Clin Endosc.
2017 Sep;50(5):446-450. 10.5946/ce.2016.118.
Pneumothorax after Colonoscopy – A Review of Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of General Surgery, Doncaster Royal Infirmary, Doncaster, UK. ajaysurgeon@gmail.com
- KMID: 2394744
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.118
Abstract
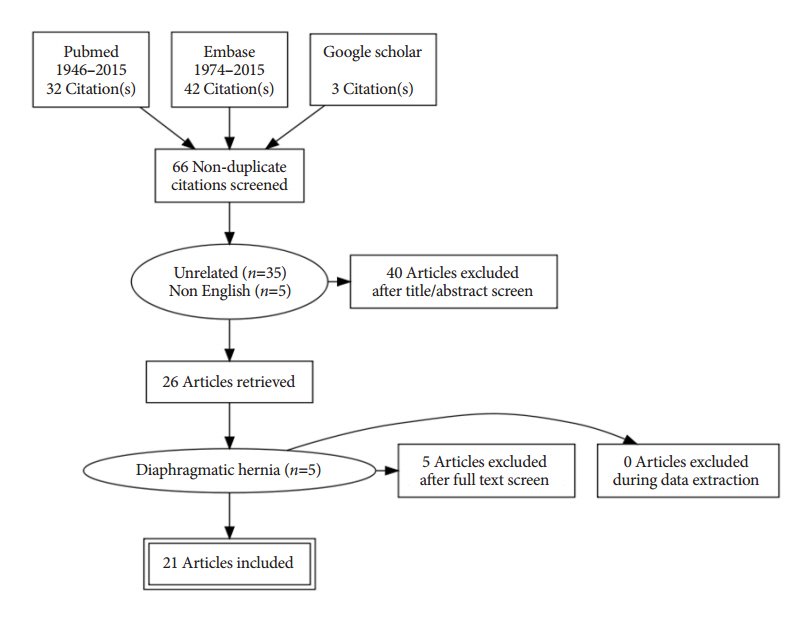
- The purpose of this study was to determine the anatomical aspects, mechanisms, risk factors and appropriate management of development of pneumothorax during a routine colonoscopy. A systematic search of the literature (MEDLINE, Embase and Google Scholar) revealed 21 individually documented patients of pneumothorax following a colonoscopy, published till December 2015. One additional patient treated at our center was added. A pooled analysis of these 22 patients was performed including patient characteristics, indication of colonoscopy, any added procedure, presenting symptoms,risk factors and treatment given. The review suggested that various risk factors may be female gender, therapeutic interventions, difficult colonoscopy and underlying bowel pathology. Diagnosis of this condition requires a high index of suspicion and treatment should be tailored to individual needs.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Damore LJ 2nd, Rantis PC, Vernava AM 3rd, Longo WE. Colonoscopic perforations. Etiology, diagnosis, and management. Dis Colon Rectum. 1996; 39:1308–1314.2. Bakker J, van Kersen F, Bellaar Spruyt J. Pneumopericardium and pneumomediastinum after polypectomy. Endoscopy. 1991; 23:46–47.
Article3. Humphreys F, Hewetson KA, Dellipiani AW. Massive subcutaneous emphysema following colonoscopy. Endoscopy. 1984; 16:160–161.
Article4. Amshel AL, Shonberg IL, Gopal KA. Retroperitoneal and mediastinal emphysema as a complication of colonoscopy. Dis Colon Rectum. 1982; 25:167–168.
Article5. Fishman EK, Goldman SM. Pneumoscrotum after colonoscopy. Urology. 1981; 18:171–172.
Article6. Ota H, Fujita S, Nakamura T, et al. Pneumoretroperitoneum, pneumomediastinum, pneumopericardium, and subcutaneous emphysema complicating sigmoidoscopy: report of a case. Surg Today. 2003; 33:305–308.
Article7. Meyers MA, Ghahremani GG. Complications of fiberoptic endoscopy. II. Colonoscopy. Radiology. 1975; 115:301–307.8. Thomas JH, Pierce GE, MacArthur RI. Bilateral pneumothoraces secondary to colonic endoscopy. J Natl Med Assoc. 1979; 71:701–702.9. Schmidt G, Börsch G, Wegener M. Subcutaneous emphysema and pneumothorax complicating diagnostic colonoscopy. Dis Colon Rectum. 1986; 29:136–138.
Article10. Tam WC, Pollard I, Johnson RD. Case report: pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax complicating colonoscopy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996; 11:789–792.
Article11. Ho HC, Burchell S, Morris P, Yu M. Colon perforation, bilateral pneumothoraces, pneumopericardium, pneumomediastinum, and subcutaneous emphysema complicating endoscopic polypectomy: anatomic and management considerations. Am Surg. 1996; 62:770–774.12. Webb T. Pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum during colonoscopy. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1998; 26:302–304.
Article13. Hearnshaw SA, Oppong K, Jaques B, Thompson NP. Tension pneumothorax as a complication of colonoscopy. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:190.
Article14. Ball CG, Kirkpatrick AW, Mackenzie S, et al. Tension pneumothorax secondary to colonic perforation during diagnostic colonoscopy: report of a case. Surg Today. 2006; 36:478–480.
Article15. Zeno BR, Sahn SA. Colonoscopy-associated pneumothorax: a case of tension pneumothorax and review of the literature. Am J Med Sci. 2006; 332:153–155.
Article16. Lovisetto F, Zonta S, Rota E, et al. Left pneumothorax secondary to colonoscopic perforation of the sigmoid colon: a case report. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2007; 17:62–64.
Article17. Marwan K, Farmer KC, Varley C, Chapple KS. Pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pneumoperitoneum, pneumoretroperitoneum and subcutaneous emphysema following diagnostic colonoscopy. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2007; 89:W20–W21.
Article18. Ignjatović M, Jović J. Tension pneumothorax, pneumoretroperitoneum, and subcutaneous emphysema after colonoscopic polypectomy: a case report and review of the literature. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2009; 394:185–189.
Article19. Chan YC, Tsai YC, Fang SY. Subcutaneous emphysema, pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, and pneumoperitoneum during colonoscopic balloon dilation: a case report. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2010; 26:669–672.
Article20. Thimmapuram J, Panchwagh R, Manzella J. Colonoscopy and biopsy associated bilateral pneumothoraces, pneumomediastinum, pneumoperitoneum, pneumoretroperitoneum and subcutaneous emphysema. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105(Suppl 1):S308.
Article21. Kipple JC. Bilateral tension pneumothoraces and subcutaneous emphysema following colonoscopic polypectomy: a case report and discussion of anesthesia considerations. AANA J. 2010; 78:462–467.22. Gorantla S, Culpepper-Morgan J. Pneumothorax following colonoscopic polypectomy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107(Suppl 1):S555.
Article23. Bonner KP, Ramcharan A. Asymptomatic isolated right sided pneumothorax after screening colonoscopy with polypectomy. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27(Suppl 1):S479.24. Durì D, Toso F, De Monte A. Pneumoperitoneum and pneumothorax complicating colonoscopy. BMJ. 2013; 346:f2516.
Article25. Sheikh R, Hou J. Case of diffuse air leak associated with colonoscopy in a patient with perianal Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19(Suppl 1):S78.26. Pourmand A, Shokoohi H. Tension pneumothorax, pneumoperitoneum, and cervical emphysema following a diagnostic colonoscopy. Case Rep Emerg Med. 2013; 2013:583287.
Article27. Dehal A, Tessier DJ. Intraperitoneal and extraperitoneal colonic perforation following diagnostic colonoscopy. JSLS. 2014; 18:136–141.
Article28. Brayko CM, Kozarek RA, Sanowski RA, Howells T. Diverticular rupture during colonoscopy. Fact or fancy? Dig Dis Sci. 1984; 29:427–431.29. Maunder RJ, Pierson DJ, Hudson LD. Subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Arch Intern Med. 1984; 144:1447–1453.
Article30. Saunders BP, Fukumoto M, Halligan S, et al. Why is colonoscopy more difficult in women? Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 43(2 Pt 1):124–126.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pneumothorax, Pneumomediastinum, Subcutaneous Emphysema, Pneumoretroperitoneum Secondary to Colonoscopic Perforation
- A case of Pneumothorax due to Paragonimiasis with Family
- Unilateral Tension Pneumothorax following Induction of Anesthesia A Case Report
- Pneumoretroperitoneum, Pneumomediastinum, Pneumothorax, and Subcutaneous Emphysema after Diagnostic Colonoscopy
- Congenital Pyriform Sinus Fistula Complicated with Pneumothorax and Pneumopericardium in a Neonate: A Case Report