J Clin Neurol.
2017 Oct;13(4):422-423. 10.3988/jcn.2017.13.4.422.
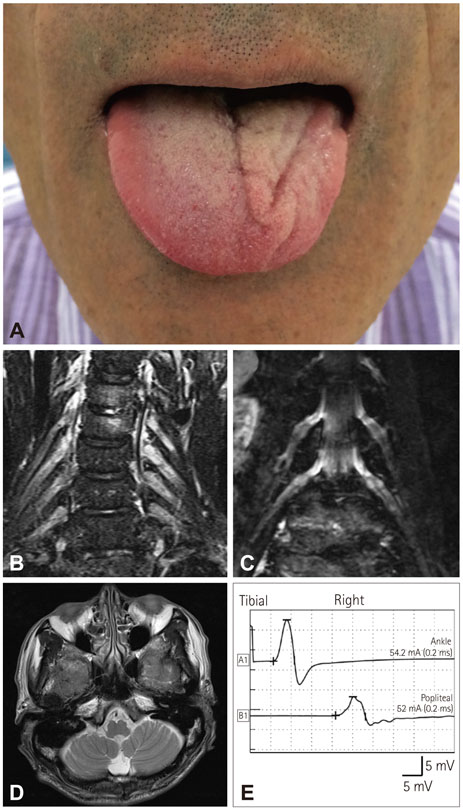
Hemiatrophy of the Tongue with Contralateral Hemiparesis in a Patient with Multifocal Acquired Demyelinating Sensory and Motor Neuropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan. y-stsh@kumamoto-u.ac.jp
- KMID: 2392139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2017.13.4.422
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sander HW, Latov N. Research criteria for defining patients with CIDP. Neurology. 2003; 60:8 Suppl 3. S8–S15.
Article2. Verschueren A, Azulay JP, Attarian S, Boucraut J, Pellissier JF, Pouget J. Lewis-Sumner syndrome and multifocal motor neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2005; 31:88–94.
Article3. Jeanjean AP, Duprez T, Van den Bergh PY. Massive peripheral nerve hypertrophy in a patient with multifocal upper limb demyelinating neuropathy (Lewis-Sumner syndrome). Acta Neurol Belg. 2001; 101:234–238.4. Weiss MD, Oakley JC, Meekins GD. Hypoglossal neuropathy in Lewis-Sumner syndrome masquerading as motor neuron disease. Neurology. 2006; 67:175–176.
Article5. Pergami P, Poloni TE, Imbesi F, Ceroni M, Simonetti F. Dejerine’s syndrome or Spiller’s syndrome. Neurol Sci. 2001; 22:333–336.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unilateral Hypoglossal Neuropathy in Multifocal Acquired Demyelinating Sensory and Motor Neuropathy: Differential Diagnosis of Motor Neuron Disease
- Electrophysiological and radiological evidence for the multifocal nature of a case of multifocal acquired demyelinating sensory and motor neuropathy
- Sensory Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy: Neglected ImmunotherapyResponsive Sensory Neuropathy
- Conduction Block in Hereditary Motor Sensory Neuropathy
- Hereditary Motor and Sensory Neuropathy Type I: A case report