J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Dec;77(6):396-403. 10.3348/jksr.2017.77.6.396.
Physiologic Flow Related Signal Intensity in Dural Sinuses on Time of Flight Magnetic Resonance Angiography: Changes Caused by Head Elevation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea. skbaik9@gmail.com
- 2Research Institute of Convergence for Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Department of Statistics, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2396498
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.77.6.396
Abstract
- PURPOSE
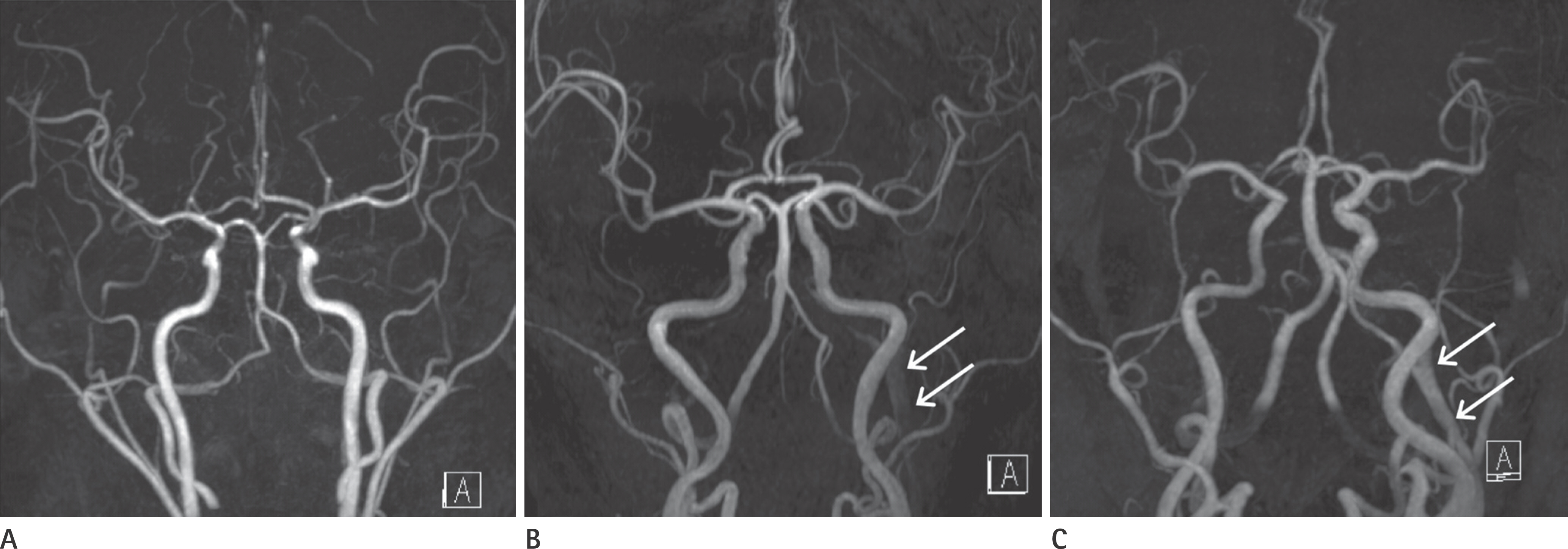
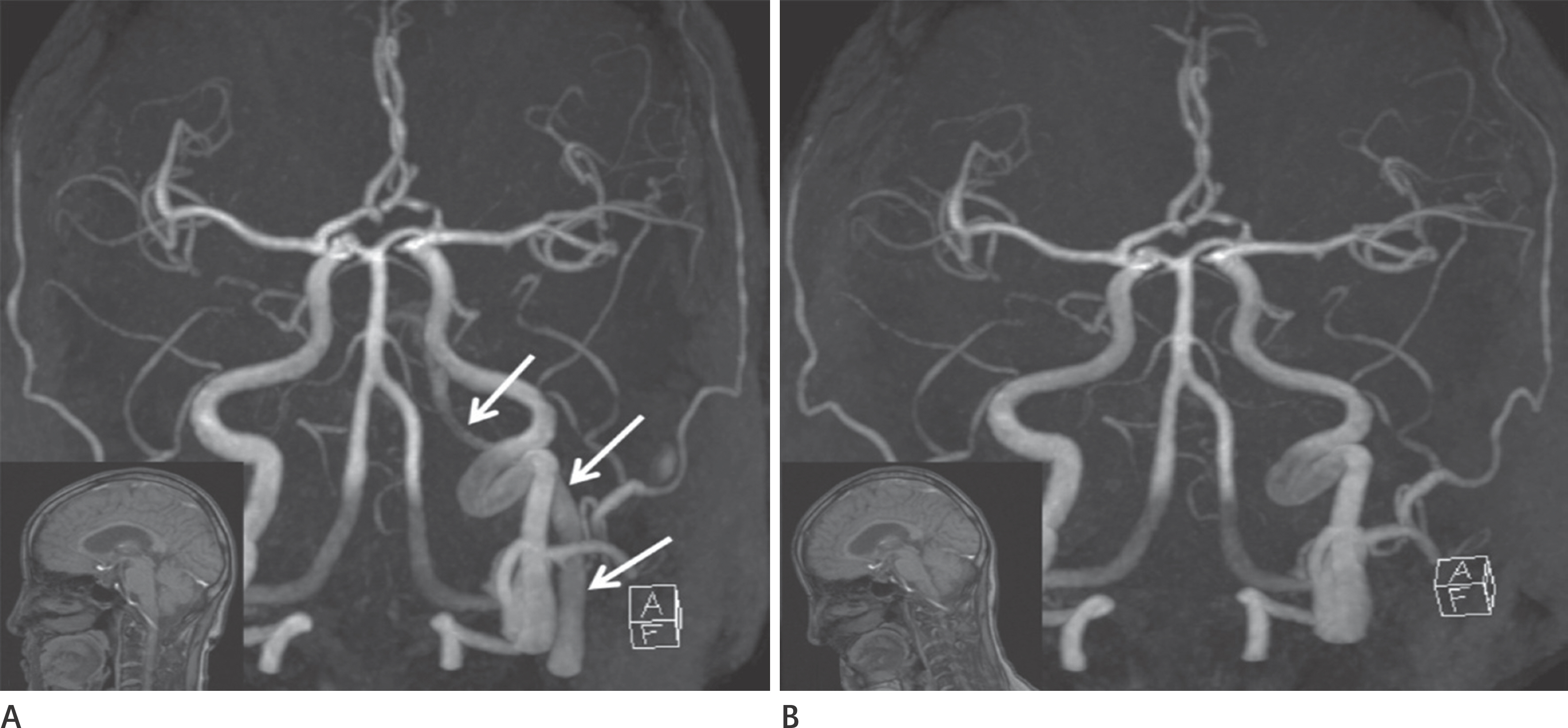
The presence of a flow-related signal in the normal dural sinus time of flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF MRA) is common. This study aimed to identify changes in signal intensity in the dural sinus caused by changes in patient position.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The researchers performed an elevation TOF MRA of the cerebral region in 52 patients, who showed abnormal flow-related signals in the dural sinuses on supine position. Flow-related signal intensity in the dural sinuses was then analyzed.
RESULTS
Flow-related signals were seen in 114 sites (52 patients), specifically in the internal jugular vein (IJV), sigmoid sinus (SS), inferior petrosal sinus (IPS), and cavernous sinus (CS) in 29 sites, 33 sites, 32 sites, and 20 sites, respectively. After head elevation, flow-related signal changes were then observed in the IJV, SS, IPS, and CS in 107 sites (107/114, 93.9%). There was loss of signal (62/114, 54.4%), or decrease (39/114, 34.2%), increase (6/114, 5.3%), or no change (7/114, 6.1%) in the signal intensity, and flow related signals were more frequent on the left than on the right.
CONCLUSION
Flow-related signals in the dural sinuses on TOF MRA were decreased or disappeared by head elevation in 88.6% of the sites. Head elevation may help distinguish between pathologic and physiologic states.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Niggemann P., Seifert M., Förg A., Schild HH., Urbach H., Krings T. Positional venous MR angiography: an operator-inde-pendent tool to evaluate cerebral venous outflow hemody-namics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012. 33:246–251.
Article2.Hirai T., Korogi Y., Hamatake S., Ikushima I., Sugahara T., Sige-matsu Y, et al. Three-dimensional FISP imaging in the eval-uation of carotid cavernous fistula: comparison with contrast-enhanced CT and spin-echo MR. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998. 19:253–259.3.Chen JC., Tsuruda JS., Halbach VV. Suspected dural arterio-venous fistula: results with screening MR angiography in seven patients. Radiology. 1992. 183:265–271.
Article4.Watanabe K., Kakeda S., Watanabe R., Ohnari N., Korogi Y. Nor-mal flow signal of the pterygoid plexus on 3T MRA in patients without DAVF of the cavernous sinus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013. 34:1232–1236.
Article5.Paksoy Y., Genç BO., Genç E. Retrograde flow in the left infe-rior petrosal sinus and blood steal of the cavernous sinus as-sociated with central vein stenosis: MR angiographic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003. 24:1364–1368.6.Ouanounou S., Tomsick TA., Heitsman C., Holland CK. Cavern-ous sinus and inferior petrosal sinus flow signal on three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999. 20:1476–1481.7.Kudo K., Terae S., Ishii A., Omatsu T., Asano T., Tha KK, et al. Physi-ologic change in flow velocity and direction of dural venous sinuses with respiration: MR venography and flow analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004. 25:551–557.8.Cornelius R. CCF: imaging evaluation. Tomsick TA, editor. , ed.Carotid cavernous fistula. Cincinnati, OH: Digital Education-al Publishing;1997. 23–31.9.Niggemann P., Kuchta J., Grosskurth D., Beyer HK., Krings T., Reinges M. Position dependent changes of the cerebral ve-nous drainage--implications for the imaging of the cervical spine. Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2011. 72:32–37.10.Epstein HM., Linde HW., Crampton AR., Ciric IS., Eckenhoff JE. The vertebral venous plexus as a major cerebral venous out-flow tract. Anesthesiology. 1970. 32:332–337.
Article11.Mehta NR., Jones L., Kraut MA., Melhem ER. Physiologic vari-ations in dural venous sinus flow on phase-contrast MR im-aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 175:221–225.
Article12.Alperin N., Hushek SG., Lee SH., Sivaramakrishnan A., Lichtor T. MRI study of cerebral blood flow and CSF flow dynamics in an upright posture: the effect of posture on the intracra-nial compliance and pressure. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2005. 95:177–181.
Article13.Valdueza JM., von Münster T., Hoffman O., Schreiber S., Ein-häupl KM. Postural dependency of the cerebral venous out-flow. Lancet. 2000. 355:200–201.14.Sakamoto M., Taoka T., Iwasaki S., Nakagawa H., Fukusumi A., Takayama K, et al. Paradoxical parasellar high signals re-sembling shunt diseases on routine 3D time-of-flight MR angiography of the brain: mechanism for the signals and dif-ferential diagnosis from shunt diseases. Magn Reson Imaging. 2004. 22:1289–1293.
Article15.Tanaka T., Uemura K., Takahashi M., Takehara S., Fukaya T., Tokuyama T, et al. Compression of the left brachiocephalic vein: cause of high signal intensity of the left sigmoid sinus and internal jugular vein on MR images. Radiology. 1993. 188:355–361.
Article16.Uchino A., Nomiyama K., Takase Y., Nakazono T., Tominaga Y., Imaizumi T, et al. Retrograde flow in the dural sinuses detect-ed by three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography. Neuroradiology. 2007. 49:211–215.
Article17.San Millán Ruíz D., Gailloud P., Rüfenacht DA., Delavelle J., Henry F., Fasel JH. The craniocervical venous system in re-lation to cerebral venous drainage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002. 23:1500–1508.18.Gisolf J., van Lieshout JJ., van Heusden K., Pott F., Stok WJ., Karemaker JM. Human cerebral venous outflow pathway depends on posture and central venous pressure. J Physiol. 2004. 560(Pt 1):317–327.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Artifacts in MR Angiography of the Intracranial Vessels Using the 3D TOF and 3D PC Techniques
- Flow Signal Characteristics in 3 Dimensional Time of Flight MR Angiography Using Flow Phantom
- Resolved Cerebral Venous Hypertension after Angioplasty of Central Venous Stenosis in a Hemodialysis Patient: A Case Report
- MR Angiography of Stenosis and Aneurysm Models in the Pulsatile Flow: Variation with Imaging Parameters and Concentration of Contrast Media
- Image Quality of the 3 Dimensional Phase-Contrast Technique in an Intracranial Magnetic Resonance Angiography with Artifacts Caused by Orthodontic Devices: A Comparison with 3 Dimensional Time-of-Flight Technique