J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Oct;77(4):211-216. 10.3348/jksr.2017.77.4.211.
Windows Setting for Low kVp Abdominal CT: Comparison to 120-kVp CT Images
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Cancer Research Institute, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. dumky@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2392116
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.77.4.211
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of the study is to identify the optimal window level (WL) and window width (WW) to maximize visualization of the findings for low kVp abdominal CT images utilizing the automated tube voltage selection (ATVS) (which produces-brightness and contrast very similar to that produced by a 120-kVp CT scanner).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
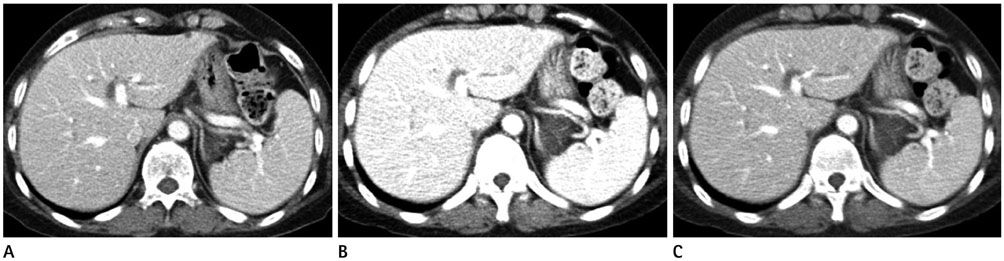
We enrolled 61 patients who underwent: 1) dynamic abdominal CT scanning using ATVS technique (in 2015) and 2) a second CT scan, on this occasion implementing a 120-kVp protocol (in 2014). With ATVS, all scans were performed using 80-kVp for the arterial phase. For the portal phase, 80-kVp and 100-kVp were applied in 27 and 34 patients, respectively. Two radiologists then over-read and compared the ATVS images to the 120-kVp images, assessing brightness and contrast. After the over-read and comparison, they selected the WL and WW for ATVS because they produced brightness and contrast very similar to that appreciated in the 120-kVp images.
RESULTS
The WL and the WW for the arterial phase (mode/mean) were 130 Hounsfield unit (HU)/120.7 HU and 230 HU/259.6 HU, respectively. For the portal phase, the WL and the WW (mode/mean) were 90 HU/109.6 HU and 450 HU/450.0 HU for 80-kVp, and 40 HU/63.5 HU and 400 HU/382.4 HU for 100-kVp, respectively. The mean values of WL and WW for 80-kVp were significantly higher than those for 100-kVp (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
Based upon the findings, it was determined that WL and WW with ATVS should be higher than those used for 120-kVp protocol in order to obtain comparable brightness and contrast in the images produced by abdominal CT scanning.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pomerantz SM, White CS, Krebs TL, Daly B, Sukumar SA, Hooper F, et al. Liver and bone window settings for soft-copy interpretation of chest and abdominal CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 174:311–314.2. Cox IH, Foley WD, Hoffmann RG. Right window for dynamic hepatic CT. Radiology. 1991; 181:18–21. discussion 21-24.3. Mayo-Smith WW, Gupta H, Ridlen MS, Brody JM, Clements NC, Cronan JJ. Detecting hepatic lesions: the added utility of CT liver window settings. Radiology. 1999; 210:601–604.4. Sabouri S, Khatami A, Azadeh P, Ghoroubi J, Azimi G. Adding liver window setting to the standard abdominal CT scan. Iran J Radiol. 2008; 5:65–70.5. Raman SP, Mahesh M, Blasko RV, Fishman EK. CT scan parameters and radiation dose: practical advice for radiologists. J Am Coll Radiol. 2013; 10:840–846.6. Gonzalez-Guindalini FD, Ferreira Botelho MP, Töre HG, Ahn RW, Gordon LI, Yaghmai V. MDCT of chest, abdomen, and pelvis using attenuation-based automated tube voltage selection in combination with iterative reconstruction: an intrapatient study of radiation dose and image quality. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 201:1075–1082.7. Desai GS, Fuentes Orrego JM, Kambadakone AR, Sahani DV. Performance of iterative reconstruction and automated tube voltage selection on the image quality and radiation dose in abdominal CT scans. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2013; 37:897–903.8. Cho PK. Radiation dose reduction from low-kilovoltage liver computed tomography using multidetector row computed tomography. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2013; 154:76–80.9. Hu L, Wang Y, Hou H, Wei F, Yang G, Chen Y. Radiation dose and image quality with abdominal computed tomography with automated dose-optimized tube voltage selection. J Int Med Res. 2014; 42:1011–1017.10. Spearman JV, Schoepf UJ, Rottenkolber M, Driesser I, Canstein C, Thierfelder KM, et al. Effect of automated attenuation-based tube voltage selection on radiation dose at CT: an observational study on a global scale. Radiology. 2016; 279:167–174.11. Raman SP, Johnson PT, Deshmukh S, Mahesh M, Grant KL, Fishman EK. CT dose reduction applications: available tools on the latest generation of CT scanners. J Am Coll Radiol. 2013; 10:37–41.12. Sigal-Cinqualbre AB, Hennequin R, Abada HT, Chen X, Paul JF. Low-kilovoltage multi-detector row chest CT in adults: feasibility and effect on image quality and iodine dose. Radiology. 2004; 231:169–174.13. Kaza RK, Platt JF, Goodsitt MM, Al-Hawary MM, Maturen KE, Wasnik AP, et al. Emerging techniques for dose optimization in abdominal CT. Radiographics. 2014; 34:4–17.14. Nakaura T, Awai K, Oda S, Funama Y, Harada K, Uemura S, et al. Low-kilovoltage, high-tube-current MDCT of liver in thin adults: pilot study evaluating radiation dose, image quality, and display settings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:1332–1338.15. De Cecco CN, Caruso D, Schoepf UJ, Wichmann JL, Ter Louw JR, Perry JD, et al. Optimization of window settings for virtual monoenergetic imaging in dual-energy CT of the liver: a multi-reader evaluation of standard monoenergetic and advanced imaged-based monoenergetic datasets. Eur J Radiol. 2016; 85:695–699.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 100 kVp Low-Tube Voltage Abdominal CT in Adults: Radiation Dose Reduction and Image Quality Comparison of 120 kVp Abdominal CT
- Effects of Dual-Energy CT with Non-Linear Blending on Abdominal CT Angiography
- Comparison of Image Quality of Shoulder CT Arthrography Conducted Using 120 kVp and 140 kVp Protocols
- The Image Quality and Radiation Dose of 100-kVp versus 120-kVp ECG-Gated 16-Slice CT Coronary Angiography
- CT Venography for Deep Vein Thrombosis Using a Low Tube Voltage (100 kVp) Setting Could Increase Venous Enhancement and Reduce the Amount of Administered Iodine