J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs.
2017 Jun;28(2):206-215. 10.12799/jkachn.2017.28.2.206.
The Evaluation of Feasibility and Predictive Validity of Comprehensive Korean Frailty Instrument: Using the 2008 and 2011 Living Profiles of Older People Survey in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. oem76@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2392861
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12799/jkachn.2017.28.2.206
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to verify the predictive validity of Comprehensive Korean Frailty Instrument (CKFI) among older adults.
METHODS
A secondary analysis of data from a prospective cohort study was conducted. Frailty was determined in older adults (N=9,188) according to the data in 2008 and the effects of frailty on adverse outcomes (such as institutionalization and death) were evaluated according to the data in 2011. The Cardiovascular Health Study (CHS) index was used to compare with the predictive validity of CKFI.
RESULTS
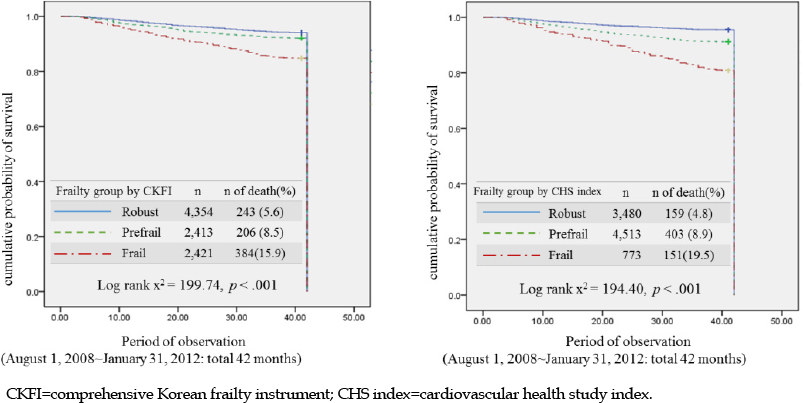
The prevalence of frailty was 26.3%. With the CKFI, the frail group had a higher risk of negative health outcomes compared to the robust and pre-frail groups after three years. The two of the highest risks identified using the CKFI and CHS index were institutionalization (5.522 times higher) and mortality (3.210 times higher). For both instruments, the survival analysis revealed that the risk of death increased as the degree of frailty increased.
CONCLUSION
The CKFI consisting of self-report items and multidimensional aspects of frailty can be used as a simple instrument for assessing the frailty of older adults residing in a local community in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Statistic Korea. 2015-2065 future population estimation [Internet]. Seoul: Statistic Korea;2016. cited 2017 March 6. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/2/2/6/index.board?bmode=read&aSeq=357935.2. Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2014 living profiles of older people survey: A national report on the living status and welfare needs of older adults. Policy Report. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2015. Report No.: 11-1352000-001426-12.3. Gobbens RJ, van Assen MA, Luijkx KG, Schols JM. Testing an integral conceptual model of frailty. J Adv Nurs. 2012; 68(9):2047–2060. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2011.05896.x.
Article4. Fried LP, Ferrucci L, Darer J, Williamson JD, Anderson G. Untangling the concepts of disability, frailty, and comorbidity: Implications for improved targeting and care. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2004; 59(3):255–263.
Article5. Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, et al. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001; 56(3):M146–M156.
Article6. Romero-Ortuno R, Walsh CD, Lawlor BA, Kenny RA. A Frailty instrument for primary care: Findings from the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE). BMC Geriatr. 2010; 10:57. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2318-10-57.
Article7. Markle-Reid M, Browne G. Conceptualizations of frailty in relation to older adults. J Adv Nurs. 2003; 44(1):58–68. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.2003.02767.x.
Article8. Rockwood K, Mitnitski A. Frailty in relation to the accumulation of deficits. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2007; 62(7):722–727.
Article9. Peters LL, Boter H, Buskens E, Slaets JP. Measurement properties of the groningen frailty indicator in home-dwelling and institutionalized elderly people. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012; 13(6):546–551. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamda.2012.04.007.10. De Witte N, Gobbens R, De Donder L, Dury S, Buffel T, Verté D. Validation of the comprehensive frailty assessment instrument against the tilburg frailty indicator. Eur Geriatr Med. 2013; 4(4):248–254. DOI: 10.1016/j.eurger.2013.03.001.
Article11. Gobbens RJ, van Assen MA, Luijkx KG, Wijnen-Sponselee MT, Schols JM. The tilburg frailty indicator: Psychometric properties. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2010; 11(5):344–355. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamda.2009.11.003.
Article12. Rolfson DB, Majumdar SR, Tsuyuki RT, Tahir A, Rockwood K. Validity and reliability of the edmonton frail scale. Age Ageing. 2006; 35(5):526–529. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afl041.
Article13. Hwang HS, Kwon IS, Park BJ, Cho B, Yoon JL, Won CW. The validity and reliability of Korean frailty index. J Korean Geriatr Soc. 2010; 14(4):191–202.
Article14. Lee I, Park YI, Park E, Lee SH, Jeong IS. Validation of instruments to classify the frailty of the elderly in community. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2011; 22(3):302–314.
Article15. Jung HW, Kim SW, Ahn S, Lim JY, Han JW, Kim TH, et al. Prevalence and outcomes of frailty in Korean elderly population: Comparisons of a multidimensional frailty index with two phenotype models. PLoS One. 2014; 9(2):e87958. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087958.
Article16. Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2011 living profiles of older people survey: A national report on the living status and welfare needs of older adults. Policy Report. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2012. Report No.: 11-1352000-000672-12.17. Gobbens RJ, Luijkx KG, Wijnen-Sponselee MT, Schols JM. Towards an integral conceptual model of frailty. J Nutr Health Aging. 2010; 14(3):175–181. DOI: 10.1007/s12603-010-0045-6.
Article18. Clegg A, Young J, Iliffe S, Rikkert MO, Rockwood K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet. 2013; 381(9868):752–762. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(12)62167-9.
Article19. Polit DF, Beck CT. The content validity index: Are you sure you know what's being reported? Critique and recommendations. Res Nurs Health. 2006; 29(5):489–497. DOI: 10.1002/nur.20147.
Article20. Greiner M, Pfeiffer D, Smith RD. Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Prev Vet Med. 2000; 45(1):23–41.
Article21. Cohen J. A power primer. Psychol Bull. 1992; 112(1):155–159.
Article22. Won CW, Yang KY, Rho YG, Kim SY, Lee E, Yoon JL, et al. The development of Korean Activities of Daily Living (K-ADL) and Korean Instrumental Activities of Daily Living(K-IADL) Scale. J Korean Geriatr Soc. 2002; 6(2):107–120.23. Cho MJ, Bae JN, Suh GH, Hahm BJ, Kim JK, Lee DW, et al. Validation of Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS), Korean version in the assessment of DSM-III-R major depression. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1999; 38(1):48–63.24. Lee DY, Lee KU, Lee JH, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Youn JC, et al. A normative study of the mini-mental state examination in the Korean elderly. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2002; 41(3):508–525.25. Ministry of Health, Welfare and Family Affairs. 2008 Living profiles of older people survey: A national report on the living status and welfare needs of older adults. Policy Report. Seoul: Ministry of Health And Welfare and Family;Keimyung University Industry-Academic Cooperation Foundation;2009. Report No.: 11-1351000-000316-12.26. Hair JF, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE. Multivariate data analysis. 7th ed. Edinburgh: Pearson;2010. p. 734.27. van Kempen JA, Schers HJ, Melis RJ, Olde Rikkert MG. Construct validity and reliability of a two-step tool for the identification of frail older people in primary care. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014; 67(2):176–183. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.08.008.
Article28. Pialoux T, Goyard J, Lesourd B. Screening tools for frailty in primary health care: A systematic review. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2012; 12(2):189–197. DOI: 10.1111/j.1447-0594.2011.00797.x.
Article29. Romero-Ortuno R, Kenny RA. The frailty index in Europeans: Association with age and mortality. Age Ageing. 2012; 41(5):684–689. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afs051.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Linear Association between Frailty as Assessed by the Kihon Checklist and Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Population-Based Study
- Social Frailty Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Recommended Assessments and Implications
- Determination of an Optimal Frailty Cutoff Score of Tilburg Frailty Indicator and Frailty Associated Factors in Community-Dwelling Turkish Older Adults
- Frailty and Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment
- Social Frailty