Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2017 Sep;21(3):125-130. 10.13104/imri.2017.21.3.125.
The Pallidal Index in Patients with Acute-on-Chronic Liver Disease: Is It a Predictor of Severe Hepatic Encephalopathy?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea. leehuijoong@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2392682
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.3.125
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical significance of T1 high signal intensity on the globus pallidus as a predictor of severe hepatic encephalopathy in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), which is a distinct syndrome characterized by multi-organ dysfunction including cerebral failure.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
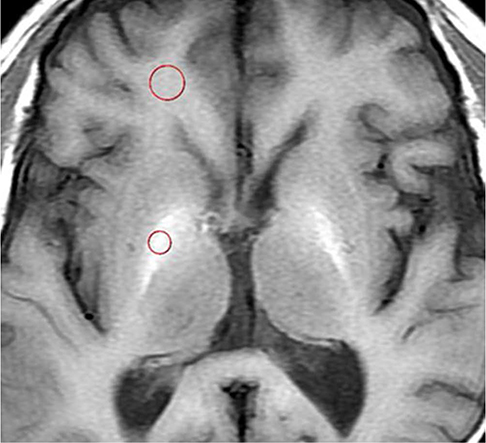
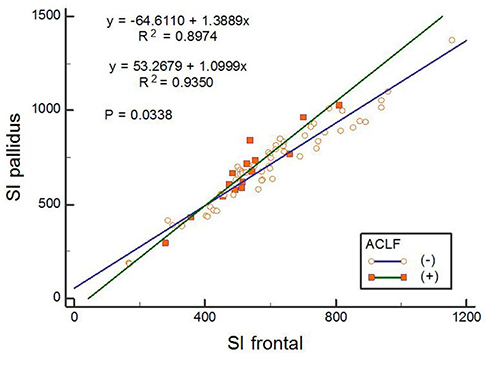
From January 2002 to April 2014, we retrospectively reviewed the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings and clinical and magnetic resonance (MR) features of 74 consecutive patients (44 men and 30 women; mean age, 59.5 years) with liver cirrhosis. The chronic liver failure-sequential organ failure assessment score was used to diagnose ACLF. The pallidal index (PI), calculated by dividing the mean signal intensity of the globus pallidus by that of the subcortical frontal white matter were compared according to ACLF. The PI was compared with the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score in predicting the development of ACLF.
RESULTS
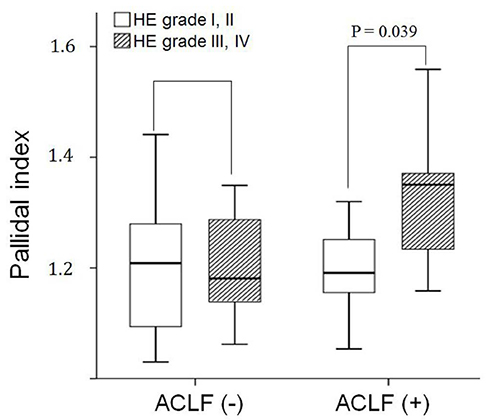
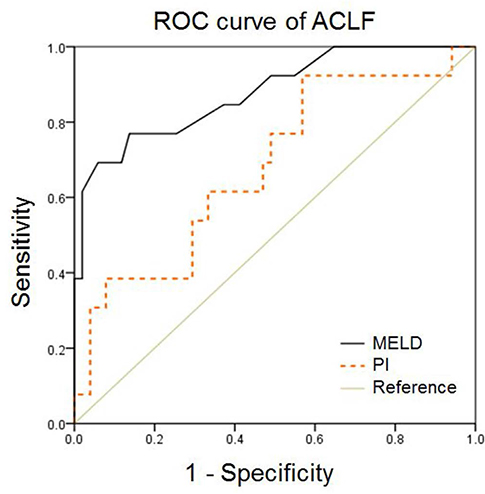
Fifteen patients who were diagnosed with ACLF had higher hepatic encephalopathy grades (initial, P = 0.024; follow-up, P = 0.002), MELD scores (P < 0.001), and PI (P = 0.048). In the ACLF group, the mean PI in patients with cerebral failure was significantly higher than that in the patients without cerebral failure (1.33 vs. 1.20, P = 0.039). In patients with ACLF, the area under the curve (AUC) for PI was 0.680 (95% confidence intervals [CI], 0.52-0.85), which was significantly lower than that for the MELD score (AUC, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.77-0.99) (P = 0.04).
CONCLUSION
The PI can be an ancillary biomarker for predicting the development of ACLF and severe hepatic encephalopathy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sherlock S. Hepatic encephalopathy. Br J Hosp Med. 1977; 17:144–146. 151–154. 1592. Romero-Gomez M, Montagnese S, Jalan R. Hepatic encephalopathy in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatol. 2015; 62:437–447.3. Wright G, Sharifi Y, Jover-Cobos M, Jalan R. The brain in acute on chronic liver failure. Metab Brain Dis. 2014; 29:965–973.4. Inoue E, Hori S, Narumi Y, et al. Portal-systemic encephalopathy: presence of basal ganglia lesions with high signal intensity on MR images. Radiology. 1991; 179:551–555.5. Pujol A, Pujol J, Graus F, et al. Hyperintense globus pallidus on T1-weighted MRI in cirrhotic patients is associated with severity of liver failure. Neurology. 1993; 43:65–69.6. Zeneroli ML, Cioni G, Crisi G, Vezzelli C, Ventura E. Globus pallidus alterations and brain atrophy in liver cirrhosis patients with encephalopathy: an MR imaging study. Magn Reson Imaging. 1991; 9:295–302.7. Burkhard PR, Delavelle J, Du Pasquier R, Spahr L. Chronic parkinsonism associated with cirrhosis: a distinct subset of acquired hepatocerebral degeneration. Arch Neurol. 2003; 60:521–528.8. Li SJ, Jiang L, Fu X, et al. Pallidal index as biomarker of manganese brain accumulation and associated with manganese levels in blood: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e93900.9. Chang Y, Woo ST, Kim Y, et al. Pallidal index measured with three-dimensional T1-weighted gradient echo sequence is a good predictor of manganese exposure in welders. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010; 31:1020–1026.10. Rovira A, Alonso J, Cordoba J. MR imaging findings in hepatic encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:1612–1621.11. Volk ML, Marrero JA. Advances in critical care hepatology. Minerva Anestesiol. 2006; 72:269–281.12. Delis SG, Bakoyiannis A, Biliatis I, Athanassiou K, Tassopoulos N, Dervenis C. Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score, as a prognostic factor for postoperative morbidity and mortality in cirrhotic patients, undergoing hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 2009; 11:351–335.13. Moreau R, Jalan R, Gines P, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144:1426–1437. 1437.e1–1437.e9.14. Blei AT, Cordoba J, Practice Parameters. Hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:1968–1976.15. Elements of research in physical therapy. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins;1990.16. Krieger D, Krieger S, Jansen O, Gass P, Theilmann L, Lichtnecker H. Manganese and chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet. 1995; 346:270–274.17. Spahr L, Butterworth RF, Fontaine S, et al. Increased blood manganese in cirrhotic patients: relationship to pallidal magnetic resonance signal hyperintensity and neurological symptoms. Hepatology. 1996; 24:1116–1120.18. Sarin SK, Kumar A, Almeida JA, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific Association for the study of the liver (APASL). Hepatol Int. 2009; 3:269–282.19. Shin YC, Kim E, Cheong HK, et al. High signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging as a predictor of neurobehavioral performance of workers exposed to manganese. Neurotoxicology. 2007; 28:257–262.20. Arroyo V, Moreau R, Jalan R, Gines P, EASL-CLIF Consotrium. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: A new syndrome that will re-classify cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2015; 62:S131–S143.21. Hoofnagle JH, Carithers RL Jr, Shapiro C, Ascher N. Fulminant hepatic failure: summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 1995; 21:240–252.22. Herrero Hernandez E, Valentini MC, Discalzi G. T1-weighted hyperintensity in basal ganglia at brain magnetic resonance imaging: are different pathologies sharing a common mechanism. Neurotoxicology. 2002; 23:669–674.23. Criswell SR, Perlmutter JS, Huang JL, et al. Basal ganglia intensity indices and diffusion weighted imaging in manganese-exposed welders. Occup Environ Med. 2012; 69:437–443.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy with Features on Diffusion-Weighted Images: Report of Two Cases
- A Case of Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy Secondary to Spontaneous Intrahepatic Portosystemic Venous Shunt
- Three Cases of Chronic Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration
- Relationship to Magnetic Resonance Signal Hyperintensity in Globus Palidus and Blood Manganese Concentration in Cirrhotic Patients with Extrapyramidal Symptoms
- Fatal neurological complication after liver transplantation in acute hepatic failure patient with hepatic encephalopathy