Yonsei Med J.
2008 Feb;49(1):151-154.
Irreversible Paraplegia Following One Time Prophylactic Intrathecal Chemotherapy in an Adult Patient with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Gyeong-Sang National University, Jinju, Korea. brightree@lycos.co.kr
- 2Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Gyeongnam Regional Cancer Center, Jinju, Korea.
Abstract
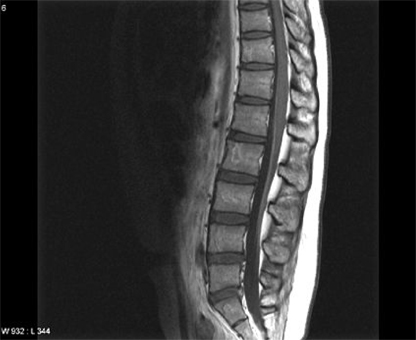
- We present an adult female patient who developed irreversible paraplegia and areflexia four days post intrathecal chemotherapy with methotrexate, cytosine arabinoside and hydrocortisone. On magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lumbar spine, diffuse gadolinium enhancement of the anterior spinal nerve roots (ventral roots) was detected. Methylprednisolone was intravenously administered at a daily dose of 30mg/kg for three days. Despite this treatment, flaccid weakness in the lower extremities and urinary retention persisted. Following consolidation chemotherapy, no improvement in neurologic status was noted. Six months later, a follow-up MRI revealed severe atrophy of the thoracic spinal cord.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bleyer WA, Poplack DG. Prophylaxis and treatment of leukemia in the central nervous system and other sanctuaries. Semin Oncol. 1985. 12:131–148.2. Bay A, Oner AF, Etlik O, Yilmaz C, Caksen H. Myelopathy due to intrathecal chemotherapy: report of six cases. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2005. 27:270–272.3. Skullerud K, Halvorsen K. Encephalomyelopathy following intrathecal methotrexate treatment in a child with acute leukemia. Cancer. 1978. 42:1211–1215.
Article4. Boogerd W, Moffie D, Smets LA. Early blindness and coma during intrathecal chemotherapy for meningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer. 1990. 65:452–457.
Article5. Breuer AC, Pitman SW, Dawson DM, Schoene WC. Paraparesis following intrathecal cytosine arabinoside: a case report with neuropathologic findings. Cancer. 1977. 40:2817–2822.
Article6. Clark AW, Cohen SR, Nissenblatt MJ, Wilson SK. Paraplegia following intrathecal chemotherapy: neuropathologic findings and elevation of myelin basic protein. Cancer. 1982. 50:42–47.
Article7. Dunton SF, Nitschke R, Spruce WE, Bodensteiner J, Krous HF. Progressive ascending paralysis following administration of intrathecal and intravenous cytosine arabinoside. A Pediatric Oncology Group Study. Cancer. 1986. 57:1083–1088.
Article8. Gagliano RG, Costanzi JJ. Paraplegia following intrathecal methotrexate: report of a case and review of the literature. Cancer. 1976. 37:1663–1668.
Article9. Grisold W, Lutz D, Wolf D. Necrotizing myelopathy associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Case report and review of literature. Acta Neuropathol. 1980. 49:231–235.
Article10. Luddy RE, Gilman PA. Paraplegia following intrathecal methotrexate. J Pediatr. 1973. 83:988–992.
Article11. Mena H, Garcia JH, Velandia F. Central and peripheral myelinopathy associated with systemic neoplasia and chemotherapy. Cancer. 1981. 48:1724–1737.
Article12. Norman M, Elinder G, Finkel Y. Vincristine neuropathy and a Guillain-Barré syndrome: a case with acute lymphatic leukemia and quadriparesis. Eur J Haematol. 1987. 39:75–76.
Article13. Ojeda VJ. Necrotizing myelopathy associated with malignancy. A clinicopathologic study of two cases and literature review. Cancer. 1984. 53:1115–1123.
Article14. Resar LM, Phillips PC, Kastan MB, Leventhal BG, Bowman PW, Civin CI. Acute neurotoxicity after intrathecal cytosine arabinoside in two adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia of B-cell type. Cancer. 1993. 71:117–123.
Article15. Saiki JH, Thompson S, Smith F, Atkinson R. Paraplegia following intrathecal chemotherapy. Cancer. 1972. 29:370–374.
Article16. Werner RA. Paraplegia and quadriplegia after intrathecal chemotherapy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1988. 69:1054–1056.17. Wolff L, Zighelboim J, Gale RP. Paraplegia following intrathecal cytosine arabinoside. Cancer. 1979. 43:83–85.
Article18. Koh S, Nelson MD Jr, Kovanlikaya A, Chen LS. Anterior lumbosacral radiculopathy after intrathecal methotrexate treatment. Pediatr Neurol. 1999. 21:576–578.
Article19. Gilbert MR, Harding BL, Grossman SA. Methotrexate neurotoxicity: In vitro studies using cerebellar explants from rats. Cancer Res. 1989. 49:2502–2505.20. Watterson J, Toogood I, Nieder M, Morse M, Frierdich S, Lee Y, et al. Excessive spinal cord toxicity from intensive central nervous system-directed therapies. Cancer. 1994. 74:3034–3041.
Article21. Bleyer WA, Drake JC, Chabner BA. Neurotoxicity and elevated cerebrospinal-fluid methotrexate concentration in meningeal leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1973. 289:770–773.
Article22. Sherman PM, Belden CJ, Nelson DA. Magnetic resonance imaging findings in a case of cytarabine-induced myelopathy. Mil Med. 2002. 167:157–160.
Article23. Shore T, Barnett MJ, Phillips GL. Sudden neurologic death after intrathecal methotrexate. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1990. 18:159–161.
Article24. von der Weid NX, de Crousaz H, Beck D, Deonna T, Miklossy J, Janzer RC. Acute fatal myeloencephalopathy after combined intrathecal chemotherapy in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1991. 19:192–198.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Paraplegia Associated with Intrathecal Methotrexate : A case report
- Paraplegia Due to Spinal Hematoma in a Patient with Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia: A case report
- Tracheoesophageal Fistula Resulting from Invasive Aspergillosis in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Case Report
- Intermittent central nervous system irradiation and intrathecal chemotherapy for recurrent central nervous system leukemia in children
- A Case of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Accompanied with Lactic Acidosis and Kidney Enlargement