J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Nov;77(5):344-347. 10.3348/jksr.2017.77.5.344.
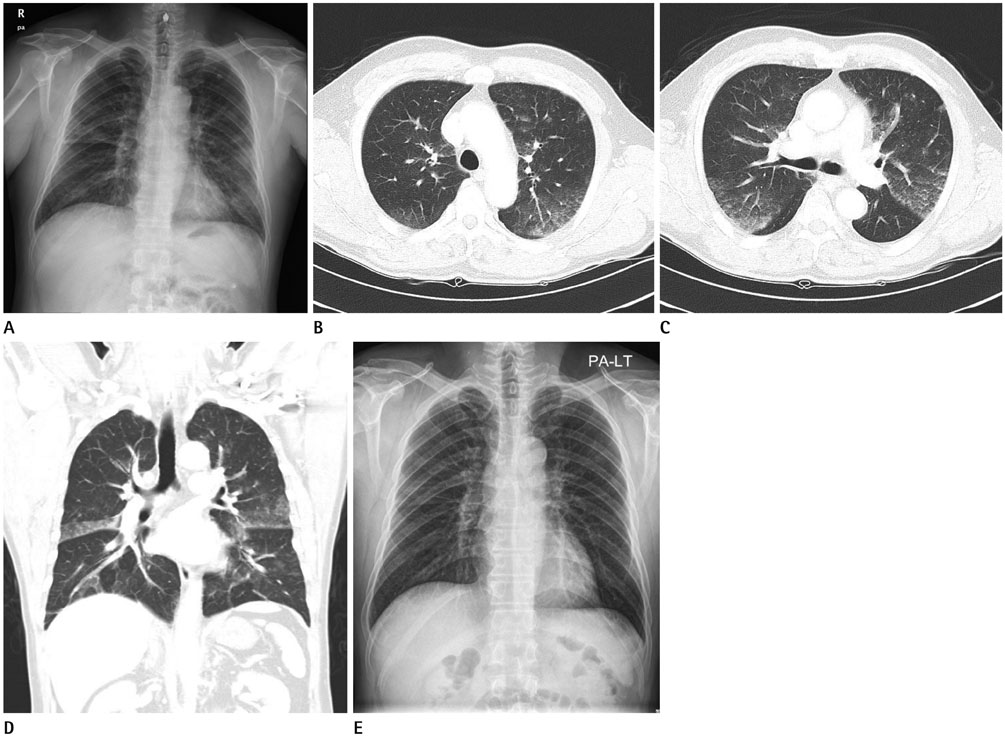
Snorkeling-Induced Pulmonary Hemorrhage: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. haneul88@hanmail.net
- 2Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2394050
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.77.5.344
Abstract
- Swimming induced pulmonary alveolar hemorrhage is a rare disease. Here, we report a case of alveolar hemorrhage after snorkeling.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Srámek P, Simecková M, Janský L, Savlíková J, Vybíral S. Human physiological responses to immersion into water of different temperatures. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2000; 81:436–442.2. Stocks JM, Patterson MJ, Hyde DE, Jenkins AB, Mittleman KD, Taylor NA. Effects of immersion water temperature on whole-body fluid distribution in humans. Acta Physiol Scand. 2004; 182:3–10.3. Coulange M, Rossi P, Gargne O, Gole Y, Bessereau J, Regnard J, et al. Pulmonary oedema in healthy SCUBA divers: new physiopathological pathways. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2010; 30:181–186.4. Boussuges A, Rostain JC. What cardiovascular changes during SCUBA diving? Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2013; 209:9–1.5. Gabrielsen A, Johansen LB, Norsk P. Central cardiovascular pressures during graded water immersion in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1993; 75:581–558.6. Tsai MJ, Tsai MS, Tsai YM, Lien CT, Hwang JJ, Huang MS. Alveolar hemorrhage after scuba diving: a case report. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2010; 26:389–392.7. Boussuges A, Pinet C, Thomas P, Bergmann E, Sainty JM, Vervloet D. Haemoptysis after breath-hold diving. Eur Respir J. 1999; 13:697–699.8. Smith DJ. Diagnosis and management of diving accidents. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1996; 28:587–590.9. Balk M, Goldman JM. Alveolar hemorrhage as a manifestation of pulmonary barotrauma after scuba diving. Ann Emerg Med. 1990; 19:930–934.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulmonary hemorrhage accompanied with pulmonary edema induced by endotracheal tube occlusion in a child: A case report
- A Case of Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia with Diffuse Pulmonary Hemorrhage
- An Unusual Radiologic Manifestation of Pulmonary Tuberculosis with Bilateral Multiple Lung Nodules and Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: A Case Report
- A Case of Successful Treatment of Pulmonary Alveolar Hemorrhage with Plasmapheresis in Child with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Pulmonary Hemorrhage with Hemoptysis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosis