Korean Circ J.
2017 Jul;47(4):432-439. 10.4070/kcj.2016.0406.
Combining Potent Statin Therapy with Other Drugs to Optimize Simultaneous Cardiovascular and Metabolic Benefits while Minimizing Adverse Events
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. kwangk@gilhospital.com
- 2Gachon Cardiovascular Research Institute, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Cardiovascular Medicine, Hokko Memorial Clinic, Health Sciences University of Hokkaido, Sapporo, Japan.
- 4Cardiovascular Medicine, Juntendo University Graduate School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
- 5Department of Geriatrics, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan.
- 6Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Nutrition, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, USA.
- KMID: 2392877
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2016.0406
Abstract
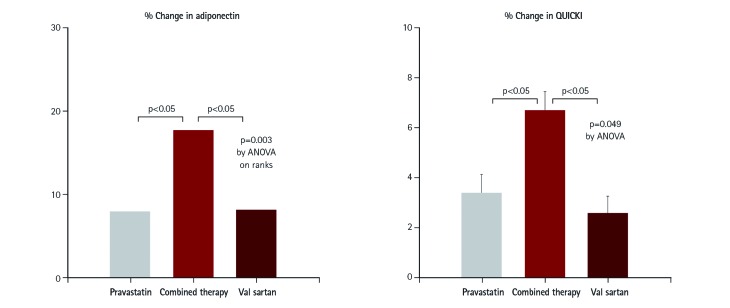
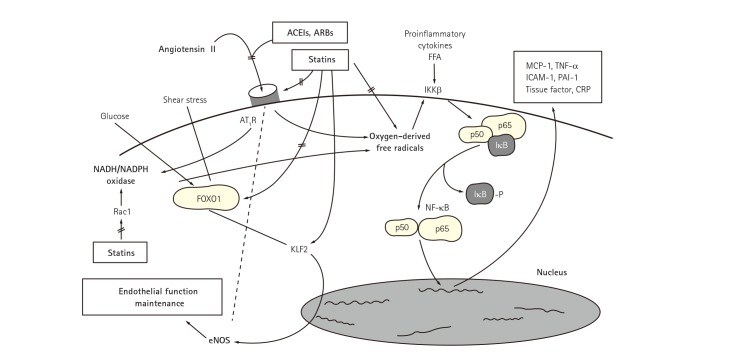
- Hypercholesterolemia and hypertension are among the most important risk factors for cardiovascular (CV) disease. They are also important contributors to metabolic diseases including diabetes that further increase CV risk. Updated guidelines emphasize targeted reduction of overall CV risks but do not explicitly incorporate potential adverse metabolic outcomes that also influence CV health. Hypercholesterolemia and hypertension have synergistic deleterious effects on interrelated insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction. Dysregulation of the renin-angiotensin system is an important pathophysiological mechanism linking insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction to atherogenesis. Statins are the reference standard treatment to prevent CV disease in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Statins work best for secondary CV prevention. Unfortunately, most statin therapies dose-dependently cause insulin resistance, increase new onset diabetes risk and exacerbate existing type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pravastatin is often too weak to achieve target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels despite having beneficial metabolic actions. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors improve both endothelial dysfunction and insulin resistance in addition to controlling blood pressure. In this regard, combined statin-based and renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor therapies demonstrate additive/synergistic beneficial effects on endothelial dysfunction, insulin resistance, and other metabolic parameters in addition to lowering both cholesterol levels and blood pressure. This combined therapy simultaneously reduces CV events when compared to either drug type used as monotherapy. This is mediated by both separate and interrelated mechanisms. Therefore, statin-based therapy combined with RAS inhibitors is important for developing optimal management strategies in patients with hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, or obesity. This combined therapy can help prevent or treat CV disease while minimizing adverse metabolic consequences.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Atherosclerosis
Blood Pressure
Cardiovascular Diseases
Cholesterol
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2
Humans
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors*
Hypercholesterolemia
Hypertension
Insulin Resistance
Lipoproteins
Metabolic Diseases
Obesity
Pravastatin
Renin-Angiotensin System
Risk Factors
Cholesterol
Lipoproteins
Pravastatin
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of Pioglitazone in Combination with Moderate Dose Statin on Atherosclerotic Inflammation: Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Using Serial FDG-PET/CT
Eun Ho Choo, Eun-Ji Han, Chan Joon Kim, Sung-Hoon Kim, Joo-Hyun O, Kiyuk Chang, Ki-Bae Seung
Korean Circ J. 2018;48(7):591-601. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2017.0029.
Reference
-
1. Go AS, Bauman MA, Coleman King SM, et al. An effective approach to high blood pressure control a science advisory from the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63:1230–1238. PMID: 24246165.2. Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, et al. American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014; 129(25 Suppl 2):S1–S45. PMID: 24222016.3. Koh KK. Effects of statins on vascular wall: Vasomotor function, inflammation, and plaque stability. Cardiovasc Res. 2000; 47:648–657. PMID: 10974215.4. Kim JW, Yun KH, Kim EK, et al. Effect of high dose rosuvastatin loading before primary percutaneous coronary intervention on infarct size in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Korean Circ J. 2014; 44:76–81. PMID: 24653736.5. Jang JY, Lee SH, Kim BS, et al. Additive beneficial effects of valsartan combined with rosuvastatin in the treatment of hypercholesterolemic hypertensive patients. Korean Circ J. 2015; 45:225–233. PMID: 26023311.6. Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, et al. Distinct vascular and metabolic effects of different classes of anti-hypertensive drugs. Int J Cardiol. 2010; 140:73–81. PMID: 19059660.7. Koh KK, Han SH, Oh PC, Shin EK, Quon MJ. Combination therapy for treatment or prevention of atherosclerosis: focus on the lipid-RAAS interaction. Atherosclerosis. 2010; 209:307–313. PMID: 19800624.8. Lee HY, Sakuma I, Ihm SH, Goh CW, Koh KK. Statins and renin-angiotensin system inhibitor combination treatment to prevent cardiovascular disease. Circ J. 2014; 78:281–287. PMID: 24401609.9. Koh KK, Sakuma I, Hayashi T, Kim SH, Chung WJ. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitor and statins combination therapeutics - what have we learnt? Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015; 16:949–953. PMID: 25747324.10. Koh KK, Ahn JY, Han SH, et al. Pleiotropic effects of angiotensin II receptor blocker in hypertensive patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003; 42:905–910. PMID: 12957441.11. Mikus CR, Boyle LJ, Borengasser SJ, et al. Simvastatin impairs exercise training adaptations. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 62:709–714. PMID: 23583255.12. Lee DS, Markwardt S, Goeres L, et al. Statins and physical activity in older men: the osteoporotic fractures in men study. JAMA Intern Med. 2014; 174:1263–1270. PMID: 24911216.13. Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, et al. Simvastatin improves flow-mediated dilation, but reduces adiponectin levels and insulin sensitivity in hypercholesterolemic patients. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:776–782. PMID: 18184901.14. Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, Lee Y, Kim SJ, Shin EK. Atorvastatin causes insulin resistance and increases ambient glycemia in hypercholesterolemic patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 55:1209–1216. PMID: 20298928.15. Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, et al. Additive beneficial effects of losartan combined with simvastatin in the treatment of hypercholesterolemic, hypertensive patients. Circulation. 2004; 110:3687–3692. PMID: 15569835.16. Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, et al. Vascular and metabolic effects of combined therapy with ramipril and simvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Hypertension. 2005; 45:1088–1093. PMID: 15883229.17. Koh KK, Lim S, Choi H, et al. Combination pravastatin and valsartan treatment has additive beneficial effects to simultaneously improve both metabolic and cardiovascular phenotypes beyond that of monotherapy with either drug in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia. Diabetes. 2013; 62:3547–3552. PMID: 23863812.18. Lim S, Sakuma I, Quon MJ, Koh KK. Potentially important considerations in choosing specific statin treatments to reduce overall morbidity and mortality. Int J Cardiol. 2013; 167:1696–1702. PMID: 23159411.19. Athyros VG, Mikhailidis DP, Papageorgiou AA, et al. Effect of statins and ACE inhibitors alone and in combination on clinical outcome in patients with coronary heart disease. J Hum Hypertens. 2004; 18:781–788. PMID: 15229622.20. Athyros VG, Katsiki N, Karagiannis A, Mikhailidis DP. Combination of statin plus renin angiotensin system inhibition for the prevention or the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2014; 20:6299–6305. PMID: 24953400.21. Yusuf S, Lonn E, Pais P, et al. Blood-pressure and cholesterol lowering in persons without cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2016; 374:2032–2043. PMID: 27039945.22. Koh KK, Quon MJ, Sakuma I, et al. Differential metabolic effects of rosuvastatin and pravastatin in hypercholesterolemic patients. Int J Cardiol. 2013; 166:509–515. PMID: 22204857.23. Koh KK, Sakuma I, Quon MJ. Differential metabolic effects of distinct statins. Atherosclerosis. 2011; 215:1–8. PMID: 21130454.24. Lim S, Sakuma I, Quon MJ, Koh KK. Differential metabolic actions of specific statins: clinical and therapeutic considerations. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014; 20:1286–1299. PMID: 23924053.25. Cederberg H, Stanč áková A, Yaluri N, Modi S, Kuusisto J, Laakso M. Increased risk of diabetes with statin treatment is associated with impaired insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion: a 6 year follow-up study of the METSIM cohort. Diabetologia. 2015; 58:1109–1117. PMID: 25754552.26. Ridker PM, Pradhan A, MacFadyen JG, Libby P, Glynn RJ. Cardiovascular benefits and diabetes risks of statin therapy in primary prevention: an analysis from the JUPITER trial. Lancet. 2012; 380:565–571. PMID: 22883507.27. Lotta LA, Sharp SJ, Burgess S, et al. Association between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol-lowering genetic variants and risk of type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016; 316:1383–1391. PMID: 27701660.28. Ference BA, Robinson JG, Brook RD, et al. Variation in PCSK9 and HMGCR and risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:2144–2153. PMID: 27959767.29. Bavishi C, Bangalore S, Messerli FH. Renin angiotensin aldosterone system inhibitors in hypertension: is there evidence for benefit independent of blood pressure reduction? Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2016; 59:253–261.30. Oh PC, Sakuma I, Hayashi T, Koh KK. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors remain the first treatment of choice. Korean J Intern Med. 2016; 31:237–241. PMID: 26932400.31. Nickenig G, Sachinidis A, Michaelsen F, Böhm M, Seewald S, Vetter H. Upregulation of vascular angiotensin II receptor gene expression by low-density lipoprotein in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation. 1997; 95:473–478. PMID: 9008466.32. Nickenig G, Bäumer AT, Temur Y, Kebben D, Jockenhövel F, Böhm M. Statin-sensitive dysregulated AT1 receptor function and density in hypercholesterolemic men. Circulation. 1999; 100:2131–2134. PMID: 10571970.33. Egan BM, Li J, Qanungo S, Wolfman TE. Blood pressure and cholesterol control in hypertensive hypercholesterolemic patients: national health and nutrition examination surveys 1988-2010. Circulation. 2013; 128:29–41. PMID: 23817481.34. Silverman MG, Ference BA, Im K, et al. Association between lowering LDL-C and cardiovascular risk reduction among different therapeutic interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016; 316:1289–1297. PMID: 27673306.35. Koh KK, Lim S, Sakuma I, Quon MJ. Caveats to aggressive lowering of lipids by specific statins. Int J Cardiol. 2012; 154:97–101. PMID: 21993228.36. Lim S, Oh PC, Sakuma I, Koh KK. How to balance cardiorenometabolic benefits and risks of statins. Atherosclerosis. 2014; 235:644–648. PMID: 24973595.37. Koh KK. Is it not timely to consider how to balance cardiorenometabolic benefits and risks of statins? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63(25 Pt A):2880–2881. PMID: 24794122.38. Koh KK, Han SH, Quon MJ, Yeal Ahn J, Shin EK. Beneficial effects of fenofibrate to improve endothelial dysfunction and raise adiponectin levels in patients with primary hypertriglyceridemia. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:1419–1424. PMID: 15920062.39. Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, et al. Additive beneficial effects of fenofibrate combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of patients with combined hyperlipidemia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 45:1649–1653. PMID: 15893182.40. Lee BS, Choi JY, Kim JY, Han SH, Park JE. Simvastatin and losartan differentially and synergistically inhibit atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein e(-/-) mice. Korean Circ J. 2012; 42:543–550. PMID: 22977450.41. Koh KK. How to control residual risk during statin era? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66:1848. PMID: 26483117.42. Koh KK, Oh PC, Sakuma I, et al. Vascular and metabolic effects of ezetimibe combined with simvastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Int J Cardiol. 2015; 199:126–131. PMID: 26188833.43. Koh KK. Intriguing off-target effects of ezetimibe. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66:2808.44. Koh KK, Oh PC, Sakuma I, Lee Y, Han SH, Shin EK. Rosuvastatin dose-dependently improves flow-mediated dilation, but reduces adiponectin levels and insulin sensitivity in hypercholesterolemic patients. Int J Cardiol. 2016; 223:488–493. PMID: 27544612.45. Han SH, Nicholls SJ, Sakuma I, Zhao D, Koh KK. Hypertriglyceridemia and cardiovascular diseases: revisited. Korean Circ J. 2016; 46:135–144. PMID: 27014342.46. Koh KK, Han SH, Sakuma I, Zhao D. Calming down chaos regarding redefining blood pressure targets- the importance of statin-based therapy. Int J Cardiol. 2016; 221:572–574. PMID: 27420580.47. Koh KK. Letter by Koh regarding article, “long-term effectiveness and safety of pravastatin in patients with coronary heart disease: 16 years of follow-up of the LIPID study”. Circulation. 2016; 134:e294–e295. PMID: 27672200.48. Koh KK. What is the best disease-guided approach to statin? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017; 69:600. PMID: 28153119.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Statin Therapy with Coronary Plaque Imaging
- Impact of Statin Treatment Intensity after Endovascular Revascularization on Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease
- Adverse effects of statin therapy and their treatment
- Fibrates Revisited: Potential Role in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
- Expanding the therapeutic landscape: ezetimibe as non-statin therapy for dyslipidemia