J Pathol Transl Med.
2017 Jul;51(4):365-373. 10.4132/jptm.2017.05.04.
Yes-Associated Protein Expression Is Correlated to the Differentiation of Prostate Adenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea. cchoi@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea.
- KMID: 2392576
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2017.05.04
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Yes-associated protein (YAP) in the Hippo signaling pathway is a growth control pathway that regulates cell proliferation and stem cell functions. Abnormal regulation of YAP was reported in human cancers including liver, lung, breast, skin, colon, and ovarian cancer. However, the function of YAP is not known in prostate adenocarcinoma. The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of YAP in tumorigenesis, differentiation, and prognosis of prostate adenocarcinoma.
METHODS
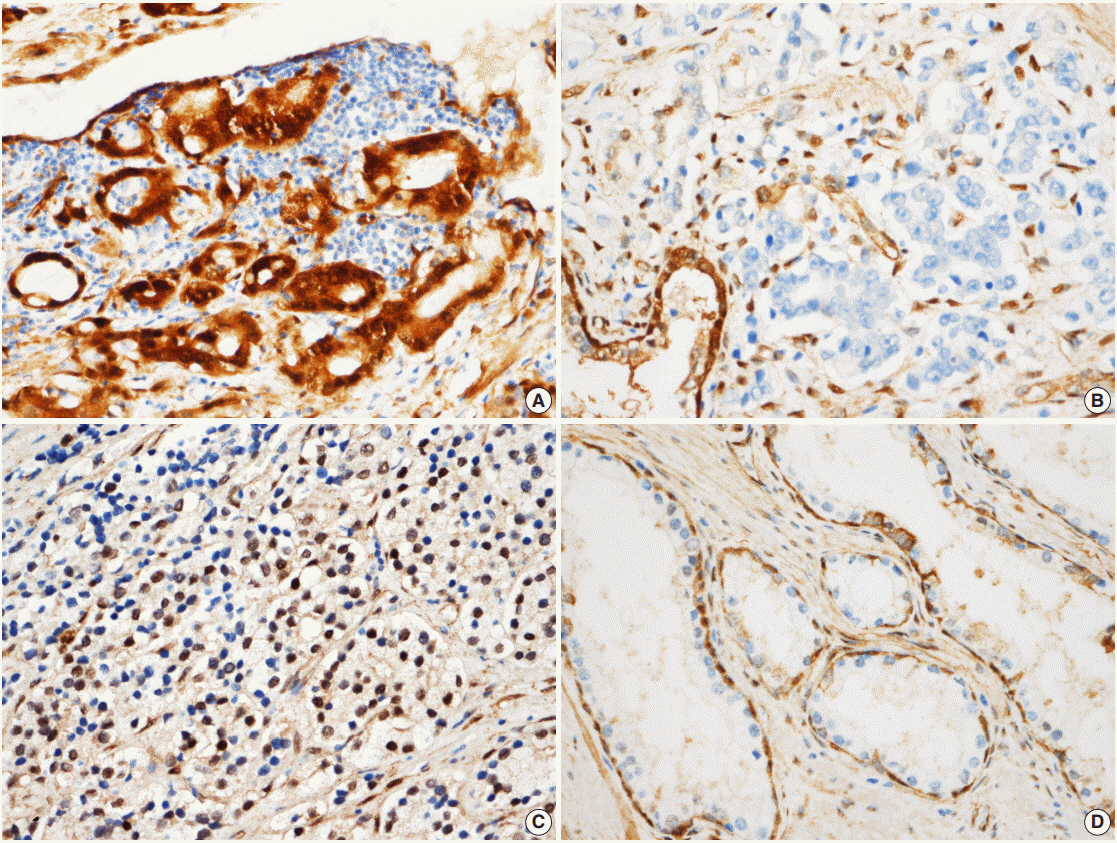
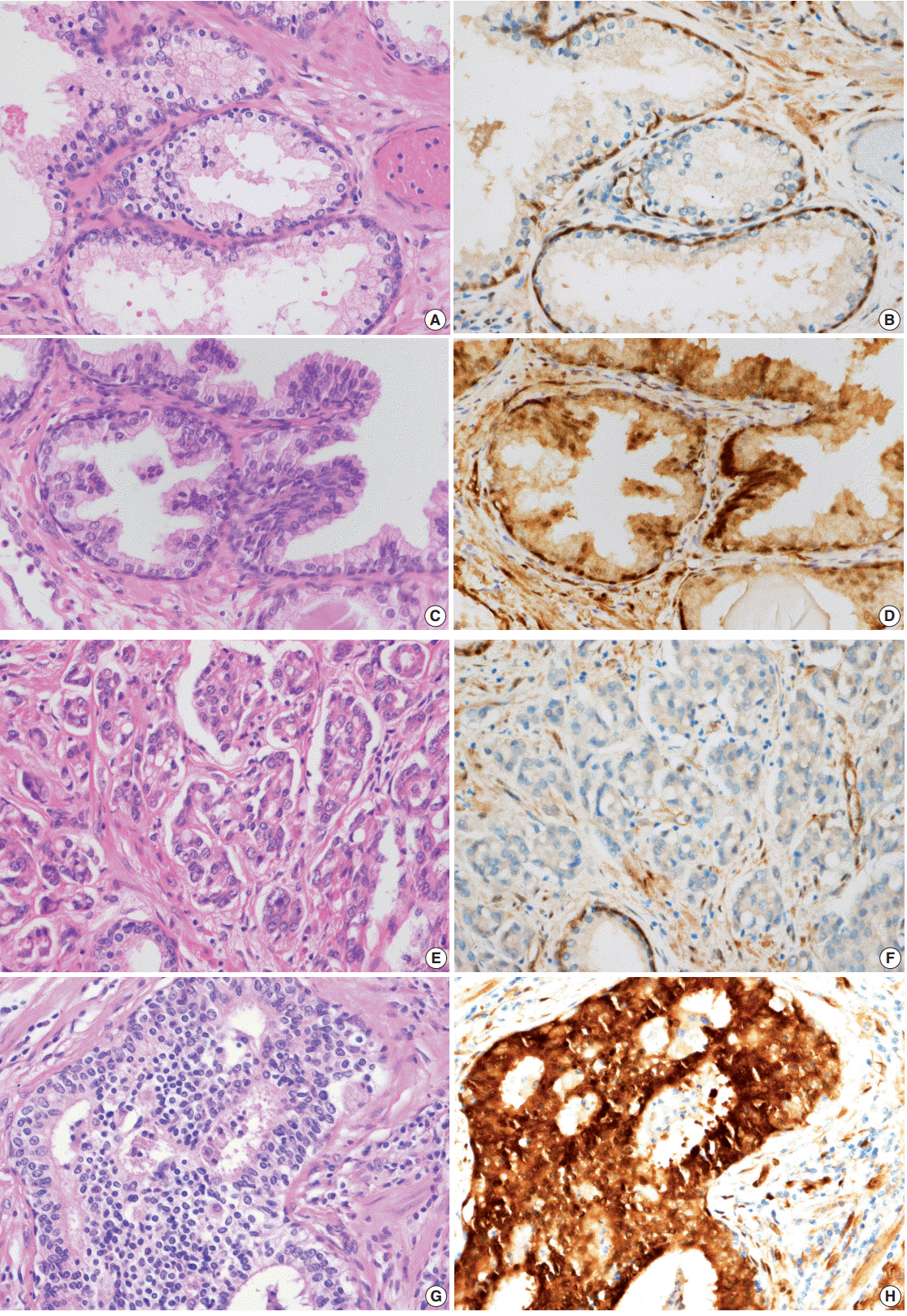
The nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of YAP was examined in 188 cases of prostate adenocarcinoma using immunohistochemistry. YAP expression levels were evaluated in the nucleus and cytoplasm of the prostate adenocarcinoma and the adjacent normal prostate tissue. The presence of immunopositive tumor cells was evaluated and interpreted in comparison with the patients' clinicopathologic data.
RESULTS
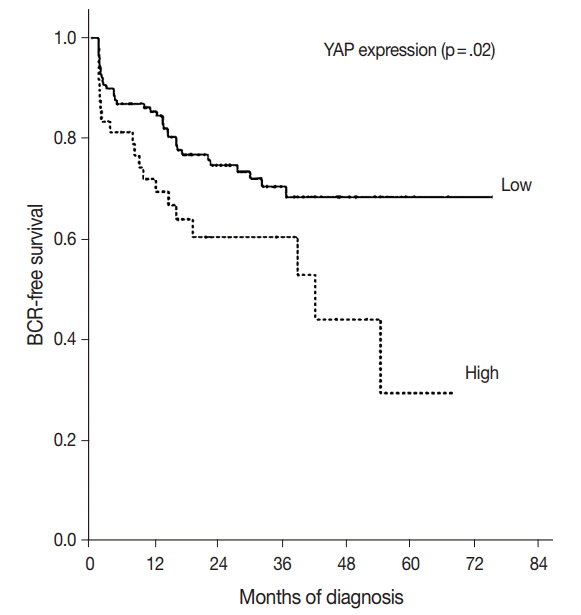
YAP expression levels were not significantly different between normal epithelial cells and prostate adenocarcinoma. However, YAP expression level was significantly higher in carcinomas with a high Gleason grades (8-10) than in carcinomas with a low Gleason grades (6-7) (p < .01). There was no statistical correlation between YAP expression and stage, age, prostate-specific antigen level, and tumor volume. Biochemical recurrence (BCR)-free survival was significantly lower in patients with high YAP expressing cancers (p = .02). However high YAP expression was not an independent prognostic factor for BCR in the Cox proportional hazards model.
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggested that YAP is not associated with prostate adenocarcinoma development, but it may be associated with the differentiation of the adenocarcinoma. YAP was not associated with BCR.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Diallo JS, Aldejmah A, Mouhim AF, et al. Co-assessment of cytoplasmic and nuclear androgen receptor location in prostate specimens: potential implications for prostate cancer development and prognosis. BJU Int. 2008; 101:1302–9.
Article2. Joung JY, Lim J, Oh CM, et al. Current trends in the incidence and survival rate of urological cancers in Korea. Cancer Res Treat. 2016; Sep. 23. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.139.
Article3. Zhang L, Yang S, Chen X, et al. The hippo pathway effector YAP regulates motility, invasion, and castration-resistant growth of prostate cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2015; 35:1350–62.
Article4. Epstein JI, Allsbrook WC Jr, Amin MB, Egevad LL; ISUP Grading Committee. The 2005 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005; 29:1228–42.
Article5. McMenamin ME, Soung P, Perera S, Kaplan I, Loda M, Sellers WR. Loss of PTEN expression in paraffin-embedded primary prostate cancer correlates with high Gleason score and advanced stage. Cancer Res. 1999; 59:4291–6.6. Edgar BA. From cell structure to transcription: Hippo forges a new path. Cell. 2006; 124:267–73.
Article7. Lai ZC, Wei X, Shimizu T, et al. Control of cell proliferation and apoptosis by mob as tumor suppressor, mats. Cell. 2005; 120:675–85.
Article8. Gayyed MF, et al. Expression of Yes-associated protein in common solid tumors. Hum Pathol. 2008; 39:1582–9.9. Wang Y, Dong Q, Zhang Q, Li Z, Wang E, Qiu X. Overexpression of yes-associated protein contributes to progression and poor prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010; 101:1279–85.
Article10. Cordenonsi M, Zanconato F, Azzolin L, et al. The Hippo transducer TAZ confers cancer stem cell-related traits on breast cancer cells. Cell. 2011; 147:759–72.
Article11. DiAgostino S, Sorrentino G, Ingallina E, et al. YAP enhances the proproliferative transcriptional activity of mutant p53 proteins. EMBO Rep. 2016; 17:188–201.12. Lee KW, Lee SS, Kim SB, et al. Significant association of oncogene YAP1 with poor prognosis and cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2015; 21:357–64.
Article13. Kim GJ, Kim H, Park YN. Increased expression of Yes-associated protein 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma with stemness and combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e75449.
Article14. Morvaridi S, Dhall D, Greene MI, Pandol SJ, Wang Q. Role of YAP and TAZ in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and in stellate cells associated with cancer and chronic pancreatitis. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:16759.
Article15. Johnson R, Halder G. The two faces of Hippo: targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and cancer treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014; 13:63–79.
Article16. Grasso CS, Wu YM, Robinson DR, et al. The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature. 2012; 487:239–43.
Article17. Hu X, Yu J, Chen J, Fu Q. Loss ofYAP protein in prostate cancer is associated with Gleason score increase. Tumori. 2015; 101:189–93.18. Varambally S, Yu J, Laxman B, et al. Integrative genomic and proteomic analysis of prostate cancer reveals signatures of metastatic progression. Cancer Cell. 2005; 8:393–406.
Article19. Chandran UR, Ma C, Dhir R, et al. Gene expression profiles of prostate cancer reveal involvement of multiple molecular pathways in the metastatic process. BMC Cancer. 2007; 7:64.
Article20. Yu YP, Landsittel D, Jing L, et al. Gene expression alterations in prostate cancer predicting tumor aggression and preceding development of malignancy. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:2790–9.
Article21. Satake H, Tamura K, Furihata M, et al. The ubiquitin-like molecule interferon-stimulated gene 15 is overexpressed in human prostate cancer. Oncol Rep. 2010; 23:11–6.
Article22. Planche A, Bacac M, Provero P, et al. Identification of prognostic molecularfeatures in the reactive stroma of human breast and prostate cancer. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e18640.23. Arredouani MS, Lu B, Bhasin M, et al. Identification of the transcription factor single-minded homologue 2 as a potential biomarker and immunotherapy target in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15:5794–802.
Article24. Nanni S, Priolo C, Grasselli A, et al. Epithelial-restricted gene profile of primary cultures from human prostate tumors: a molecular approach to predict clinical behavior of prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2006; 4:79–92.
Article25. Rosenbluh J, Nijhawan D, Cox AG, et al. beta-Catenin-driven cancers require a YAP1 transcriptional complex for survival and tumorigenesis. Cell. 2012; 151:1457–73.26. Dong J, Feldmann G, Huang J, et al. Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in Drosophila and mammals. Cell. 2007; 130:1120–33.27. Shen S, Guo X, Yan H, et al. AmiR-130a-YAP positive feedback loop promotes organ size and tumorigenesis. Cell Res. 2015; 25:997–1012.28. Xiao W, Wang J, Ou C, et al. Mutual interaction between YAP and c-Myc is critical for carcinogenesis in liver cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 439:167–72.
Article29. Zhang W, Nandakumar N, Shi Y, et al. Downstream of mutant KRAS, the transcription regulator YAP is essential for neoplastic progression to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci Signal. 2014; 7:ra42.
Article30. Zanconato F, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S. YAP/TAZ at the roots of cancer. Cancer Cell. 2016; 29:783–803.
Article31. Guo Y, Pan Q, Zhang J, et al. Functional and clinical evidence that TAZ is a candidate oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 2015; 116:2465–75.
Article32. Bartucci M, Dattilo R, Moriconi C, et al. TAZ is required for metastatic activity and chemoresistance of breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene. 2015; 34:681–90.
Article33. Han KR, Seligson DB, Liu X, et al. Prostate stem cell antigen expression is associated with gleason score, seminal vesicle invasion and capsularinvasion in prostate cancer. J Urol. 2004; 171:1117–21.34. Kim DH, Kim SH, Lee OJ, et al. Differential expression of Yes-associated protein and phosphorylated Yes-associated protein is correlated with expression of Ki-67 and phospho-ERK in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Histol Histopathol. 2013; 28:1483–90.35. Hu X, Xin Y, Xiao Y, Zhao J. Overexpression of YAP1 is correlated with progression, metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with gastric carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 2014; 20:805–11.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Significance of S100A2 and S100A4 Expression in the Progression of Prostate Adenocarcinoma
- Expression of Osteopontin, ZO-1 and E-cadherin in Adenoma and Adenocarcinoma of the Colon
- Immunohistochemical Study on the Expression of p53 and bcl-2 Protein in Gallbladder Adenocarcinoma
- Correlation between Histologic Differentiation and Prognosis of Prostate Adenocarcinoma
- Ductal Adenocarcinoma of Prostate