 118(3):394–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adenoviral vector mediated in vivo gene transfer of BDNF promote functional recovery after facial nerve crush injury
- Expression of Neurotrophic Factors and Their Receptors mRNAs in the Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Following Peripheral Nerve Injury
- Expression of Toll-Like Receptor Messenger Ribonucleic Acid in the Distal Facial Nerve After Facial Nerve Injury
- Enhancing the Effect of Placental Extract on the Regeneration of Crush Injured Facial Nerve
- Relationship of Insulin like Growth Factor I with Pharmacologically Stimulated Growth Hormone Secretion in Growth Hormone Deficient Children