Determinants of Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control in New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pourlife@naver.com
- KMID: 2392469
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.4.284
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Long-term durable glycemic control is a difficult goal in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We evaluated the factors associated with durable glycemic control in a real clinical setting.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 194 new-onset, drug-naïve patients with T2DM who were diagnosed between January 2011 and March 2013, and were followed up for >2 years. Glycemic durability was defined as the maintenance of optimal glycemic control (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] <7.0%) for 2 years without substitution or adding other glucose-lowering agents. Clinical factors and glycemic markers associated with glycemic durability were compared between two groups: a durability group and a non-durability group.
RESULTS
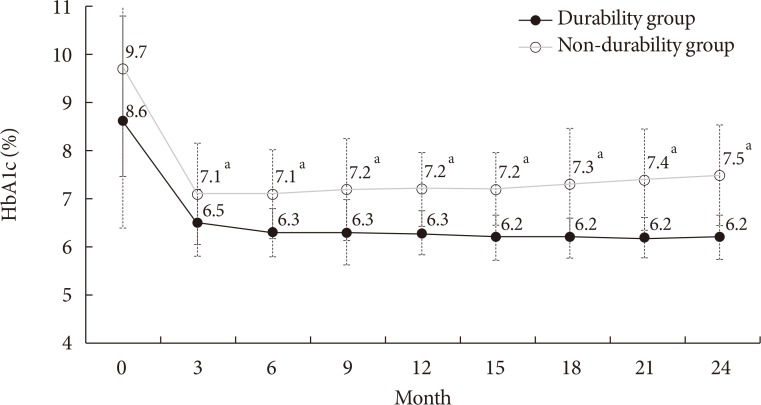
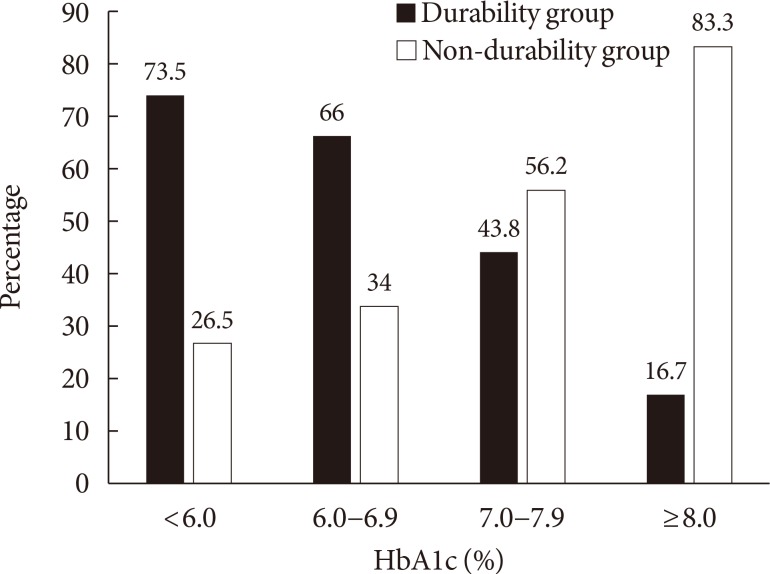
Patients in the durability group had a higher baseline body mass index (26.1 kg/m² vs. 24.9 kg/m²) and lower HbA1c (8.6% vs. 9.7%) than the non-durability group. The initial choice of glucose-lowering agents was similar in both groups, except for insulin and sulfonylureas, which were more frequently prescribed in the non-durability group. In multiple logistic regression analyses, higher levels of education, physical activity, and homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function (HOMA-β) were associated with glycemic durability. Notably, lower HbA1c (<7.0%) at baseline and first follow-up were significantly associated with glycemic durability (adjusted odds ratio [OR], 7.48; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.51 to 22.3) (adjusted OR, 9.27; 95% CI, 1.62 to 53.1, respectively), after adjusting for confounding variables including the types of glucose-lowering agents.
CONCLUSION
Early achievement of HbA1c level within the glycemic target was a determinant of long-term glycemic durability in new-onset T2DM, as were higher levels of education, physical activity, and HOMA-β.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):368-378. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0046.Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (
Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):613-614. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0129.
Reference
-
1. Ramlo-Halsted BA, Edelman SV. The natural history of type 2 diabetes. Implications for clinical practice. Prim Care. 1999; 26:771–789. PMID: 10523459.2. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998; 352:837–853. PMID: 9742976.3. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, Marre M, Cooper M, Glasziou P, Grobbee D, Hamet P, Harrap S, Heller S, Liu L, Mancia G, Mogensen CE, Pan C, Poulter N, Rodgers A, Williams B, Bompoint S, de Galan BE, Joshi R, Travert F. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2560–2572. PMID: 18539916.4. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-Year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1577–1589. PMID: 18784090.
Article5. Hayward RA, Reaven PD, Wiitala WL, Bahn GD, Reda DJ, Ge L, McCarren M, Duckworth WC, Emanuele NV. VADT Investigators. Follow-up of glycemic control and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:2197–2206. PMID: 26039600.
Article6. Kahn SE, Haffner SM, Heise MA, Herman WH, Holman RR, Jones NP, Kravitz BG, Lachin JM, O'Neill MC, Zinman B, Viberti G. ADOPT Study Group. Glycemic durability of rosiglitazone, metformin, or glyburide monotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:2427–2443. PMID: 17145742.
Article7. Mamza J, Mehta R, Donnelly R, Idris I. Important differences in the durability of glycaemic response among second-line treatment options when added to metformin in type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Med. 2016; 48:224–234. PMID: 26982210.
Article8. Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). JAMA. 1999; 281:2005–2012. PMID: 10359389.9. Ekstrom N, Svensson AM, Miftaraj M, Andersson Sundell K, Cederholm J, Zethelius B, Eliasson B, Gudbjornsdottir S. Durability of oral hypoglycemic agents in drug naive patients with type 2 diabetes: report from the Swedish National Diabetes Register (NDR). BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2015; 3:e000059.10. Ridderstrale M, Andersen KR, Zeller C, Kim G, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. EMPA-REG H2H-SU trial investigators. Comparison of empagliflozin and glimepiride as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 104-week randomised, active-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014; 2:691–700. PMID: 24948511.11. Umpierrez G, Tofe Povedano S, Perez Manghi F, Shurzinske L, Pechtner V. Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide monotherapy versus metformin in type 2 diabetes in a randomized controlled trial (AWARD-3). Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:2168–2176. PMID: 24842985.
Article12. Kramer CK, Zinman B, Retnakaran R. Short-term intensive insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013; 1:28–34. PMID: 24622264.
Article13. Weng J, Li Y, Xu W, Shi L, Zhang Q, Zhu D, Hu Y, Zhou Z, Yan X, Tian H, Ran X, Luo Z, Xian J, Yan L, Li F, Zeng L, Chen Y, Yang L, Yan S, Liu J, Li M, Fu Z, Cheng H. Effect of intensive insulin therapy on beta-cell function and glycaemic control in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a multicentre randomised parallel-group trial. Lancet. 2008; 371:1753–1760. PMID: 18502299.14. Kruger DF. Managing diabetes from first diagnosis: choosing well-tolerated therapies with durability. Diabetes Educ. 2012; 38(4 Suppl):4S–11S. PMID: 22713263.15. Nathan DM, Buse JB, Kahn SE, Krause-Steinrauf H, Larkin ME, Staten M, Wexler D, Lachin JM. GRADE Study Research Group. Rationale and design of the glycemia reduction approaches in diabetes: a comparative effectiveness study (GRADE). Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:2254–2261. PMID: 23690531.
Article16. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:140–149. PMID: 25538310.
Article17. Genuth S, Alberti KG, Bennett P, Buse J, Defronzo R, Kahn R, Kitzmiller J, Knowler WC, Lebovitz H, Lernmark A, Nathan D, Palmer J, Rizza R, Saudek C, Shaw J, Steffes M, Stern M, Tuomilehto J, Zimmet P. Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:3160–3167. PMID: 14578255.18. Woerle HJ, Neumann C, Zschau S, Tenner S, Irsigler A, Schirra J, Gerich JE, Goke B. Impact of fasting and postprandial glycemia on overall glycemic control in type 2 diabetes Importance of postprandial glycemia to achieve target HbA1c levels. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007; 77:280–285. PMID: 17240473.19. Del Prato S. Role of glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and emerging treatment strategies. Diabet Med. 2009; 26:1185–1192. PMID: 20002468.
Article20. Smith RJ, Nathan DM, Arslanian SA, Groop L, Rizza RA, Rotter JI. Individualizing therapies in type 2 diabetes mellitus based on patient characteristics: what we know and what we need to know. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:1566–1574. PMID: 20194712.
Article21. Kubota A, Yabe D, Kanamori A, Kuroe A, Takahashi N, Saito T, Matsuba I, Nabe K, Kurose T, Seino Y. Factors influencing the durability of the glucose-lowering effect of sitagliptin combined with a sulfonylurea. J Diabetes Investig. 2014; 5:445–448.
Article22. Chaturvedi N, Stephenson JM, Fuller JH. The relationship between socioeconomic status and diabetes control and complications in the EURODIAB IDDM Complications Study. Diabetes Care. 1996; 19:423–430. PMID: 8732703.
Article23. Hassan K, Loar R, Anderson BJ, Heptulla RA. The role of socioeconomic status, depression, quality of life, and glycemic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr. 2006; 149:526–531. PMID: 17011326.
Article24. Connolly V, Unwin N, Sherriff P, Bilous R, Kelly W. Diabetes prevalence and socioeconomic status: a population based study showing increased prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in deprived areas. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2000; 54:173–177. PMID: 10746110.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
- Initial Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes
- Growth Status in Children with Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study
- Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)