Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Oct;36(5):719-723.
Ulnar Neuropathy Around the Mid-Arm Combined with Martin-Gruber Anastomosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul 136-705, Korea. rmkdh@korea.ac.kr
Abstract
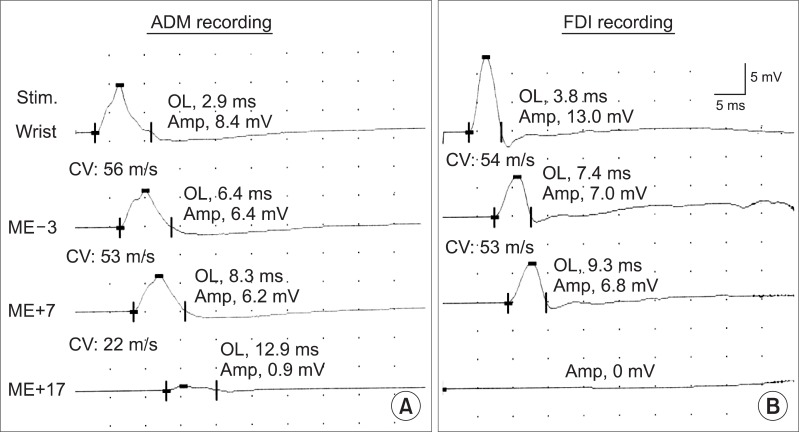
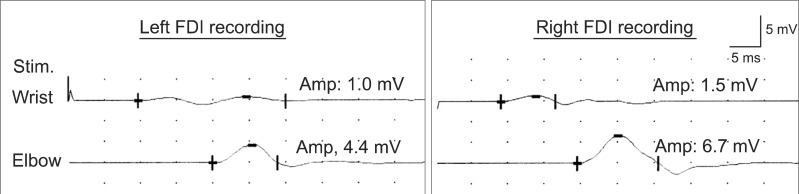
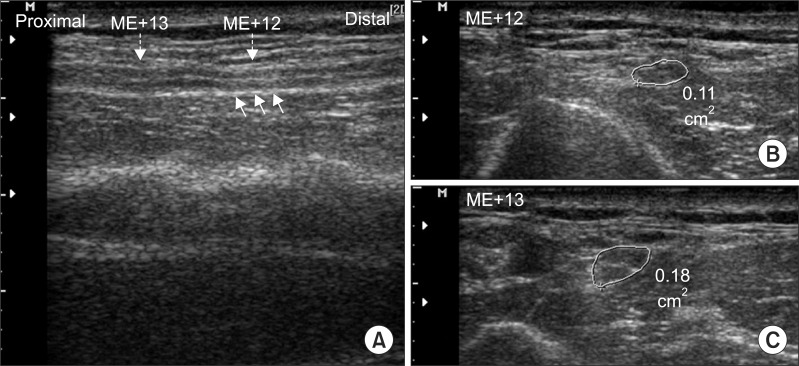
- This study reports a rare case of ulnar neuropathy around the arm with Martin-Gruber anastomosis of a moderate conduction block in the forearm segment and a severe conduction block in the arm segment. Inching tests and ultrasonography showed a lesion between 12 and 14 cm from the medial epicondyle. It is concluded that axilla stimulation may provide diagnostic clues, and inching tests and ultrasonography may be helpful for localizing a lesion.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dawson DM, Hallett M, Wilbourn AJ. Entrapment neuropathies. 1999. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;p. 134–135.2. Whitaker CH, Felice KJ. Apparent conduction block in patients with ulnar neuropathy at the elbow and proximal Martin-Gruber anastomosis. Muscle Nerve. 2004; 30:808–811. PMID: 15316981.
Article3. Marras C, Midroni G. Proximal Martin-Gruber anastomosis mimicking ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Muscle Nerve. 1999; 22:1132–1135. PMID: 10417799.
Article4. Stewart JD. Focal peripheral neuropathies. 2010. 4th ed. Vancouver: JBJ Publishing;p. 196–198.5. Amoiridis G, Vlachonikolis IG. Verification of the median-to-ulnar and ulnar-to-median nerve motor fiber anastomosis in the forearm: an electrophysiological study. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003; 114:94–98. PMID: 12495769.
Article6. Lee KS, Oh CS, Chung IH, Sunwoo IN. An anatomic study of the Martin-Gruber anastomosis: electrodiagnostic implications. Muscle Nerve. 2005; 31:95–97. PMID: 15389650.
Article7. Erdem HR, Ergun S, Erturk C, Ozel S. Electrophysiological evaluation of the incidence ofmartin-gruber anastomosis in healthy subjects. Yonsei Med J. 2002; 43:291–295. PMID: 12089734.8. Rodriguez-Niedenfuhr M, Vazquez T, Parkin I, Logan B, Sanudo JR. Martin-Gruber anastomosis revisited. Clin Anat. 2002; 15:129–134. PMID: 11877791.9. Kim DH, Kang YK, Hwang MR, Jo HS. Martin-Gruber anastomosis in ulnar neuropathy around the elbow. J Korean Assoc EMG-Electrodiagn Med. 2002; 4:97–100.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Electrophysiological Evaluation of the Incidence of Martin-Gruber Anastomosis in Healthy Subjects
- Anastomosis of Motor Fibers between Median and Ulnar Nerve in the Forearm: an Electrophysiological Study
- The Electrodiagnostic Findings in Martin-Gruber Anastomosis
- Livedo Reticularis Idiopathica Associated with Mononeuropathy Multiplex Syndrome and Bilateral Ulnar-median Nerve Anastomosis
- Ulnar Neuropathy Caused by a Schwannoma in the Guyon's Cannal