Korean Circ J.
2017 Jul;47(4):477-483. 10.4070/kcj.2017.0004.
Increased Arterial Stiffness in Behçet's Disease: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Bassett Medical Center and Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, Cooperstown, NY, USA. waichung.yong@outlook.com
- 2Department of Preventive and Social Medicine, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand.
- KMID: 2392885
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2017.0004
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Behçet's disease (BD) is a systemic vasculitis that is characterized by genital, oral, or skin lesions, uveitis, and vascular complications. Studies have shown that increased arterial stiffness is common in systemic immune and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. However, current research has not yet determined whether patients with BD have increased arterial stiffness. This meta-analysis compares arterial stiffness parameters in subjects with a BD diagnosis to normal subjects.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
A comprehensive search of the MEDLINE and EMBASE databases was performed from the database beginning through May 2016. Observation studies were included in this analysis if they assessed the association between BD and arterial stiffness in adult subjects. BD patients met the International Study Group criteria for a diagnosis of Behçet's disease. Aortic stiffness was assessed using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (PWV) measurements as an indicator. Pooled mean difference (MD) of PWV and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using a random-effect, generic inverse variance meta-analysis. The between-study heterogeneity of effect-size was quantified using the Q statistic and I².
RESULTS
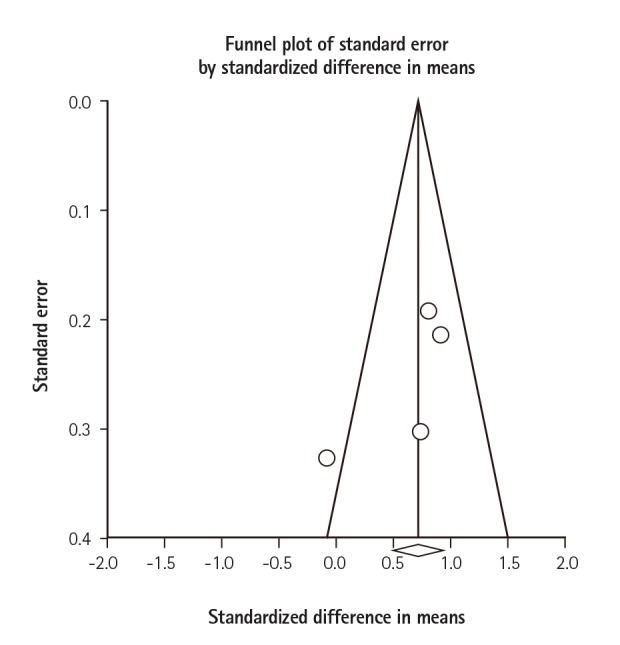
Data were extracted from four observational studies that included 303 subjects. PWV is significantly higher in patients with Behçet's disease compared with controls (MD=0.74;95%, CI: 0.28-1.20, p=0.002, I²=63%).
CONCLUSION
In this meta-analysis, we observed that PWV, an ideal indicator of arterial stiffness, is increased in patients with Behçet's disease compared with the controls. Prospective studies in a large population should be done to determine the pathophysiological and prognostic implications of increased arterial stiffness in BD.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Seyahi E. Behçet's disease: how to diagnose and treat vascular involvement. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2016; 30:279–295. PMID: 27886800.2. Hingorani AD, Cross J, Kharbanda RK, et al. Acute systemic inflammation impairs endothelium-dependent dilatation in humans. Circulation. 2000; 102:994–999. PMID: 10961963.3. Klocke R, Cockcroft JR, Taylor GJ, Hall IR, Blake DR. Arterial stiffness and central blood pressure, as determined by pulse wave analysis, in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003; 62:414–418. PMID: 12695151.4. Kayikçioğlu M, Aksu K, Hasdemir C, et al. Endothelial functions in behçet's disease. Rheumatol Int. 2006; 26:304–308. PMID: 15739096.5. Haznedaroglu E, Karaaslan Y, Büyükaşik Y, et al. Selectin adhesion molecules in behçet's disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000; 59:61–63. PMID: 10627429.6. Oztürk MA, Unverdi S, Oktar SO, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with behçet's disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2008; 27:961–966. PMID: 18204875.7. Kiraz S, Ertenli I, Oztürk MA, Haznedaroğlu IC, Celik I, Calgüneri M. Pathological haemostasis and “prothrombotic state” in behçet's disease. Thromb Res. 2002; 105:125–133. PMID: 11958802.8. Rhee MY, Chang HK, Kim SK. Intima-media thickness and arterial stiffness of carotid artery in Korean patients with behçet's disease. J Korean Med Sci. 2007; 22:387–392. PMID: 17596642.9. Patel RS, Al Mheid I, Morris AA, et al. Oxidative stress is associated with impaired arterial elasticity. Atherosclerosis. 2011; 218:90–95. PMID: 21605864.10. Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA. 2000; 283:2008–2012. PMID: 10789670.11. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the newcastle-ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010; 25:603–605. PMID: 20652370.12. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327:557–560. PMID: 12958120.13. Sterne JA, Egger M. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: guidelines on choice of axis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2001; 54:1046–1055. PMID: 11576817.14. Caldas CA, Borba EF, Bortolotto LA, Medeiros DM, Bonfa E, Gonçalves CR. Increased arterial stiffness assessed by pulse wave velocity in behçet's disease and its association with the lipid profile. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013; 27:454–459. PMID: 22329367.15. Kürüm T, Yildiz M, Soy M, Ozbay G, Alimgil L, Tüzün B. Arterial distensibility as determined by carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity in patients with behçet's disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2005; 24:134–138. PMID: 15365878.16. Chang HK, Kim SK, Lee SS, Rhee MY. Arterial stiffness in behçet's disease: increased regional pulse wave velocity values. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006; 65:415–416. PMID: 16474038.17. Yilmaz S, Celik G, Esmen SE. Assessment of arterial stiffness in patients with inactive and active behçet's disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2014; 43:63–69. PMID: 24015673.18. Butta NV, Fernández-Bello I, López-Longo FJ, Jiménez-Yuste V. Endothelial dysfunction and altered coagulation as mediators of thromboembolism in behçet disease. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2015; 41:621–628. PMID: 26276934.19. Mattace-Raso FU, van der Cammen TJ, Hofman A, et al. Arterial stiffness and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: the rotterdam study. Circulation. 2006; 113:657–663. PMID: 16461838.20. Imura T, Yamamoto K, Kanamori K, Mikami T, Yasuda H. Non-invasive ultrasonic measurement of the elastic properties of the human abdominal aorta. Cardiovasc Res. 1986; 20:208–214. PMID: 3518941.21. Izzo JL Jr. Arterial stiffness and the systolic hypertension syndrome. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2004; 19:341–352. PMID: 15218394.22. Davies JI, Struthers AD. Pulse wave analysis and pulse wave velocity: a critical review of their strengths and weaknesses. J Hypertens. 2003; 21:463–472. PMID: 12640232.23. Seyahi E, Ugurlu S, Cumali R, et al. Atherosclerosis in behçet's syndrome. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 38:1–12. PMID: 18221989.24. Alan S, Ulgen MS, Akdeniz S, Alan B, Toprak N. Intima-media thickness and arterial distensibility in behçet's disease. Angiology. 2004; 55:413–419. PMID: 15258687.25. Oztürk MA, Oktar SO, Unverdi S, et al. Morphologic evidence of subclinical atherosclerosis obtained by carotid ultrasonography in patients with behçet's disease. Rheumatol Int. 2006; 26:867–872. PMID: 16402216.26. Hong SN, Park JC, Yoon NS, et al. Carotid artery intima-media thickness in behçet's disease patients without significant cardiovascular involvement. Korean J Intern Med. 2008; 23:87–93. PMID: 18646511.27. Balta I, Balta S, Koryurek OM, et al. Mean platelet volume is associated with aortic arterial stiffness in patients with behçet's disease without significant cardiovascular involvement. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014; 28:1388–1393. PMID: 24164056.28. Celik G, Yilmaz S, Ergulu Esmen S. Non-dipping blood pressure patterns and arterial stiffness parameters in patients with behçet's disease. Hypertens Res. 2015; 38:856–861. PMID: 26268564.29. Uyar B, Solak A, Genç B, et al. Evaluation of arterial stiffness in patients with behçet's disease by using noninvasive radiological methods such as intima-media thickness of the carotid, ankle-brachial pressure index, coronary artery calcium scoring, and their relation to serum fetuin-a levels: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol. 2015; 27:702–708. PMID: 26719639.30. Davatchi F. Diagnosis/classification criteria for behçet's disease. Patholog Res Int. 2012; 2012:607921. PMID: 21961081.