Korean J Ophthalmol.
2017 Dec;31(6):568-569. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0109.
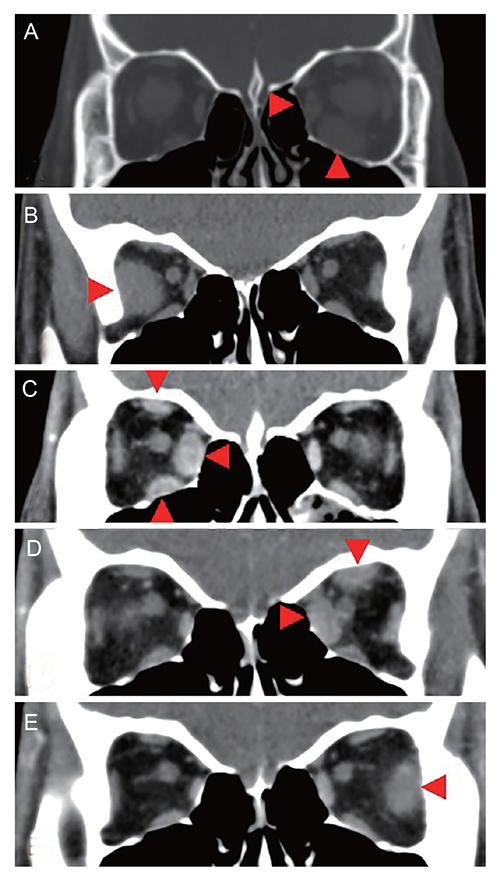
Alternating and Relapsing Migratory Orbital Myositis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yswoph@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2396708
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0109
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kennerdell JS, Dresner SC. The nonspecific orbital inflammatory syndromes. Surv Ophthalmol. 1984; 29:93–103.2. Lutt JR, Lim LL, Phal PM, Rosenbaum JT. Orbital inflammatory disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 37:207–222.3. Mombaerts I, Koornneef L. Current status in the treatment of orbital myositis. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104:402–408.4. Swamy BN, McCluskey P, Nemet A, et al. Idiopathic orbital inflammatory syndrome: clinical features and treatment outcomes. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007; 91:1667–1670.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Idiopathic Orbital Myositis Involving All Extraocular Muscles of Both Eyes
- A Case of Oribital Myositis
- Effect of Corticosteroid on Orbital Pseudotumor Caused by Orbital Myositis
- Superior Rectus-Levator Palpebrae Complex Myositis Presenting as Isolated Painless Ptosis
- A Case of Idiopathic Orbital Myositis